
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified
Communications Manager
First Published: 2015-07-13
Last Modified: 2023-06-16
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH
THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY,
CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class A devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15
of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required to correct the interference at their own expense.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of
the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, users are
encouraged to try to correct the interference by using one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Modifications to this product not authorized by Cisco could void the FCC approval and negate your authority to operate the product.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public domain version of
the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright
©
1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS.
CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network
topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional
and coincidental.
All printed copies and duplicate soft copies of this document are considered uncontrolled. See the current online version for the latest version.
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide. Addresses and phone numbers are listed on the Cisco website at www.cisco.com/go/offices.
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on
age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that
is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on standards documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/legal/trademarks.html. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a
partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1721R)
©
2015–2023 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.

CONTENTS
Preface xiii
PREFACE
Overview xiii
Audience xiii
Guide Conventions xiii
Related Documentation xiv
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Documentation xiv
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation xv
Cisco Business Edition 6000 Documentation xv
Documentation, Support, and Security Guidelines xv
Cisco Product Security Overview xv
New and Changed Information 1
CHAPTER 1
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.2(1) 1
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.1(1) 2
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.0(1) 2
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.8(1) 2
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.7(1) 3
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.6(1) 3
New Information for Firmware Release 12.5(1)SR3 4
New Information for Firmware Release 12.5(1)SR1 4
New Information for Firmware Release 12.1(1)SR1 5
New Information for Firmware Release 12.1(1) 5
New Information for Firmware Release 12.0(1) 6
New Information for Firmware Release 11.7(1) 6
New Information for Firmware Release 11.5(1)SR1 6
New Information for Firmware Release 11.5(1) 7
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
iii

New Information for Firmware Release 11.0 7
About the Cisco IP Phone 9
PART I
Technical Details 11
CHAPTER 2
Physical and Operating Environment Specifications 11
Cable Specifications 12
Network and Computer Port Pinouts 12
Network Port Connector 12
Computer Port Connector 13
Phone Power Requirements 14
Power Outage 15
Power Reduction 15
Power Negotiation Over LLDP 15
Network Protocols 16
VLAN Interaction 19
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Interaction 20
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express Interaction 20
Voice Messaging System Interaction 21
Phone Startup Overview 21
External Devices 23
USB Port Information 23
Phone Configuration Files 24
Phone Behavior During Times of Network Congestion 24
Phone Behavior on a Network with Two Network Routers 25
Application Programming Interface 25
Cisco IP Phone Hardware 27
CHAPTER 3
Phone Overview 27
Cisco IP Phone 8811 29
Phone Connections 29
Cisco IP Phones 8841 and 8845 30
Phone Connections 30
Cisco IP Phones 8851 and 8851NR 31
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
iv
Contents

Phone Connections 32
Cisco IP Phones 8861, 8865, and 8865NR 33
Phone Connections 33
Buttons and Hardware 34
Softkey, Line, and Feature Buttons 35
Protect Your Video Phone Camera 36
Cisco IP Phone Installation 39
PART II
Cisco IP Phone Installation 41
CHAPTER 4
Verify the Network Setup 41
Activation Code Onboarding for On-premises Phones 42
Activation Code Onboarding and Mobile and Remote Access 43
Enable Autoregistration for Phones 43
Install Cisco IP Phone 45
Share a Network Connection with Your Phone and Computer 46
Set Up Phone from Setup Menus 47
Apply a Phone Password 48
Text and Menu Entry from Phone 48
Enable the Wireless LAN on the Phone 49
Set Up the Wireless LAN from Cisco Unified Communications Manager 50
Set Up Wireless LAN from Phone 50
Set the Number of WLAN Authentication Attempts 52
Enable WLAN Prompt Mode 53
Set Up a Wi-Fi Profile using Cisco Unified Communications Manager 53
Set Up a Wi-Fi Group using Cisco Unified Communications Manager 55
Configure Network Settings 55
Ethernet Setup Fields 56
IPv4 Fields 57
IPv6 Fields 59
Set Up Phone to Use DHCP 60
Set Up Phone to Not Use DHCP 61
Load Server 61
Phone Startup Verification 62
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
v
Contents

