
Version 1
July 2015
Incident Management
09/02/2015

Incident Management
Page 2 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Table of Contents
Introduction ...............................................................................................................................................................................................4
Overview ....................................................................................................................................................................................................5
Description ............................................................................................................................................................................................5
Scope.....................................................................................................................................................................................................5
Goal .......................................................................................................................................................................................................5
Objectives..............................................................................................................................................................................................5
Roles......................................................................................................................................................................................................6
Process Control ..........................................................................................................................................................................................8
Controls .................................................................................................................................................................................................8
Metrics ..................................................................................................................................................................................................9
Policies ................................................................................................................................................................................................18
Workflow .................................................................................................................................................................................................20
Inputs ..................................................................................................................................................................................................20
Outputs ...............................................................................................................................................................................................21
Activities..............................................................................................................................................................................................22
INC 1.0: Detect & Record................................................................................................................................................................23
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram ......................................................................................................................................................25
INC 1.1: Start..............................................................................................................................................................................26
INC 1.2: Generate Record ..........................................................................................................................................................26
INC 1.3: Open New Incident ......................................................................................................................................................27
INC 1.4: Verify User’s Information .............................................................................................................................................28
INC 1.5: Capture Incident Details/Categorize ............................................................................................................................28
INC 1.6: Provide Unique Number ..............................................................................................................................................29
INC 1.7: Incident? ......................................................................................................................................................................30
INC 2.0: Initial Support ...................................................................................................................................................................31
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram ......................................................................................................................................................33
INC 2.1: Prioritize & Identify SLA ...............................................................................................................................................34
INC 2.2: Known Alert?................................................................................................................................................................34
INC 2.3: Attempt SOP Use..........................................................................................................................................................35
INC 2.4: Resolved? .....................................................................................................................................................................35
INC 2.5: Major Incident?............................................................................................................................................................36
INC 2.6: Notify Stakeholders/Declare Major Incident ...............................................................................................................36
INC 2.7: Perform Incident Matching ..........................................................................................................................................37
INC 2.8: Matched .......................................................................................................................................................................38
INC 2.9: Escalate ........................................................................................................................................................................38
INC 2.10: Handle Duplicate Incident..........................................................................................................................................39
INC 2.11: Link Incident to Problem ............................................................................................................................................40
INC 2.12: Workaround? .............................................................................................................................................................40
INC 2.13: Wait for Problem Resolution......................................................................................................................................41
INC 3.0: Investigate & Diagnose .....................................................................................................................................................42
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram ......................................................................................................................................................44
INC 3.1: Accept Assignment.......................................................................................................................................................45
INC 3.2: Acknowledge Assignment ............................................................................................................................................45
INC 3.3: Acquire Additional Information if Required .................................................................................................................46
INC 3.4: Re-evaluate Category/Priority......................................................................................................................................46
INC 3.5: Categorization Change? ...............................................................................................................................................47
INC 3.6: Additional Searches......................................................................................................................................................48
INC 3.7: Match Found? ..............................................................................................................................................................48
INC 3.8: Create Problem ............................................................................................................................................................49
INC 3.9: Workaround Possible? .................................................................................................................................................49
INC 3.10: Develop Workaround.................................................................................................................................................50

Incident Management
Page 3 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 3.11: Wait for Problem Resolution......................................................................................................................................50
INC 4.0: Resolve & Recover ............................................................................................................................................................52
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram ......................................................................................................................................................53
INC 4.1: CR Required?................................................................................................................................................................54
INC 4.2: Create CR......................................................................................................................................................................54
INC 4.3: Implement Resolution/Workaround............................................................................................................................55
INC 4.4: Recover the Environment ............................................................................................................................................55
INC 5.0: Close Incident....................................................................................................................................................................57
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram ......................................................................................................................................................58
INC 5.1: Confirm User Acceptance.............................................................................................................................................59
INC 5.2: User Confirmation? ......................................................................................................................................................59
INC 5.3: Capture User Feedback ................................................................................................................................................60
INC 5.4: Resolution/Recovery Details ........................................................................................................................................60
INC 5.5: Close Incident...............................................................................................................................................................61
INC 5.6: Process End ..................................................................................................................................................................62
States .......................................................................................................................................................................................................63
Process States .....................................................................................................................................................................................63
Process State Diagram....................................................................................................................................................................64
Appendix ..................................................................................................................................................................................................65
Attachments and Links ........................................................................................................................................................................65
Definitions ...........................................................................................................................................................................................66

Incident Management
Page 4 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Introduction
The following Incident Management Process has been designed for the Stanford University IT Service Management program.
Departments that participate in the University IT Service Management program will adhere to this Incident Process. Procedures
developed around this Incident Management process will need to be validated by the Incident Process Owner and Process Manager(s)
so as to standardize across the institution. This Process will have relationships with other Processes and those documents should be
read and understood along with this, the primary related processes being Problem and Change Management.

Incident Management
Page 5 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Overview
A process is defined as a set of linked activities that transform specified inputs into specified outputs, aimed at accomplishing an
agreed-upon goal in a measurable manner. The process definition laid out in this document further breaks down these Activities into
Tasks, each of which have a complete set of attributes defined such as data and tool specifications and the role(s) responsible for
executing the tasks. The document also includes process goal and objectives, metrics, role definitions, policies and other process
related attributes.
Description
This is the process that deals with all Incidents. Incidents can include failures or degradation of your services reported by users
of those services; by your own technical staff; or automatically from monitoring tools. The ability to respond to an Incident and
restore the level of service as quickly as possible or to what was agreed to with customers or at least alleviate the impact on
them is the primary concern of the process.
Scope
The scope of Incident management for Stanford University IT and other University support entities for Production services
Goal
The process goal describes a specific purpose or achievement toward which the efforts of the process are directed. Each ITSM
process has a specific focus and when combined with the other ITSM processes, forms a comprehensive framework for
delivering and managing services.
Incident Management exists to get the operation of a service back to 'normal' as quickly as possible in order to minimize any
adverse affects on the supported Academic, business and research processes. This requires the continuous monitoring of the
incident mitigation process through the collecting of heuristic information in order to improve the time to resolution,
communicate effectively and eliminate incident re-occurrence.
Objectives
Process objectives describe material outcomes that are produced or achieved by the process. The following is a list of objectives
for this process:
To record, categorize, diagnose and resolve Incidents as quickly as possible
To provide workarounds to users that allow them to continue with their work while a resolution is pursued (if necessary)
To escalate Incidents to higher levels of support (functional) as well as management (hierarchical) as required
To create a Problem for an Incident having a new unknown cause to allow the Problem Management process to investigate
and identify the root cause and if viable eliminate it.
To keep all affected customers and stakeholders informed on the Status of Incidents throughout their lifecycle
Upon confirmation from the user in receipt of a resolution or a workaround closure of the incident can proceed

Incident Management
Page 6 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Roles
Each process defines at least one role. Each role is assigned to perform specific tasks within the process. The responsibilities of a
role are confined to the specific process. They do not imply any functional standing within the hierarchy of an organization. For
example, the process manager role does not imply the role is associated with or fulfilled by someone with functional
management responsibilities within the organization. Within a specific process, there can be more than one individual
associated with a specific role. Additionally, a single individual can assume more than one role within the process although
typically not at the same time. The following describes the roles defined for this process:
Name
Description
Incident Process Owner
A senior leader with the ability and authority to ensure the process is rolled out and used
by all departments within the Stanford University IT and other supported entities.
Specific responsibilities include: Defining the overall mission of the process; establishing
and communicating the process mission, goals and objectives to all stakeholders;
resolving any cross-functional (departmental) issues; ensuring consistent execution of
the process across departments; reporting on the effectiveness of the process to senior
management; initiating any process improvement initiatives
Incident Process Manager
Responsible for the day-to-day execution of the process. The Process Manager(s) take
direction from the Process Owner in order to ensure consistent execution of the process
across all areas of the organization. Specific responsibilities include: managing the day
to day activities of the process; gathering and reporting on process metrics; tracking
compliance to the process; escalating any issues with the process; acting as chairperson
for process meetings
Incident Coordinator
This role is the "point person" within a support group that is accountable for all Incidents
assigned to their group. Is responsible for monitoring their respective queues for
assigned Incidents, and re-assigning them to the appropriate individuals for further
investigation. Also plays a role in escalations to other groups. This role may also be
referred to as the queue manager
Incident Support
Responsible for: incident investigation and diagnosis for Incidents escalated from the
Service Desk; development of Workarounds; identification and creation of Problems; the
resolution and recovery of assigned Incidents; the creation of Incidents where they
themselves detect a service failure or quality degradation or a situation that may result
in one. Escalation of Incidents where necessary.
Service Desk Agent
Responsible for: incident registration; ownership, monitoring, tracking and
communication; Incident investigation and diagnosis; the provision of resolutions and
workarounds that can be retrieved from Standard Operating Procedures and existing
Problems and Known Errors; escalation of Incidents to Incident Support groups where a
resolution or workaround cannot be retrieved from one of those sources; closure of FCR
Incidents. Handles transfer of ownership to Incident Support where needed
Service Desk Manager
Provides guidance to Service Desk staff on issues such as escalation and setting Priority.
Also ensures that appropriate communications takes place ensuring that all affected
stakeholders are kept abreast of Incident status. May have a key role to play in the
Major Incident procedures. Often responsible for, or involved in producing management
reports for the Incident Management process. Represents the Service Desk at Incident
Management meetings.
User
Responsible for bringing Incidents to the attention of the Service Desk along with
detailed information as requested by the Desk. May also be required to participate in
the implementation of a fix or workaround and verifying correct operation once
implemented.
Problem Process Manager
This role relates to the Problem Management Process. It is included here as it may play
a part in the handling of a Major Incident

Incident Management
Page 7 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Name
Description
Major Incident Owner (MIO)
A person to manage and co-ordinate the resolution to a Major Incident. The
responsibilities are to gather a team to identify and resolve the incident, comply with
any required communications, maintain incident alert status, document incident actions
and information

Incident Management
Page 8 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Process Control
Process controls represent the policies and guiding principles on how the process will operate along with the metrics for measuring
the process and they provide direction over the operation of process by defining constraints or boundaries within which the process
must operate.
Controls
The controls listed are those identified by COBIT 5 as important for an Incident Management process.
Name
Description
DSS02.01 Define the Incident
Classification Scheme
Define the incident classification scheme and incident models.
DSS02.02 Record, Classify and
Prioritize Incidents
Identify, record and classify incidents, and assign a priority according to business
criticality and service agreements.
DSS02.04 Investigate, Diagnose
and Allocate Incidents
Identify and record incident symptoms, determine possible causes, and allocate for
resolution.
DSS02.05 Resolve and Recover
from Incidents
Document, apply and test the identified fix or workarounds and perform recovery
actions to restore the IT-related service.
DSS02.06 Close Incidents
Verify satisfactory incident resolution and close.
DSS02.07 Track Status and
Produce Reports
Regularly track, analyze and report incident trends to provide information for continual
improvement.