Configure Phone Services for Users 62
Change a User's Phone Model 63
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Phone Setup 65
CHAPTER 5
Set Up Cisco IP Phone 65
Determine the Phone MAC Address 68
Phone Addition Methods 68
Add Phones Individually 69
Add Phones with a BAT Phone Template 69
Add Users to Cisco Unified Communications Manager 70
Add a User from an External LDAP Directory 70
Add a User Directly to Cisco Unified Communications Manager 71
Add a User to an End User Group 71
Associate Phones with Users 72
Survivable Remote Site Telephony 72
Enhanced Survivable Remote Site Telephony 75
Application Dial Rules 75
Configure Application Dial Rules 75
Self Care Portal Management 77
CHAPTER 6
Self Care Portal Overview 77
Set Up User Access to the Self Care Portal 77
Customize the Self Care Portal Display 78
Cisco IP Phone Administration 79
PART III
Cisco IP Phone Security 81
CHAPTER 7
Security Enhancements for Your Phone Network 81
Supported Security Features 82
Set Up a Locally Significant Certificate 87
Enable FIPS Mode 88
Phone Call Security 88
Secure Conference Call Identification 89
Secure Phone Call Identification 90
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
vi
Contents

Provide Encryption for Barge 91
WLAN Security 91
Set Up Authentication Mode 94
Wireless Security Credentials 94
Set Up Username and Password 95
Pre-Shared Key Setup 95
Wireless Encryption 96
Export CA certificate from ACS using Microsoft Certificate Services 97
PEAP Setup 101
Wireless LAN Security 102
Cisco IP Phone Administration Page 102
SCEP Setup 105
802.1X Authentication 106
Access 802.1X Authentication 107
Set Device Authentication Field 108
Cisco IP Phone Customization 109
CHAPTER 8
Custom Phone Rings 109
Custom Background Images 109
Set Up Wideband Codec 111
Set Up Idle Display 111
Customize the Dial Tone 112
Phone Features and Setup 115
CHAPTER 9
Phone Features and Setup Overview 115
Cisco IP Phone User Support 115
Telephone Features 116
Feature Buttons and Softkeys 133
Phone Feature Configuration 135
Set Up Phone Features for All Phones 135
Set Up Phone Features for a Group of Phones 136
Set Up Phone Features for a Single Phone 136
Product Specific Configuration 136
Feature Configuration Best Practices 154
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
vii
Contents

High Call Volume Environments 154
Multiline Environments 155
Session Line Mode Environment 155
Field: Always Use Prime Line 156
Disable Transport Layer Security Ciphers 156
Enable Call History for Shared Line 156
Schedule Power Save for Cisco IP Phone 157
Schedule EnergyWise on Cisco IP Phone 158
Set Up Do Not Disturb 162
Enable Agent Greeting 163
Set Up Monitoring and Recording 164
Set Up Call Forward Notification 164
Enable BLF for Call Lists 165
Set Up Energy Efficient Ethernet for Switch and PC Port 166
Set Up RTP/sRTP Port Range 167
Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway 167
Deployment Scenarios 168
Media Paths and Interactive Connectivity Establishment 169
Phone Features Available for Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway 169
Configure User Credentials Persistent for Expressway Sign-In 171
Generate a QR Code for MRA Sign-In 172
Problem Report Tool 172
Configure a Customer Support Upload URL 173
Set the Label for a Line 174
Set Up Dual Bank Information 174
Park Monitoring 175
Set Up Park Monitoring Timers 175
Set Park Monitoring Parameters for Directory Numbers 176
Set Up Park Monitoring for Hunt Lists 177
Set Up the Audio and Video Port Range 177
Set up Cisco IP Manager Assistant 178
Set up Visual Voicemail 180
Set Up Visual Voicemail for a Specific User 181
Visual Voicemail Setup for a User Group 182
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
viii
Contents

Assured Services SIP 182
Migration of your Phone to a Multiplatform Phone Directly 183
Multilevel Precedence and Preemption 183
Set Up Softkey Template 183
Phone Button Templates 185
Modify Phone Button Template 185
Assign Phone Button Template for All Calls 186
Set Up PAB or Speed Dial as IP Phone Service 186
Modify Phone Button Template for PAB or Fast Dial 188
VPN Configuration 188
Set Up Additional Line Keys 189
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode 190
Set Up TLS Resumption Timer 192
Enable Intelligent Proximity 193
Video Transmit Resolution Setup 193
Headset Management on Older Versions of Cisco Unified Communications Manager 195
Download the Default Headset Configuration File 195
Modify the Default Headset Configuration File 196
Install the Default Configuration File on Cisco Unified Communications Manager 198
Restart the Cisco TFTP Server 198
Corporate and Personal Directory 201
CHAPTER 10
Corporate Directory Setup 201
Personal Directory Setup 201
User Personal Directory Entries Setup 202
Download Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer 202
Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer Deployment 203
Install Synchronizer 203
Set Up Synchronizer 203
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting 205
PART IV
Monitoring Phone Systems 207
CHAPTER 11
Cisco IP Phone Status 207
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
ix
Contents

Display Phone Information Window 207
Phone Information Fields 208
Display Status Menu 208
Display Status Messages Window 209
Display Network Information Screen 213
Display Network Statistics Screen 213
Display Wireless Statistics Screen 216
Display Call Statistics Window 218
Display Current Access Point Window 220
Cisco IP Phone Web Page 222
Access Web Page for Phone 222
Device Information 223
Network Setup 225
Network Statistics 230
Device Logs 233
Streaming Statistics 233
Request Information from the Phone in XML 237
Sample CallInfo Output 238
Sample LineInfo Output 238
Sample ModeInfo Output 239
Troubleshooting 241
CHAPTER 12
General Troubleshooting Information 241
Startup Problems 242
Cisco IP Phone Does Not Go Through the Normal Startup Process 243
Cisco IP Phone Does Not Register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager 244
Phone Displays Error Messages 244
Phone Cannot Connect to TFTP Server or to Cisco Unified Communications Manager 244
Phone Cannot Connect to TFTP Server 244
Phone Cannot Connect to Server 245
Phone Cannot Connect Using DNS 245
Cisco Unified Communications Manager and TFTP Services Are Not Running 245
Configuration File Corruption 245
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Phone Registration 246
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
x
Contents

Cisco IP Phone Cannot Obtain IP Address 246
Phone Not Registering 246
Phone Reset Problems 246
Phone Resets Due to Intermittent Network Outages 247
Phone Resets Due to DHCP Setting Errors 247
Phone Resets Due to Incorrect Static IP Address 247
Phone Resets During Heavy Network Usage 247
Phone Resets Due to Intentional Reset 248
Phone Resets Due to DNS or Other Connectivity Issues 248
Phone Does Not Power Up 248
Phone Cannot Connect to LAN 248
Cisco IP Phone Security Problems 249
CTL File Problems 249
Authentication Error, Phone Cannot Authenticate CTL File 249
Phone Cannot Authenticate CTL File 249
CTL File Authenticates but Other Configuration Files Do Not Authenticate 249
ITL File Authenticates but Other Configuration Files Do Not Authenticate 250
TFTP Authorization Fails 250
Phone Does Not Register 250
Signed Configuration Files Are Not Requested 251
Video Call Problems 251
No Video Between Two Cisco IP Video Phones 251
Video Stutters or Drops Frames 251
Cannot Transfer a Video Call 252
No Video During a Conference call 252
General Telephone Call Problems 252
Phone Call Cannot Be Established 252
Phone Does Not Recognize DTMF Digits or Digits Are Delayed 253
Troubleshooting Procedures 253
Create a Phone Problem Report from Cisco Unified Communications Manager 253
Create a Console Log from Your Phone 253
Check TFTP Settings 254
Determine DNS or Connectivity Issues 254
Check DHCP Settings 255
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
xi
Contents