Incident Management
Page 9 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Metrics
Metrics are used for the quantitative and periodic assessment of a process. They should be associated with targets that are set
based on specific business objectives. Metrics provide information related to the goals and objectives of a process and are used
to take corrective action when desired results are not being achieved and can be used to drive continual improvement of
process effectiveness and efficiency.
First Time Resolution Rate by Category
Description:
The Service Desk resolved the Incident directly by referring to capitalized knowledge
without any referral support groups.
Type:
Ratio
Supporting Details:
This can be considered an Efficiency metric as much as an Effectiveness metrics and
Service Desk resolution via retrieved Workarounds tends to both resolve the Incident
quicker and more consistently AND cost less than escalating it to Incident Support roles
in other functional areas. Being able to report on this metric with Category breakdowns
and cost breakdowns (if that information is available) will provide invaluable support for
further knowledge capitalization initiatives.
Opportunity For Defect:
A target will be set for some point into implementation for a minimum ratio of Service
Desk resolved Incidents to total Incidents. As the process matures, this target ratio is
likely to increase
Measurement Procedure:
Total Incidents Resolved with no escalations / Total Incidents X 100
Additional Details:
The Service Desk retrieved and employed a Workaround (from a Problem, Known Error
or other source) to resolve the Incident, without escalating the Incident to Incident
Support
Category:
Efficiency
Average time for Resolving Incidents by Category
Description:
The mean (average) time taken to resolve an Incident. Resolution is attained through the
use of a Workaround that will either restore a service to its normal mode of operation or
provide some sort of circumvention to (at least partially) alleviate the impact on the
user. The workaround will either be retrieved by linking the Incident to an existing
Problem or Known Error (or possibly some other repository of Workarounds) or the
workaround may be created for this particular Incident
Type:
Mean
Supporting Details:
This is the primary effectiveness metric of Incident Management. Breaking down the
metric by Incident Category (at various levels), Incident Priority, etc. then the metric will
be of optimal use both for effectiveness reporting and intervention.
Opportunity For Defect:
A Mean time that exceeds a target set for a particular category and/or priority of
Incident
Measurement Procedure:
Select all Incidents that were resolved during the period. The time to resolve a given
incident is the difference between the Incident Occurred Timestamp and the Incident
Resolved Timestamp This metric is the average (mean) of this time for all incidents. The
Incident Occurred Timestamp should be a defined field to allow it to be different from
the Incident Record Created Timestamp. Closure code filtering might be needed to
eliminate noise records
Additional Details:
The time elapsed from the occurrence of the Incident to the time the workaround was
applied and verified.
Category:
Effectiveness

Incident Management
Page 10 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Incidents Assigned multiple times by Category (to be validated)
Description:
Re-assignments can result in delays in getting to incident resolution. May speak to
inaccurate group assignments; either lack of knowledge or incorrectly defined to the
tool.
Type:
Ratio
Supporting Details:
It may be difficult to distinguish between a re-assignment and a subsequent functional
escalation. Both may use the same mechanism. Note as well that there are
effectiveness aspects and implications to this metric as any delay in resolution impacts
the primary "speed of resolution" effectiveness metric. Reporting on re-assignments
broken down by Category will provide optimized intervention information
Opportunity For Defect:
An Incident that is re-assigned to another support group after the initial escalation for
the Service Desk
Measurement Procedure:
Traverse the Activity Log looking for entries with a category that signifies an assignment
to another group or individual after initial escalation. Or if the tool has a assignment
count field, that data is immediately available
Additional Details:
An assignment of an Incident to a support group other than the support group that first
received the Incident by escalation from the Service Desk
Category:
Efficiency
Average Cost per Incident Workaround
Description:
The expense required resolving an Incident. For repetitive Incidents, this information is
also valuable for Problem Management to use when evaluating whether to pursue root
cause of the Problem associated with the Incidents or to pursue a fix for a Known Error.
Type:
Mean
Supporting Details:
This is the primary efficiency metric for Incident Management. Having a cost associated
with each Incident is also invaluable for Service Costing if you report not on average but
on total Incident Cost broken down for a period by Category.
Opportunity For Defect:
Cost targets may be set for different categories or priorities of Incident. A defect would
be an Incident whose cost exceeded this target
Measurement Procedure:
In most cases, the only factor that will be significant is the time devoted by staff (or
other resources) to the Incident. This implies that people accurately record their time
efforts in the Incident record or (more likely) that they track their time in a another tool
by charging time to an Incident number (and possibly down to which activity level they
were operating in)
Additional Details:
The effective cost in a currency unit to bring an Incident to resolution.
Category:
Efficiency
Percent of Incidents Incorrectly Categorized
Description:
Correct categorization is critical to both Incident Matching and Functional Escalation.
Type:
Ratio
Supporting Details:
There are both efficiency and effectiveness aspects to this metric. Being able to
breakdown the report by From values, To values and a combination of both will be
invaluable to directing remedial action.
Opportunity For Defect:
An Incident whose Category is changed after initial setting
Measurement Procedure:
A recognition of a change in categorization may be obtained either through an audit log
analysis for changes to the Category fields or by testing a flag that would be set if one of
these fields is modified after a specified point in the process flow

Incident Management
Page 11 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Additional Details:
An Incident whose initial categorization is later changed
Category:
Effectiveness
Incident Creation Patterns against Time
Description:
A mapping of when Incidents (and various types of Incidents) are created over time.
When combined with data about Service Desk staffing patterns this gives the ability to
fine-tune the staffing patterns.
Type:
Ratio
Supporting Details:
The mapping of numbers and types of Incidents to staffing patterns of the Service Desk
will provide the information required to tune the staffing pattern. Note that other
information may be required regarding other Service Desk duties (e.g., Request
Fulfillment patterns and involvement in other processes e.g. Change Management)
Opportunity For Defect:
Time periods where Incident Creation rate exceeds handling capability
Measurement Procedure:
Incident Creation Timestamps (plus Categorization information)
Additional Details:
Counts and Categories of Incidents Created with Creation Timestamps
Category:
Efficiency
Closed Incidents this month by Category/Assignee
Description:
The number of incidents closed this month, grouped by category or assignee group.
The out of box report called "Closed Incidents this month by Category" may be used for
this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report called "Closed Incidents this month by Category" may be used for
this metric.
Additional Details:
The out of box report called "Closed Incidents this month by Category" may be used for
this metric.
Category:
Value
Number of Incidents per Month by Category
Description:
The number of incidents created each month grouped by category.
The out of box report called "All Incidents by Category" may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report called "All Incidents by Category" may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
The out of box report called "All Incidents by Category" may be used for this metric.
Category:
Value
Performance by Category / Tech / Priority (to be revisted when TD is being completed)
Description:
Performance grouped by Category / Tech / Priority
Type:
Number
Category:
Efficiency
Resolved by Known Error

Incident Management
Page 12 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Description:
On resolution, if the incident references a Problem that is a Known Error, create one of
these.
Type:
Duration
Measurement Procedure:
ServiceNow script
Category:
Value
Create to Resolve Duration
Description:
When an incident goes into state resolved or closed, calculate the duration from open.
Type:
Duration
Measurement Procedure:
ServiceNow script
Category:
Value
Assigned to Duration
Description:
Assigned to Duration. This metric captures how long the Incident was in the Assigned
To state.
Type:
Duration
Measurement Procedure:
ServiceNow script
Category:
Value
Incident State Duration
Description:
Incident State Duration. This metric captures how long the Incident was in any
particular state.
Type:
Duration
Measurement Procedure:
ServiceNow script
Category:
Value
First Call Resolution
Description:
Overly simplified definition of first call resolution.
If the incident is inactive and the update count (sys_mod_count) is zero, create a First
call resolution record using the Service Now Script.
Type:
Duration
Measurement Procedure:
Run the ServiceNow script to create the FCR record
Category:
Value
Assignment Group Duration
Description:
Assignment Group. This metric captures how long the Incident was in the Assigned To
Group state.
Type:
Duration
Measurement Procedure:
ServiceNow script
Category:
Value

Incident Management
Page 13 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Total Number of Incidents
Description:
By itself, not terribly useful. Presented (typically) by Period / by Priority and depicted
over time will indicate a trend that can be observed and acted upon.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
Simply a count of all Incidents created during the period. This count may be further
grouped by Category, Assignment Group or any other relevant field.
Additional Details:
A subset of this is used for the following ServiceNow reports:
All Incidents by Assignment (and All Incidents by Assignment for My Group)
All Incidents by Category
All Incidents by Location
All Incidents by State
All Incidents Closed By (and All Incidents Closed By for My Group)
Closed Incidents this month by Category
Incident Breakdown
Incident Trend By Priority (and Incident Trend By Priority for My Group)
My Incidents by State
Open Incidents by Assignment (and Open Incidents by Assignment for My Group)
Open Incidents by Category (and Open Incidents by Category for My Group)
Open Incidents by Escalation (and Open Incidents by Escalation for My Group)
Open Incidents by Priority
Open Incidents by State (and Open Incidents by State for My Group)
Opened Incidents this month by Priority
Process Exceptions by Month
Category:
Efficiency
All Incidents by Assignment
Description:
All Incidents by Assignment (and All Incidents by Assignment for My Group) - This metric
captures a count of all Incidents broken out by Assignment.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
All Incidents by Location
Description:
All Incidents by Location - This metric captures a count of all Incidents broken out by
Location.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
All Incidents by State

Incident Management
Page 14 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Description:
All Incidents by State - This metric captures a count of all Incidents broken out by State.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
All Incidents Closed By
Description:
All Incidents Closed By (and All Incidents Closed By for My Group) - This metric captures
a count of all Incidents broken out by Closed By.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Incident Breakdown
Description:
Incident Breakdown - This metric captures a count of all Incidents broken out by
Assignment and Category.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Incident Trend By Priority
Description:
Incident Trend By Priority (and Incident Trend By Priority for My Group) - This metric
captures a count of Closed Incidents broken out by Priority; trended over the last 3
months.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Open Incidents by Assignment
Description:
Open Incidents by Assignment (and Open Incidents by Assignment for My Group) - This
metric captures a count of Open Incidents broken out by Assignment.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.

Incident Management
Page 15 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Open Incidents by Category
Description:
Open Incidents by Category (and Open Incidents by Category for My Group) - This metric
captures a count of Open Incidents broken out by Category.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Open Incidents by Escalation
Description:
Open Incidents by Escalation (and Open Incidents by Escalation for My Group) - This
metric captures a count of Open Incidents broken out by Escalation.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Open Incidents by Priority
Description:
Open Incidents by Priority - This metric captures a count of Open Incidents broken out by
Priority.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Open Incidents by State
Description:
Open Incidents by State (and Open Incidents by State for My Group) - This metric
captures a count of Open Incidents broken out by State.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Opened Incidents this month by Priority

Incident Management
Page 16 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Description:
Opened Incidents this month by Priority - This metric captures a count of Open Incidents
opened this month broken out by Priority.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Process Exceptions by Month
Description:
Process Exceptions by Month - This metric captures a count of all Incidents that were
caused by Changes; trended month-by-month.
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Type:
Number
Measurement Procedure:
The out of box report by the same name may be used for this metric.
Additional Details:
There is a ServiceNow out-of-the-box report for this metric.
Category:
Value
Mean time between incidents
Description:
Mean time between incidents - is calculated as the time between incidents occurring.
This value is often based on a per service basis; e.g., what is the mean time between
incidents related to the email service.
Type:
Number
Supporting Details:
This when analyzed as a trend may indicate how the process is working and how the
service is working.
Measurement Procedure:
Broken out by service, what is the mean time between incidents occurring? This may
also be calculated for the mean time between any incidents occurring. Calculate the
time from when one incident for a service occurred and the next incident for the same
service occurred and average it over the historical calculations for the same service
instances.
Category:
Effectiveness
Percentage of Incidents resolved within service target
Description:
Percentage of Incidents resolved within agreed-on/acceptable period of time.
Type:
Ratio
Measurement Procedure:
Each incident resolution is compared against its service level agreement objective/level
to determine whether it was resolved in the appropriate amount of time (or not). The
total within the appropriate time frame is compared against the total incidents and
stated as a percentage.
Category:
Effectiveness
Percentage of Major incidents for which Problems were Logged
Description:
Percentage of Major incidents for which Problems were Logged.
Type:
Ratio

Incident Management
Page 17 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Measurement Procedure:
Each Major Incident is counted and compared against how many of these had a Problem
record logged and related to it.
Additional Details:
This value may be redundant if the process forces a Problem record to be created
automatically when it identifies a Major Incident has occurred. It will always be 100% if
this is enforced.
Category:
Compliance
Percentage of Incidents responded to within service target
Description:
Percentage of Incidents responded to within agreed-on/acceptable period of time.
Type:
Ratio
Measurement Procedure:
Each incident response time is compared against its service level objective level to
determine whether it was responded to in the appropriate amount of time (or not). The
total within the appropriate time frame is compared against the total incidents and
stated as a percentage.
Category:
Effectiveness
# of Closed Incidents without Problems
Description:
Closed Incidents Sorted by Priority and are not FCR (First Call Resolution)
Type:
Number
Category:
Compliance

Incident Management
Page 18 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Policies
Policies outline a set of plans or courses of action that are intended to influence and determine decisions or actions of a
process. Policies provide an element of governance over the process that provides alignment to business vision, mission and
goals.
Single Tool - Service-Now
Statement:
There will be a single tool (Service-Now) to be used consistently by all Stanford University IT
teams.
Rationale:
To ensure consistency in process execution, as well as ease in exchanging information and
generating reports on an enterprise wide basis
Prioritization
Statement:
All incidents must be prioritized based on impact to the business and urgency. Incidents shall
be managed in priority sequence
Rationale:
A group may have numerous incidents assigned to them. People need to know what to work
on first.
Incident Escalation
Statement:
Incidents must be escalated as defined in related SLAs and SLOs, or in accordance with
operational policies and procedures
Rationale:
Failure to escalate in a timely manner can result in unnecessary delays in incident resolution
Service Interruption
Statement:
High impact incidents for which the cause is unknown shall be flagged as problem candidates
for further investigation
Rationale:
Getting to the root cause of these incidents will aid in ensuring that they do not reoccur
Review
Statement:
Prior to closure, all incidents causing a service breach or failure to meet the Service Level
Agreement should be reviewed by management for accuracy, completeness and compliance
to the process.
Rationale:
Such incidents may become the focus of attention after the fact and need to contain accurate
and thorough information for subsequent reviews.
Major Incident
Statement:
University IT intends to carefully and consistently manage critical system outages in order to
minimize down time for business users, ensure timely response by UIT staff, keep
management, business users and the Stanford community informed, and provide appropriate
escalation paths while providing excellent support.
Incident communication

Incident Management
Page 19 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Statement:
The Incident progress will be communicated to the relevant stakeholders in a timely manner

Incident Management
Page 20 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Workflow
Inputs
Process inputs are used as triggers to initiate the process and to produce the desired outputs. Users, stakeholders or other
processes provide inputs. The following is a list of inputs for this process:
Name
Description
Supplier
Is Trigger
Task
Details
Incident details from various sources
Users, Service Desk,
network or computer
operations, systems
management tools
No
Configuration
Configuration Details
Configuration
Management
Database (CMDB)
No
Incident Matching
Response from matching an Incident
against other Incidents, Problems and
Known Errors
Problem
Management,
Incident Management
No
Resolution
Resolution details
Incident Management
Support Groups,
Knowledge
Management
No
Request for Status
A query from a user or stakeholder on the
status of an Incident or Problem
User or stakeholder
No
A Newly Detected
Incident
Detection, through automated or manual
means, of a new Incident
Anyone, systems
management tools,
Event Management
Yes
Progress Updates
Ongoing updates to the Incident -
captured in the Activity Log
Users, Service desk,
network or computer
operations, systems
management tools
No
Call Record
Call Record will determine the type of
record needed Incident/Request
Yes
Open New Incident

Incident Management
Page 21 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Outputs
Each process produces tangible outputs. These outputs can take the form of products or data and can be delivered to a user or
stakeholder, or, they can be used as inputs to other processes. Outputs are measurable in terms of quantity and quality. The
following is a list of outputs for this process:
Name
Description
Recipient
Task
Change Request
CR for Incident resolution; updated
Incident record (including resolution
and/or workarounds)
Change Management
Resolutions
Resolved and closed Incidents
Service Desk, Problem
Management, Users
Communication
Communication to Customers and
stakeholders
Customers
Management
Information
Reports
Identified stakeholders
Status Update
An update on the status/progress of an
Incident or a Problem
Requester
A Problem Record
For Incidents with an unknown root
cause, a Problem record is created if
one does not already exist.
Problem Management
Incident Model
A pre-determined, optimized way of
approaching and diagnosing a specific
type or class of Incidents. Will often
include tailored screens for information
capture and specific instructions for the
Service Desk an/or Incident Support
Service Desk, Incident
Support
Workaround
A Workaround is a means of alleviating
the effect of an Incident on a user
without eliminating the root cause of
that Incident. Incident Management is
solely responsible for creating
Workarounds. Incident Management
cannot create a fix as that implies
understanding and eliminating the root
cause of the Incident. That is solely
within the scope of Problem
Management. Note however, that
Problem Management IS responsible
for reviewing Workarounds created by
Incident Management and where
applicable optimizing them for re-use.
User, Incident
Management, Problem
Management

Incident Management
Page 22 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Activities
ID
Name
Description
INC 1.0
Detect & Record
It is within this activity that Incidents are detected, either by human means or
through systems management tools that monitor the system for events.
Capturing all of the relevant information at the time of the creation of the
Incident is a key focus of this activity. Categorization (what is failing and the
symptom) is determined here, and if it is determined that we are dealing with a
Service Request rather than an Incident, the Incident is re-designated as a Service
Request and steered to the Request Fulfillment process.
INC 2.0
Initial Support
During this activity the Incident is associated with a relevant Service Level
Agreement. Impact, Urgency and Priority parameter values are determined, and
Major Incident procedures will be invoked where applicable. Incident Matching
is performed in an attempt to identify duplicate Incidents and locate a fix or
Workaround. Appropriate stakeholders are notified as mandated by parameters
such as Priority.
INC 3.0
Investigate & Diagnose
This activity is where Workarounds are located or developed. Escalations to
other support groups may occur during this activity. If the Incident cannot be
related to an existing Problem, one is created.
INC 4.0
Resolve & Recover
This activity includes those tasks required to implement the fix or Workaround
located or developed in the previous activity. A CR will be submitted if required
and, if so, the Change Management process will manage the implementation.
Depending on the damage done by the Incident, recovery actions may also take
place.
INC 5.0
Close Incident
Having implemented a Workaround or fix, it is now time to close the Incident.
The affected user(s) should be contacted to solicit their acceptance of the
Workaround or fix, and to obtain any additional feedback on the handling of their
issue. Details of the resolution and an appropriate closure and cause code should
be captured.