Create a New Phone Configuration File 255
Identify 802.1X Authentication Problems 256
Verify DNS Settings 256
Start Service 257
Control Debug Information from Cisco Unified Communications Manager 257
Additional Troubleshooting Information 258
Maintenance 259
CHAPTER 13
Basic Reset 259
Reset the Phone to the Factory Settings from the Phone Keypad 259
Perform Reset All Settings from Phone Menu 260
Reboot Your Phone from the Backup Image 260
Perform Network Configuration Reset 261
Perform User Network Configuration Reset 261
Remove CTL File 261
Quality Report Tool 262
Voice Quality Monitoring 262
Voice Quality Troubleshooting Tips 262
Cisco IP Phone Cleaning 263
International User Support 265
CHAPTER 14
Unified Communications Manager Endpoints Locale Installer 265
International Call Logging Support 265
Language Limitation 266
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
xii
Contents

Preface
• Overview, on page xiii
• Audience, on page xiii
• Guide Conventions, on page xiii
• Related Documentation, on page xiv
• Documentation, Support, and Security Guidelines, on page xv
Overview
The Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager provides
the information you need to understand, install, configure, manage, and troubleshoot the phones on a VoIP
network.
Because of the complexity of an IP telephony network, this guide does not provide complete and detailed
information for procedures that you need to perform in Cisco Unified Communications Manager or other
network devices.
Audience
Network engineers, system administrators, and telecom engineers should review this guide to learn the steps
that are required to set up Cisco IP Phones. The tasks described in this document involve configuring network
settings that are not intended for phone users. The tasks in this manual require a familiarity with Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
Guide Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
DescriptionConvention
Commands and keywords are in boldface.boldface font
Arguments for which you supply values are in italics.italic font
Elements in square brackets are optional.[]
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
xiii

DescriptionConvention
Alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars.{x | y | z}
Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by vertical bars.[x | y | z]
A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string or the string will
include the quotation marks.
string
Terminal sessions and information the system displays are in screen font.screen font
Information you must enter is in input font.input font
Arguments for which you supply values are in italic screen font.italic screen font
The symbol ^ represents the key labeled Control - for example, the key combination ^D in a screen
display means hold down the Control key while you press the D key.
^
Nonprinting characters such as passwords are in angle brackets.<>
Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
publication.
Note
Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage or
loss of data.
Caution
Warnings use the following convention:
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work
on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard
practices for preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each warning to locate
its translation in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device. Statement 1071
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Attention
Related Documentation
Use the following sections to obtain related information.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Documentation
Find documentation specific to your language, phone model, and call control system on the product support
page for the Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
xiv
Preface
Related Documentation

For help information about Cisco Video Phone 8875, see Cisco Video Phone 8875.
The Deployment Guide is located at the following URL:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/collaboration-endpoints/unified-ip-phone-8800-series/
products-implementation-design-guides-list.html
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation
See the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation Guide and other publications that are specific
to your Cisco Unified Communications Manager release on the product support page.
Cisco Business Edition 6000 Documentation
Refer to the Cisco Business Edition 6000 Documentation Guide and other publications that are specific to
your Cisco Business Edition 6000 release. Navigate from the following URL:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/unified-communications/business-edition-6000/
tsd-products-support-series-home.html
Documentation, Support, and Security Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback, reviewing
security guidelines, and also recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly What’s New
in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
Cisco Product Security Overview
This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to U.S. and local country laws that govern import,
export, transfer, and use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply third-party authority to
import, export, distribute, or use encryption. Importers, exporters, distributors, and users are responsible for
compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product, you agree to comply with applicable
laws and regulations. If you are unable to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately.
Further information regarding U.S. export regulations can be found at https://www.bis.doc.gov/
policiesandregulations/ear/index.htm.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
xv
Preface
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation

Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
xvi
Preface
Cisco Product Security Overview

CHAPTER 1
New and Changed Information
• New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.2(1), on page 1
• New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.1(1), on page 2
• New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.0(1), on page 2
• New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.8(1), on page 2
• New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.7(1), on page 3
• New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.6(1), on page 3
• New Information for Firmware Release 12.5(1)SR3, on page 4
• New Information for Firmware Release 12.5(1)SR1, on page 4
• New Information for Firmware Release 12.1(1)SR1, on page 5
• New Information for Firmware Release 12.1(1), on page 5
• New Information for Firmware Release 12.0(1), on page 6
• New Information for Firmware Release 11.7(1), on page 6
• New Information for Firmware Release 11.5(1)SR1, on page 6
• New Information for Firmware Release 11.5(1), on page 7
• New Information for Firmware Release 11.0, on page 7
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.2(1)
The following information is new or changed for Firmware Release 14.2(1).
New or ChangedFeature
Security Enhancements for Your Phone Network, on
page 81
Support for SIP OAuth on SRST
Telephone Features, on page 116Simplified Extension Mobility Login with Cisco
Headset 730 USB Adapter
Telephone Features, on page 116Bluetooth Mute Sync for Cisco Headset 700 Series
Telephone Features, on page 116New settings for Cisco Headset 500 Series: Dock
Event and Always On Mode
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
1

New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.1(1)
The following information is new or changed for Firmware Release 14.1(1).
New or ChangedFeature
Security Enhancements for Your Phone Network, on
page 81
SIP OAuth for Proxy TFTP support
Telephone Features, on page 116Improved Call Alert for Hunt Group
Product Specific ConfigurationConfigurable Calling Number Display for Enhanced
Line Mode
Telephone Features, on page 116Configurable Delayed PLAR
Telephone Features, on page 116MRA Support for Extension Mobility Login with
Cisco Headsets
Migration of your Phone to a Multiplatform Phone
Directly, on page 183
Phone Migration without Transition Load
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.0(1)
Table 1: New and Changed Information
New or ChangedFeature
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136Call Park Monitoring Enhancement
Security Enhancements for Your Phone Network, on
page 81
SIP OAuth Enhancements
Survivable Remote Site Telephony, on page 72
Telephone Features, on page 116
User Interface Enhancements
Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway, on
page 167
OAuth Enhancements for MRA
As of Firmware Release 14.0, the phones support DTLS 1.2. DTLS 1.2 requires Cisco Adaptive Security
Appliance (ASA) Release 9.10 or later. You configure the minimum DTLS version for a VPN connection in
ASA. For more information, see ASDM Book 3: Cisco ASA Series VPN ASDM Configuration Guide at
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/security/asa-5500-series-next-generation-firewalls/
products-installation-and-configuration-guides-list.html
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.8(1)
The following information is new or changed for Firmware Release 12.8(1).
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
2
New and Changed Information
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 14.1(1)

New or Changed ContentFeature
Change a User's Phone Model, on page 63Phone Data Migration
Device Information, on page 223Headset Update Enhancement
Telephone Features, on page 116Simplify Extension Mobility Login with Cisco
Headsets
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136, new
fields Lower Your Voice Alert and Mark Call As
Spam
Feature Control Changes
Clarify Wi-Fi and the PC Port:
• Set Up Phone from Setup Menus, on page 47
• Enable the Wireless LAN on the Phone, on page
49
General changes
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136Add additional information about the Web Access
field
Telephone Features, on page 116Remove unsupported feature
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.7(1)
Table 2: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide Revisions for Firmware Release 12.7(1)
Updated SectionRevision
Custom Background Images, on page 109Updated for wallpaper support on key expansion
modules.
Device Information, on page 223Updated for Cisco Headset 730 support
Device Information, on page 223
Headset Management on Older Versions of Cisco
Unified Communications Manager, on page 195
Updated for Cisco Headset 500 Series Firmware
Release 2.0
Telephone Features, on page 116Updated for incoming hunt group calls.
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136E-hook configuration information was removed.
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.6(1)
All references into Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation have been updated to support all
Cisco Unified Communications Manager releases.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
3
New and Changed Information
New and Changed Information for Firmware Release 12.7(1)