Incident Management
Page 23 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 1.0: Detect & Record
It is within this activity that Incidents are detected, either by human means or through systems management tools that monitor
the system for events. Capturing all of the relevant information at the time of the creation of the Incident is a key focus of this
activity. Categorization (what is failing and the symptom) is determined here, and if it is determined that we are dealing with a
Service Request rather than an Incident, the Incident is re-designated as a Service Request and steered to the Request
Fulfillment process.
INC 1.1: Start
An Incident record to recognize and track the incident may created by the Service Desk or Incident Support, whichever role is
first aware of the Incident.
If the record is created by Incident Support then Incident Support must then provide all the details required for the record
and not rely on Service desk to 'pick up' the pieces
INC 1.2: Generate Record
It is entirely possible (and indeed desirable) that an Incident (Level N) Support group will discover the Incident and create an
Incident record before any users are aware of it. This is especially desirable if Incident Support finds a defect or trend in a
Configuration Item (CI) that if dealt with in a timely manner will prevent a Service outage.
Annotation:
Incident Support generated records will have all details entered at generation time
INC 1.3: Open New Incident
For all reported Incidents, it is essential that an Incident record be created to capture the details of it and track it to
resolution. An Incident record must be created for all situations (even those for which the Service Desk is already aware).
Failure to do so will result in inaccurate management reports as well as the inability to contact affected users for follow-up
and closure. Additionally, users and other stakeholders may at times during the Incident lifecycle call to request a status
(progress) update. This information should be readily available within the Incident record and can be provided to the
requester. A log of the request should be made in the Incident record.
Annotation:
New Incidents may be opened in a number of ways, e.g., though Event Management,
Self-Service portal, email, etc.
INC 1.4: Verify User’s Information
The purpose of this task is to ensure that user information is accurate. This includes not only personal information such as
phone number and location, but possibly organizational and entitlement information. This task affords the Service Desk the
opportunity to ensure that this information is kept current and may aid in categorizing or resolving the Incident.
INC 1.5: Capture Incident Details/Categorize
Capturing sufficient and relevant detail at this stage is very important, as it will aid in diagnosis should the Incident require
escalation. Additionally, others looking for similar situations can use the details to locate this Incident. The basic information
that should be collected must be defined as part of the process and made available to the Service Desk. A description of the
Incident in the caller’s own words should be recorded, so that future contact with the user can be made in their terms. At
this point Service Category and Symptom can be determined. This categorization can be used to generate Heads Up alerts to
certain support groups and also to trigger category/symptom specific data recording screens to help the Service Desk Agent
obtain and format the required data effectively and efficiently.
Annotation:
ITIL® says Categorization occurs in "Initial Support". As the information is available now
and categorization may drive Incident Model use we do it here

Incident Management
Page 24 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 1.6: Provide Unique Number
Although the expectation was we were dealing with an incident a request for service may be initiated through the Incident
Management process. Although the actual handling of the request falls within another process (Service Request
Management), if the request is initiated here the basic details of the request are captured. The nature of the request will
dictate the actual information that is gathered from the user. Once the Service Request has been entered, the user should be
provided with a record number for future reference.
At this point the agent will know whether this is an Incident or a Service Request. The user is provided with the reference
number for all future calls regarding the Incident /request.
Annotation:
At this point we know the record is an Incident or a Service Request and have either
updated the Incident record or created a draft Service Request
INC 1.7: Incident?
Direct the record to the correct process for handling
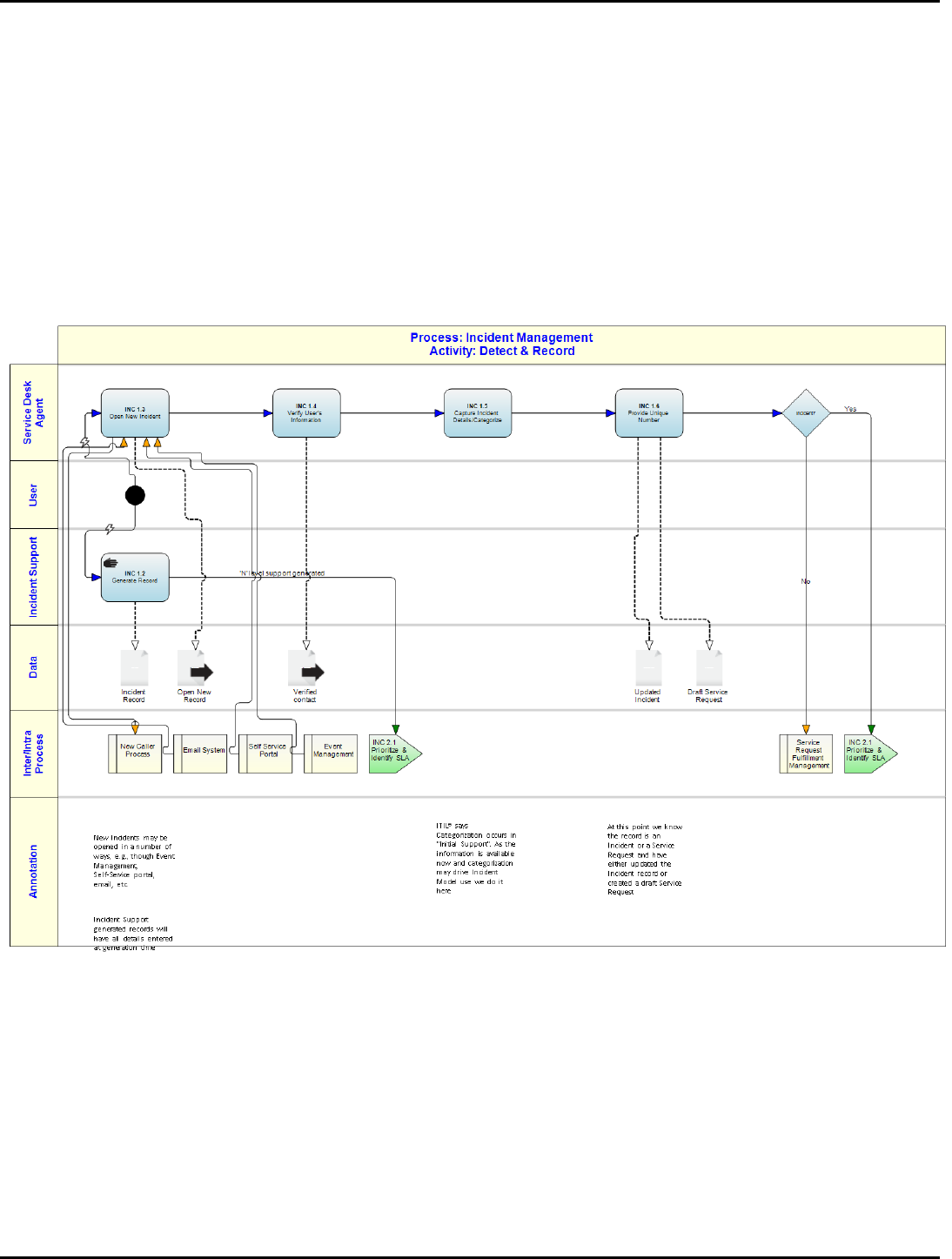
Incident Management
Page 25 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram

Incident Management
Page 26 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 1.1: Start
An Incident record to recognize and track the incident may created by the Service Desk or Incident Support, whichever role is
first aware of the Incident.
If the record is created by Incident Support then Incident Support must then provide all the details required for the record and
not rely on Service desk to 'pick up' the pieces
INC 1.1: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.3
Open New Incident
INC 1.2
Generate Record
INC 1.1: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
User
R
INC 1.2: Generate Record
It is entirely possible (and indeed desirable) that an Incident (Level N) Support group will discover the Incident and create an
Incident record before any users are aware of it. This is especially desirable if Incident Support finds a defect or trend in a
Configuration Item (CI) that if dealt with in a timely manner will prevent a Service outage.
INC 1.2: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.1
Start
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.1
Prioritize & Identify SLA
'N' level support generated
INC 1.2: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Create a new Incident record with all the details and mandatory fields completed
R/A

Incident Management
Page 27 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 1.2: Task Notes
Task Notes
Description
The "user" information in the case of an Incident created by Incident Support should be auto-filled from the identity of the
person who opens the Incident.
Incidents created by Incident Support are routed to the Service Desk so that the Service Desk can apply the same
Prioritization methods and search for existing Workarounds and fix as for Incidents identified by Users.
INC 1.3: Open New Incident
For all reported Incidents, it is essential that an Incident record be created to capture the details of it and track it to resolution.
An Incident record must be created for all situations (even those for which the Service Desk is already aware). Failure to do so
will result in inaccurate management reports as well as the inability to contact affected users for follow-up and closure.
Additionally, users and other stakeholders may at times during the Incident lifecycle call to request a status (progress) update.
This information should be readily available within the Incident record and can be provided to the requester. A log of the
request should be made in the Incident record.
INC 1.3: Task Inter Process
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Event Management
Create a record
automatically.
In
Self Service Portal
Create an Incident record
automatically from a self
service portal.
In
Email System
Create a new Incident record
via email transposed into the
record data.
In
New Caller Process
Record created via the New
Call Management process.
Out
INC 1.3: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.1
Start
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.4
Verify User’s Information
INC 1.3: Task Inputs
Task Inputs

Incident Management
Page 28 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Name
Description
Supplier
Is Trigger
Call Record
Call Record will determine the type of record needed
Incident/Request
Yes
INC 1.3: Task Roles
Name
Duties
R
A
CI
Service Desk Agent
Identify that the user does in fact have an Incident, and proceed to create a new
Incident record.
R/A
User
Articulate their issue so that the Service Desk agent can ascertain that an Incident is
being raised.
C
INC 1.4: Verify User’s Information
The purpose of this task is to ensure that user information is accurate. This includes not only personal information such as
phone number and location, but possibly organizational and entitlement information. This task affords the Service Desk the
opportunity to ensure that this information is kept current and may aid in categorizing or resolving the Incident.
INC 1.4: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.3
Open New Incident
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.5
Capture Incident Details/Categorize
INC 1.4: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
The user's contact & entitlement information is retrieved and verified with the user.
Appropriate actions are taken if the information is found to be inaccurate. Depending
on the perceived urgency of the incident, this step may involve verifying only minimal
information (e.g., phone number).
R/A
User
Confirming that the information on record is accurate and providing corrections as
appropriate.
C
INC 1.5: Capture Incident Details/Categorize
Capturing sufficient and relevant detail at this stage is very important, as it will aid in diagnosis should the Incident require
escalation. Additionally, others looking for similar situations can use the details to locate this Incident. The basic information
that should be collected must be defined as part of the process and made available to the Service Desk. A description of the

Incident Management
Page 29 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Incident in the caller’s own words should be recorded, so that future contact with the user can be made in their terms. At this
point Service Category and Symptom can be determined. This categorization can be used to generate Heads Up alerts to certain
support groups and also to trigger category/symptom specific data recording screens to help the Service Desk Agent obtain and
format the required data effectively and efficiently.
INC 1.5: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.4
Verify User’s Information
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.6
Provide Unique Number
INC 1.5: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
A "Heads Up" alert may be sent under some circumstances to a Support Group that
may need to be involved later.
I
Service Desk Agent
Ensure that all relevant details about the Incident are captured.
R/A
User
Provides the Service Desk with all details of the Incident, which may include sending
relevant information via email (e.g., screenshots, logs).
C
INC 1.6: Provide Unique Number
Although the expectation was we were dealing with an incident a request for service may be initiated through the Incident
Management process. Although the actual handling of the request falls within another process (Service Request Management),
if the request is initiated here the basic details of the request are captured. The nature of the request will dictate the actual
information that is gathered from the user. Once the Service Request has been entered, the user should be provided with a
record number for future reference.
At this point the agent will know whether this is an Incident or a Service Request. The user is provided with the reference
number for all future calls regarding the Incident /request.
INC 1.6: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.5
Capture Incident Details/Categorize
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.7
Incident?
INC 1.6: Task Roles

Incident Management
Page 30 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
Provide the user with the unique identifier/number of the Incident record. If this is
not an incident then generate the service request record draft, inform the user that a
service request has been generated and provide them with that identifier/number
instead.
R/A
User
If this is not an incident, provide the Service Desk with the details of the service that
they are requesting.
Receives the newly created Incident or Service Request identifier/number.
C
INC 1.7: Incident?
Direct the record to the correct process for handling
INC 1.7: Task Inter Process
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Service Request Fulfillment
Management
Determine nature of Service
Request
No
Out
INC 1.7: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.6
Provide Unique Number
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.1
Prioritize & Identify SLA
Yes
INC 1.7: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
Provide the user with the unique identifier/number of the Incident record. If this is not
an Incident then generate the service request record draft, inform the user that a
service request has been generated and provide them with that identifier/number
instead.
R/A
User
Provide the Service Desk with the details of the service that they are requesting.
C

Incident Management
Page 31 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 2.0: Initial Support
During this activity the Incident is associated with a relevant Service Level Agreement. Impact, Urgency and Priority parameter
values are determined, and Major Incident procedures will be invoked where applicable. Incident Matching is performed in an
attempt to identify duplicate Incidents and locate a fix or Workaround. Appropriate stakeholders are notified as mandated by
parameters such as Priority.
INC 2.1: Prioritize & Identify SLA
The purpose of this task is to use the Service Categorization and Affiliation established earlier to determine if an SLA is
associated with the Incident, and also identify the Priority of the Incident through the Impact (scope of user community
affected) and the Urgency (how fast this must be resolved). This will determine the position in the work queue for this
Incident. The SLA may dictate or influence escalation patterns.
INC 2.2: Known Alert?
Verify if there is an active alert for this issue.
INC 2.3: Attempt SOP Use
Many incidents may be resolved through the use of Standard Operating Procedures (SOP's), and require no further
workflow other than closure of the incident. SOPs may be found in the Knowledge database
INC 2.4: Resolved?
Did the SOP resolve the incident?
INC 2.5: Major Incident?
For Incidents at or above a specific Priority, the agent should alert the Service Desk Manager. Policies and procedures will
guide the agent in this task.
INC 2.6: Notify Stakeholders/Declare Major Incident
An entry should be made in the Incident record to reflect the time that this escalation was made. These procedures should
also clearly specify when a Major Incident is to be declared, how to do it, and the Roles and Responsibilities for a Major
Incident.
Annotation:
A major incident requires special handling and will have a predefined procedure that
must be followed. Once the procedure is completed the process advances to the Close
activity
INC 2.7: Perform Incident Matching
The purpose of the task is to attempt to locate possible workarounds or resolutions from existing Incidents, Problems,
Known Errors, and to determine if this Incident is just a duplicate report of another open Incident. The primary basis of the
search is Service Categorization and Symptom. Other information, such keywords that may be found in the description or
incident details may be used in the search.
Annotation:
The preferred search order should be:
1) Knowledge Database
2) Problem Database
3) Incident Database

Incident Management
Page 32 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 2.8: Matched
Which path to take
INC 2.9: Escalate
The Incident has to be escalated to Level N for additional investigation, the appropriate Support Group should be identified
in the Incident.
Control now passes to incident Support.
Annotation:
There is nothing more Service Desk can do to resolve the incident and the record will
be escalated to Incident Support based on the Categorization for the affected service
INC 2.10: Handle Duplicate Incident
If the current incident is found to be a duplicate report of a currently open incident and refers to the same instance, then
the duplicate report incident should be linked to the original one. Since this is just a duplicate report of the same event, no
additional action is required now. When the incident is resolved, all additional reporters may need to be notified
INC 2.11: Link Incident to Problem
If a Problem was found that matches the current Incident, then a bi-directional link is created between the two records. If a
Workaround is specified in the Problem record, it will be provided at this point. The increase in Incident count may cause
the Priority of the problem to be adjusted. Depending on the Priority of the Incident (or if the Priority changes), the current
assignee of the Problem may be notified.
INC 2.12: Workaround?
INC 2.13: Wait for Problem Resolution
It may not be feasible to develop a workaround for all Incidents and hence, we may have to wait for a resolution from the
Problem Management process.
Annotation:
Although not desirable, if the incident matches an existing problem with no
workaround already defined at this point then the only option is to wait for a
permanent resolution

Incident Management
Page 33 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram

Incident Management
Page 34 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 2.1: Prioritize & Identify SLA
The purpose of this task is to use the Service Categorization and Affiliation established earlier to determine if an SLA is
associated with the Incident, and also identify the Priority of the Incident through the Impact (scope of user community
affected) and the Urgency (how fast this must be resolved). This will determine the position in the work queue for this Incident.
The SLA may dictate or influence escalation patterns.
INC 2.1: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 1.7
Incident?
Yes
INC 1.2
Generate Record
'N' level support generated
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.2
Known Alert?
INC 2.1: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
Set the impact and urgency based on User information. Determine and set the
Priority based on the impact and urgency. Determine if there is an SLA support target
associated with the impacted service and relate it to the incident record.
R/A
Service Desk Manager
Provide the agent with assistance in setting the Impact and/or Urgency.
C
User
Provide the Service Desk with information regarding the scope of the issue and how
quickly they need to have it resolved.
C
INC 2.2: Known Alert?
Verify if there is an active alert for this issue.
INC 2.2: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.1
Prioritize & Identify SLA
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.3
Attempt SOP Use
NO
INC 2.10
Handle Duplicate Incident
Yes
INC 2.2: Task Roles

Incident Management
Page 35 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
R
INC 2.3: Attempt SOP Use
Many incidents may be resolved through the use of Standard Operating Procedures (SOP's), and require no further workflow
other than closure of the incident. SOPs may be found in the Knowledge database
INC 2.3: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.2
Known Alert?
NO
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.4
Resolved?
INC 2.3: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
Search the Knowledge database to find an SOP that relates to the incident description,
Service and symptom.
Using available SOPs, attempt to resolve the Incident. If successful, update the
Incident with the identifier of the SOP that was used.
R/A
User
The user may be required to participate in the SOP execution.
R
INC 2.4: Resolved?
Did the SOP resolve the incident?
INC 2.4: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.3
Attempt SOP Use
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.5
Major Incident?
No
INC 5.1
Confirm User Acceptance
Yes
INC 2.4: Task Roles