Table 3: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide Revisions for Firmware Release 12.6(1)
Updated SectionRevision
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136
Session Line Mode Environment, on page 155
Updated for Revert to Primary Line in Session line
mode.
New Information for Firmware Release 12.5(1)SR3
All references into Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation have been updated to support all
Cisco Unified Communications Manager releases.
Table 4: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide Revisions for Firmware Release 12.5(1)SR3
Updated SectionRevision
Activation Code Onboarding and Mobile and Remote
Access, on page 43
Support for Activation Code Onboarding and Mobile
and Remote Access
Create a Phone Problem Report from Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, on page 253
Support for Problem Report Tool use from Cisco
Unified Communications Manager.
Share a Network Connection with Your Phone and
Computer, on page 46
New topic
Protect Your Video Phone Camera, on page 36New topic
New Information for Firmware Release 12.5(1)SR1
All references into Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation have been updated to support all
Cisco Unified Communications Manager releases.
Table 5: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide Revisions for Firmware Release 12.5(1)SR1
Updated SectionRevision
Supported Security Features, on page 82Support for Elliptic Curve support
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode, on page
190
Support for Call History enhancements for Enhanced
line mode with rollover lines
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express
Interaction, on page 20
Support for Whisper Paging on Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Express support
Language Limitation, on page 266Support for Chinese language support
Activation Code Onboarding for On-premises Phones,
on page 42
Support for Activation Code Onboarding
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
4
New and Changed Information
New Information for Firmware Release 12.5(1)SR3

Updated SectionRevision
Media Paths and Interactive Connectivity
Establishment, on page 169
Support for Media Paths and Interactive Connectivity
Establishment
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136Support for Disable TLS Ciphers
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136Support for Disable handset so audio path can be kept
on headset
Headset Management on Older Versions of Cisco
Unified Communications Manager, on page 195
Support for Remote Configuration of Headset
Parameters
New Information for Firmware Release 12.1(1)SR1
All references into Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation have been updated to support all
Cisco Unified Communications Manager releases.
Table 6: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide Revisions for Firmware Release 12.1(1)SR1
Updated SectionRevision
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136Enbloc Dialing for Inter-Digit Timer T.302
Enhancement.
New Information for Firmware Release 12.1(1)
All references into Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation have been updated to support all
Cisco Unified Communications Manager releases.
Table 7: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide Revisions for Firmware Release 12.1(1)
Updated SectionRevision
Phone Features Available for Mobile and Remote
Access Through Expressway, on page 169
Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway now
supports Enhanced line mode.
Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway, on
page 167
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode, on page
190
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136
Enabling or disabling TLS 1.2 for web server access
is now supported.
Phone Overview, on page 27The G722.2 AMR-WB audio codec is now supported.
Call Statistics Fields, on page 218
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
5
New and Changed Information
New Information for Firmware Release 12.1(1)SR1

New Information for Firmware Release 12.0(1)
All new features have been added to Telephone Features, on page 116.
All references into Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation have been updated to support all
Cisco Unified Communications Manager releases.
Table 8: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide Revisions for Firmware Release 12.0(1)
Updated SectionRevision
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode, on page
190
Updated for Call Park, Call Park Line Status, Group
Pickup, and Hunt Groups support on Enhanced Line
Mode
New Information for Firmware Release 11.7(1)
No administration updates were required for firmware release 11.7(1).
New Information for Firmware Release 11.5(1)SR1
All new features have been added to Telephone Features, on page 116.
All references into Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation have been updated to support all
Cisco Unified Communications Manager releases.
Table 9: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide Revisions for Firmware Release 11.5(1)SR1
Updated SectionRevision
• Phone Power Requirements, on page 14
• Network Protocols, on page 16
• Phone Overview, on page 27
• Buttons and Hardware, on page 34
Updated for Cisco IP Phone 8865NR support
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode, on page
190
Updated for Recording and Monitoring support on
Enhanced Line Mode
Enable the Wireless LAN on the Phone, on page 49Updated for WLAN Scan List support
Set Up Wireless LAN from Phone, on page 50
Configure Network Settings, on page 55
Set Up Do Not Disturb, on page 162
Updated for Do not disturb with MLPP support
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136Updated for