Incident Management
Page 36 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
R
INC 2.5: Major Incident?
For Incidents at or above a specific Priority, the agent should alert the Service Desk Manager. Policies and procedures will guide
the agent in this task.
INC 2.5: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.4
Resolved?
No
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.7
Perform Incident Matching
No
INC 2.6
Notify Stakeholders/Declare Major Incident
Yes
INC 2.5: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Verify with ITOC if major Incident
A
Service Desk Agent
Based on the criteria defined determine if this incident qualifies as a Major Incident
R
INC 2.6: Notify Stakeholders/Declare Major Incident
An entry should be made in the Incident record to reflect the time that this escalation was made. These procedures should also
clearly specify when a Major Incident is to be declared, how to do it, and the Roles and Responsibilities for a Major Incident.
INC 2.6: Task Inter Process
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Problem Management
Problem Manager
notification required
Notification
Out
INC 2.6: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label

Incident Management
Page 37 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.5
Major Incident?
Yes
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.4
Resolution/Recovery Details
Resolved
INC 2.6: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Process Manager
Perform tasks as defined in the Major Incident Procedure
I
Incident Support
Notify Major stakeholders and coordinate tasks defined in the Major Incident
Procedure.
I
Problem Process Manager
Perform tasks as defined in the Major Incident Procedure
I
Major Incident Owner
(MIO)
MIO to setup up DOC activities
A
INC 2.6: Task Notes
Task Notes
Description
Stakeholders may include any person/group who needs to be informed of an Incident e.g. Application Development
If the Incident meets the criteria for a Major Incident, the Major Incident procedures would be invoked at this point. Criteria
specifications for declaring a Major Incident and the procedures to be followed need to be clear and unequivocal.
The Service Desk usually owns the incidents through to closure. For Major Incidents, a specific individual may be assigned to
the Incident to drive it through to resolution.
For most Incidents, Problem Management usually lags Incident Management. In other words, effort is made to provide a
workaround for the Incident before root cause is investigated. For Major Incidents, Problem Management may be asked to
pursue root cause immediately if there is a concern that a workaround is not viable or not adequate. ITIL® specifies that the
Problem Manager should be involved immediately.
INC 2.7: Perform Incident Matching
The purpose of the task is to attempt to locate possible workarounds or resolutions from existing Incidents, Problems, Known
Errors, and to determine if this Incident is just a duplicate report of another open Incident. The primary basis of the search is
Service Categorization and Symptom. Other information, such keywords that may be found in the description or incident details
may be used in the search.
INC 2.7: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.5
Major Incident?
No
Successors

Incident Management
Page 38 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.8
Matched
INC 2.7: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
Perform searches of open Problems and Known Errors in an attempt to locate a
resolution or Workaround, and other open Incidents, as this may be a duplicate report
of an existing Incident currently being managed.
R/A
INC 2.8: Matched
Which path to take
INC 2.8: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.7
Perform Incident Matching
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.9
Escalate
No Match
INC 2.10
Handle Duplicate Incident
Incident Match
INC 2.11
Link Incident to Problem
Problem Match
INC 2.8: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
R
INC 2.9: Escalate
The Incident has to be escalated to Level N for additional investigation, the appropriate Support Group should be identified in
the Incident.
Control now passes to incident Support.
INC 2.9: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.8
Matched
No Match

Incident Management
Page 39 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.1
Accept Assignment
INC 2.9: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
Ensure that the Incident is placed on the appropriate support group queue for further
investigation.
R/A
INC 2.10: Handle Duplicate Incident
If the current incident is found to be a duplicate report of a currently open incident and refers to the same instance, then the
duplicate report incident should be linked to the original one. Since this is just a duplicate report of the same event, no
additional action is required now. When the incident is resolved, all additional reporters may need to be notified
INC 2.10: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.2
Known Alert?
Yes
INC 2.8
Matched
Incident Match
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.10: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
Create a link (or relationship) from the new Incident to the original one that was
found during Incident Matching.
R/A
INC 2.10: Task Notes
Task Notes
Description
Floods of calls involving duplicate reports can severely hamper the ability of the Service Desk to handle non-related calls and
frustrate those people attempting to make the duplicate reports. As soon as the extent of a widespread Incident is known,
mechanisms that can expedite the dissemination of information on widespread service impacts (usually outages, feature
failures or capacity issues) to the right people with minimal effort by the Service Desk can have dramatic payoffs. Both
system-supported mechanisms (e.g., banners, emails) and less automated procedures (a tree of local contacts) may be
employed.

Incident Management
Page 40 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 2.11: Link Incident to Problem
If a Problem was found that matches the current Incident, then a bi-directional link is created between the two records. If a
Workaround is specified in the Problem record, it will be provided at this point. The increase in Incident count may cause the
Priority of the problem to be adjusted. Depending on the Priority of the Incident (or if the Priority changes), the current
assignee of the Problem may be notified.
INC 2.11: Task Inter Process
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Problem Management
Match the incident to an
open Problem or Known
error
Link
Out
INC 2.11: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.7
Match Found?
Yes
INC 2.8
Matched
Problem Match
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.12
Workaround?
INC 2.11: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
Ensure that the identified Problem record is noted in and/or related to the current
Incident record.
R/A
INC 2.12: Workaround?
INC 2.12: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.11
Link Incident to Problem
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label

Incident Management
Page 41 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.13
Wait for Problem Resolution
No
INC 4.1
CR Required?
Yes
INC 2.12: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
R
INC 2.13: Wait for Problem Resolution
It may not be feasible to develop a workaround for all Incidents and hence, we may have to wait for a resolution from the
Problem Management process.
INC 2.13: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.12
Workaround?
No
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.13: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Manager
Periodically monitor (or receive notification) for an available resolution. All Incidents
Pending Problem Resolution should be reviewed and the appropriate support group
contacted to determine the status of the resolution development.
R/A
INC 2.13: Task Notes
Task Notes
Description
Use of this path should be minimal. Incident Management should always endeavor to come up with some mechanism of
allowing the users to workaround the Incident and in some way alleviate the pain experienced. Even a minimal Workaround
has more value than not providing any at all.

Incident Management
Page 42 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 3.0: Investigate & Diagnose
This activity is where Workarounds are located or developed. Escalations to other support groups may occur during this
activity. If the Incident cannot be related to an existing Problem, one is created.
INC 3.1: Accept Assignment
It is now up to the assigned group's Incident Coordinator to review the incident and either accept it or re-queue it to another
group. The Coordinator must also select an appropriate individual within their group and assign the record to that individual
in the role of Incident Support. The status of the record should be changed accordingly and the assignee notified.
INC 3.2: Acknowledge Assignment
Once the Incident Coordinator has designated a suitable individual to fill the initial role of Incident Support for the incident,
the individual must acknowledge their acceptance. Doing so signifies that the individual is ready to assume the
responsibilities of Incident Support.
INC 3.3: Acquire Additional Information if Required
The details captured thus far in the Incident record are now reviewed. Additionally, relevant error logs, dumps, journals, and
other sources of information are reviewed to gain a full appreciation of the events leading to the Incident. If necessary, the
user (s) and other parties may be contacted to provide additional information and clarifications. The Incident record should
be updated with any relevant findings and additional information.
Annotation:
Access additional sources of information and additional information from the impacted
user
INC 3.4: Re-evaluate Category/Priority
The initial categorization is reviewed and verified. If it is incorrect it is updated and the incident is re-queued to the
appropriate support group. Conditions may also have changed that would merit a change in the Impact or Urgency and
therefore priority of the incident.
INC 3.5: Categorization Change?
INC 3.6: Additional Searches
The purpose of this task is to search the Problem and Knowledge databases in a greater breadth and depth than was done in
Initial Diagnosis and Escalation. If a match is found, the Incident flow is returned to the Service Desk to implement the
workaround. If no matching Problem record can be found, one will be created in the next task.
Annotation:
Incident Support will have a greater depth of knowledge to draw on than Service Desk
and may be able to formulate better search criteria
INC 3.7: Match Found?
INC 3.8: Create Problem
The purpose of this task is to create a Problem record and queue the Problem to the appropriate support group when
necessary based on Problem management Policies. The Problem Management process is now responsible for identifying the
root cause and ensuring that a permanent fix is implemented to avoid subsequent incidents. Problem Management will also
look at any workaround created in Incident Management and optimize it (if required) for re-use.

Incident Management
Page 43 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 3.9: Workaround Possible?
Is there a real possibility of coming up with a viable workaround?
INC 3.10: Develop Workaround
The purpose of this task is to develop a Workaround.
Annotation:
The developed workaround will be recorded in both the Incident record and the related
Problem record
Problem Management may optimize the workaround for future incident resolutions
INC 3.11: Wait for Problem Resolution
It may not be feasible to develop a workaround for all incidents and hence, we may have to wait for a resolution from the
Problem Management process.
Annotation:
It is not feasible to develop a workaround, work on the Incident is halted and we must
wait for a permanent resolution to be identified and implemented by Problem
Management

Incident Management
Page 44 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram

Incident Management
Page 45 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 3.1: Accept Assignment
It is now up to the assigned group's Incident Coordinator to review the incident and either accept it or re-queue it to another
group. The Coordinator must also select an appropriate individual within their group and assign the record to that individual in
the role of Incident Support. The status of the record should be changed accordingly and the assignee notified.
INC 3.1: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.9
Escalate
INC 3.5
Categorization Change?
Yes
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.2
Acknowledge Assignment
INC 3.1: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Coordinator
Monitors their respective queues for Incidents assigned to their group. Responsible
for assigning Incidents to the most suitable individuals for investigation. If the
Incident was incorrectly assigned to the group, the Incident Coordinator will re-queue
it accordingly.
R/A
INC 3.2: Acknowledge Assignment
Once the Incident Coordinator has designated a suitable individual to fill the initial role of Incident Support for the incident, the
individual must acknowledge their acceptance. Doing so signifies that the individual is ready to assume the responsibilities of
Incident Support.
INC 3.2: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.1
Accept Assignment
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.3
Acquire Additional Information if Required
INC 3.2: Task Roles

Incident Management
Page 46 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
The individual must acknowledge the assignment and signify that they are ready to
start working on a resolution.
R/A
INC 3.3: Acquire Additional Information if Required
The details captured thus far in the Incident record are now reviewed. Additionally, relevant error logs, dumps, journals, and
other sources of information are reviewed to gain a full appreciation of the events leading to the Incident. If necessary, the user
(s) and other parties may be contacted to provide additional information and clarifications. The Incident record should be
updated with any relevant findings and additional information.
INC 3.3: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.2
User Confirmation?
No
INC 3.2
Acknowledge Assignment
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.4
Re-evaluate Category/Priority
INC 3.3: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Requests additional information necessary to proceed with Incident investigation.
The Incident record must be updated to reflect the nature of the information
requested.
R/A
Service Desk Agent
Depending on the Incident and established procedures, the Service Desk may play in
role in obtaining the additional information from the user.
C
User
Provides any additional information requested.
C
INC 3.3: Task Notes
Task Notes
Description
It is important that any findings, suspicions and relevant information be captured in the Incident record, so that subsequent
investigation by others (if required) can leverage such information.
INC 3.4: Re-evaluate Category/Priority
The initial categorization is reviewed and verified. If it is incorrect it is updated and the incident is re-queued to the appropriate
support group. Conditions may also have changed that would merit a change in the Impact or Urgency and therefore priority of
the incident.
INC 3.4: Task Workflow

Incident Management
Page 47 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.3
Acquire Additional Information if Required
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.5
Categorization Change?
INC 3.4: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Coordinator
May assist Incident Support with re-categorizing the Incident.
C
Incident Support
Based on the current situation, the person now assigned to the Incident needs to re-
evaluate the categorization, impact, urgency and priority and update the Incident
accordingly. Should the categorization be changed they will re-assign the incident to
the correct support group
R/A
INC 3.4: Task Notes
Task Notes
Description
The number of times an Incident is re-queued should be monitored. Re-queuing may mean an incident is being 'bounced'
from support group to support group with no group taking responsibility for attempting to resolve the incident and,
consequently, no real work on the resolution happening.
INC 3.5: Categorization Change?
INC 3.5: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.4
Re-evaluate Category/Priority
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.6
Additional Searches
No
INC 3.1
Accept Assignment
Yes
INC 3.5: Task Roles

Incident Management
Page 48 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Coordinator
Responsible for ensuring that escalation occurs within identified timeframes and to
the correct group or individual.
R
Incident Support
R
INC 3.6: Additional Searches
The purpose of this task is to search the Problem and Knowledge databases in a greater breadth and depth than was done in
Initial Diagnosis and Escalation. If a match is found, the Incident flow is returned to the Service Desk to implement the
workaround. If no matching Problem record can be found, one will be created in the next task.
INC 3.6: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.5
Categorization Change?
No
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.7
Match Found?
INC 3.6: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Search for potential matching Problems, Known Errors and Knowledge articles for the
Incident.
R/A
INC 3.7: Match Found?
INC 3.7: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.6
Additional Searches
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.8
Create Problem
No
INC 2.11
Link Incident to Problem
Yes
INC 3.7: Task Roles

Incident Management
Page 49 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Coordinator
May be consulted by Incident Support to ensure proper group assignment and the
viability of developing a Workaround.
C
Incident Support
R
INC 3.8: Create Problem
The purpose of this task is to create a Problem record and queue the Problem to the appropriate support group when necessary
based on Problem management Policies. The Problem Management process is now responsible for identifying the root cause
and ensuring that a permanent fix is implemented to avoid subsequent incidents. Problem Management will also look at any
workaround created in Incident Management and optimize it (if required) for re-use.
INC 3.8: Task Inter Process
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Problem Management
Create new Problem Record
Out
INC 3.8: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.7
Match Found?
No
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.9
Workaround Possible?
INC 3.8: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Coordinator
May be consulted by Incident Support to ensure proper group assignment and the
viability of developing a Workaround.
C
Incident Support
Create a Problem record. Relevant info from the Incident should be copied to the
Problem (may be executed automatically by the tool). Ensure that the Problem is
assigned to the correct group. Should make a determination about whether
developing a Workaround is worthwhile.
R/A
Problem Process Manager
May be consulted by Incident support to clarify if a Problem Record needs to be
created
C
INC 3.9: Workaround Possible?
Is there a real possibility of coming up with a viable workaround?

Incident Management
Page 50 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 3.9: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.8
Create Problem
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.10
Develop Workaround
Yes
INC 3.11
Wait for Problem Resolution
No
INC 3.9: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
R
INC 3.10: Develop Workaround
The purpose of this task is to develop a Workaround.
INC 3.10: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.9
Workaround Possible?
Yes
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 4.1
CR Required?
INC 3.10: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Coordinator
May be required to provide additional resources or aid in developing the workaround
C
Incident Support
Take actions to develop an appropriate Workaround. May involve escalating to or
consulting with another individual or group with the requisite skills to accomplish.
Incident should be updated to reflect that a Workaround is under development.
R/A
INC 3.11: Wait for Problem Resolution
It may not be feasible to develop a workaround for all incidents and hence, we may have to wait for a resolution from the
Problem Management process.
INC 3.11: Task Inter Process

Incident Management
Page 51 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Problem Management
Problem record updated that
no workaround will be
developed
No Workaround
Both
INC 3.11: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.9
Workaround Possible?
No
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.11: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Incident support retains ownership of the Incident while waiting on information to be
returned from Problem Management.
R/A

Incident Management
Page 52 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 4.0: Resolve & Recover
This activity includes those tasks required to implement the fix or Workaround located or developed in the previous activity. A
CR will be submitted if required and, if so, the Change Management process will manage the implementation. Depending on
the damage done by the Incident, recovery actions may also take place.
INC 4.1: CR Required?
Change Management Policies will identify when a CR is required.
Annotation:
Does implementing the workaround require changing something that is under Change
Management control? If so a CR is required to trigger actions from Change
Management.
INC 4.2: Create CR
The purpose of this task is to create a Change Request. If a change to the environment is required to resolve the Incident
then the Change Management Process is responsible for managing the Change.
Annotation:
Change Management will facilitate the implementation of the workaround
INC 4.3: Implement Resolution/Workaround
The purpose of this task is to implement the Resolution or Workaround. The Workaround or Resolution may be approved,
scheduled and executed by the Change Management process.
INC 4.4: Recover the Environment
The purpose of this task is to recover after the Resolution or Workaround has been implemented. For example, after a disk
drive is replaced (the resolution), the data may need to be restored (the recovery) from a backup.
Annotation:
Workaround has been implemented, either by Incident Support or by a successful
change implementation. The production environment may need additional resetting
to be operational
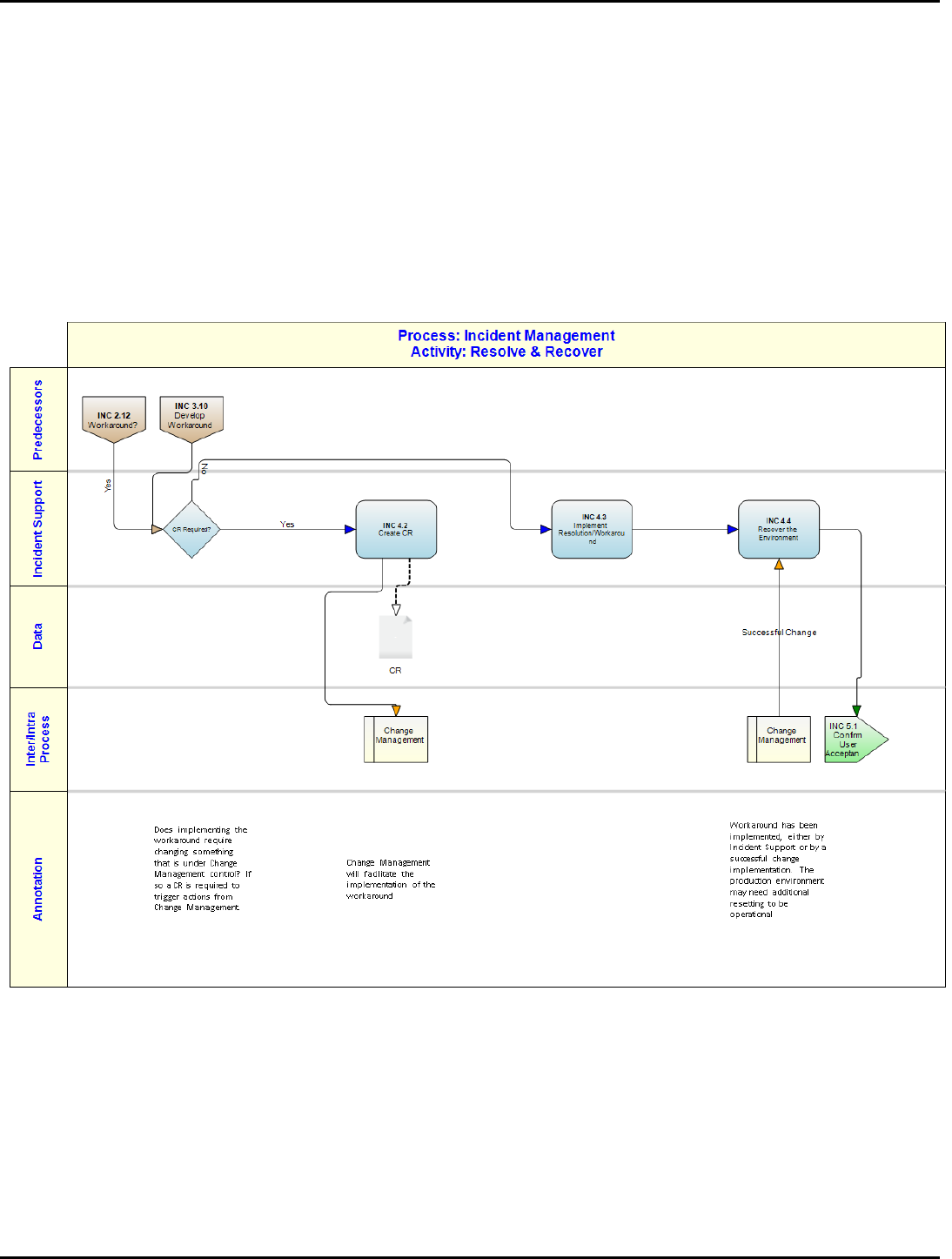
Incident Management
Page 53 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram

Incident Management
Page 54 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 4.1: CR Required?
Change Management Policies will identify when a CR is required.
INC 4.1: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.12
Workaround?
Yes
INC 3.10
Develop Workaround
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 4.2
Create CR
Yes
INC 4.3
Implement Resolution/Workaround
No
INC 4.1: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Determine the need for an CR
R
INC 4.2: Create CR
The purpose of this task is to create a Change Request. If a change to the environment is required to resolve the Incident then
the Change Management Process is responsible for managing the Change.
INC 4.2: Task Inter Process
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Change Management
Change Management will
implement the resolution
Out
INC 4.2: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 4.1
CR Required?
Yes
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 4.2: Task Roles

Incident Management
Page 55 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Coordinator
May provide guidance in determining if a CR is required or if restoration of service
would be accomplished thru established SOPs.
C
Incident Support
Create and submit a CR for the restoration of service.
R/A
INC 4.3: Implement Resolution/Workaround
The purpose of this task is to implement the Resolution or Workaround. The Workaround or Resolution may be approved,
scheduled and executed by the Change Management process.
INC 4.3: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 4.1
CR Required?
No
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 4.4
Recover the Environment
INC 4.3: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Participate as required in the implementation of the Workaround or resolution. May
need to solicit the assistance of team members, or re-assign the incident.
R/A
Service Desk Manager
Is notified of the planned implementation so that they can in turn notify affected
users, or make their staff aware should users call with queries regarding the status of
the Incident.
I
User
The user may be asked to participate in the implementation or verification of the
Change.
C
User
Depending on the nature of the Incident, individual user(s) may be notified of the
planned implementation.
I
INC 4.3: Task Notes
Task Notes
Description
The Service Desk must coordinate the implementation of the Workaround or Resolution with all affected users.
INC 4.4: Recover the Environment
The purpose of this task is to recover after the Resolution or Workaround has been implemented. For example, after a disk drive
is replaced (the resolution), the data may need to be restored (the recovery) from a backup.

Incident Management
Page 56 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 4.4: Task Inter Process
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Change Management
Close Change Request
Successful Change
In
INC 4.4: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 4.3
Implement Resolution/Workaround
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.1
Confirm User Acceptance
INC 4.4: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Performs the steps necessary to recover the environment to its previous good state
(e.g., restoring a database from a checkpoint or backup). May solicit assistance or
escalate Incident in order to accomplish this task.
R/A

Incident Management
Page 57 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 5.0: Close Incident
Having implemented a Workaround or fix, it is now time to close the Incident. The affected user(s) should be contacted to
solicit their acceptance of the Workaround or fix, and to obtain any additional feedback on the handling of their issue. Details
of the resolution and an appropriate closure and cause code should be captured.
INC 5.1: Confirm User Acceptance
The purpose of this task is to confirm that the User is satisfied that the workaround or resolution has made it possible for
them to do what they need to do.
Annotation:
The affected user should confirm that the workaround or permanent resolution
(Problem Management) is able to get what they need to continue to work
INC 5.2: User Confirmation?
Results of User Confirmation
INC 5.3: Capture User Feedback
The purpose of this task is to capture User feedback. Satisfaction surveys are important in order to measure the
effectiveness of the Service Desk and the Incident Management Process
Annotation:
This is not a Customer Satisfaction survey. Simply capture any comments the user has
about how this incident was handled
INC 5.4: Resolution/Recovery Details
The purpose of this task is to ensure all details of the Resolution, as well as a suitable Closure Code and Cause Code are
identified and recorded in the Incident.
Annotation:
If Change Management verified the incident resolution as part of its implementation to
resolve the incident the details need to be recorded in the Incident record before
closure
INC 5.5: Close Incident
The purpose of this task is to close the Incident
INC 5.6: Process End

Incident Management
Page 58 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Cross-Functional Flow Diagram

Incident Management
Page 59 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 5.1: Confirm User Acceptance
The purpose of this task is to confirm that the User is satisfied that the workaround or resolution has made it possible for them
to do what they need to do.
INC 5.1: Task Inter Process
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Problem Management
Known error closed, incident
resolution to be verified
In
INC 5.1: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.4
Resolved?
Yes
INC 4.4
Recover the Environment
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.2
User Confirmation?
INC 5.1: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Contacts the affected user(s) to confirm that the implemented
Workaround/resolution has in fact addressed their original Incident.
R
User
Takes any steps necessary to verify that their incident has been resolved to their
satisfaction.
C
INC 5.1: Task Notes
Task Notes
Description
It may not be practical or feasible – depending on the nature of the Incident and its resolution or Workaround – to contact all
the affected users. However, every attempt should be made to do so where it makes sense, even if that is only a subset of
the affected users (e.g., a user from each region).
Contact with the User will be attempted 3 times before the incident is placed into Resolved status either by email or
Telephone
INC 5.2: User Confirmation?
Results of User Confirmation

Incident Management
Page 60 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 5.2: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.1
Confirm User Acceptance
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 3.3
Acquire Additional Information if Required
No
INC 5.3
Capture User Feedback
Yes
INC 5.2: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
R
INC 5.3: Capture User Feedback
The purpose of this task is to capture User feedback. Satisfaction surveys are important in order to measure the effectiveness of
the Service Desk and the Incident Management Process
INC 5.3: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.2
User Confirmation?
Yes
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.4
Resolution/Recovery Details
INC 5.3: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Solicits /accepts feedback from the user and enters it into the Incident record.
R
User
Provides feedback either to the Service Desk Agent or via the electronic survey they
received.
C
INC 5.4: Resolution/Recovery Details
The purpose of this task is to ensure all details of the Resolution, as well as a suitable Closure Code and Cause Code are
identified and recorded in the Incident.

Incident Management
Page 61 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 5.4: Task Inter Process
Inter Process defines the connections between external Processes.
Process
Task ID
Description
Label
Direction
Change Management
Successful change
implementation to resolve
incident, Incident resolution
with user verified at Change
close
In
INC 5.4: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 2.6
Notify Stakeholders/Declare Major Incident
Resolved
INC 5.3
Capture User Feedback
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.5
Close Incident
INC 5.4: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Incident Support
Captures or ensures that all of the necessary closure information is recorded in the
Incident. If the Incident had been escalated to 2nd or 3rd level support groups, they
may have completed this information.
R
INC 5.5: Close Incident
The purpose of this task is to close the Incident
INC 5.5: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.4
Resolution/Recovery Details
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.6
Process End

Incident Management
Page 62 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
INC 5.5: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
Close the incident record with the appropriate closure code
R/A
Service Desk Manager
For high-priority service-impacting Incidents, reviews the quality and completeness of
the information captured in the Incident record.
C
INC 5.5: Task Notes
Task Notes
Description
Records will be automatically closed after 5 days
INC 5.6: Process End
INC 5.6: Task Workflow
Predecessors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.5
Close Incident
Successors
Task ID
Task Name
Diagram Label
INC 5.6: Task Roles
Name
Duties
RACI
Service Desk Agent
R

Incident Management
Page 63 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
States
States are used to indicate points of progress of an instance through the lifecycle of the process.
Process States
The following lists the discrete State values that can be assumed by a specific instance in this process.
Name
Description
New
The first state of the Incident. The incident has been created and assigned but is not being worked on
yet.
Active
The incident has been acknowledged by Incident support and is being actively worked on
Awaiting Problem
A problem has been created to determine root cause before the incident can be resolved. This puts the
incident in a wait mode and the clock may be stopped
Awaiting User Info
Support is waiting for the user to provide additional information before the incident can be resolved. The
clock may be stopped at this time
Awaiting Evidence
Support is waiting for confirmation or evidence that the implemented resolution has fixed the issue
Resolved
The incident has been resolved and the user has been notified. The user may choose to re-open the
incident if they are still experiencing problems.

Incident Management
Page 64 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Process State Diagram

Incident Management
Page 65 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Appendix
Attachments and Links
Incident Management
Page 66 of 66
©2014 Navvia, a division of Consulting-Portal, Inc.
9/2/2015
Definitions
Term
Definition
RACI Model
The RACI-method is based on the principle that people act in one of four ways
when executing a task. It accounts for the fact that more than one role may be
active in performing a specific task while clearly defining specific responsibilities
for that role. While many roles may be involved in a task only one is Accountable
for the results. The actions are:
R Responsible for the action (may do the task)
A Accountable for the action (including approval)
C Required to be Consulted on the action
I Required to be Informed of the action
If a task does not have an Accountable role indicated then the Responsible role is
assumed to be accountable for the task.
Resolved
An incident may be placed into Resolved when a proposed technical resolution has
been provided or implemented and the Technician believes has restored the
service
Closed
TBA
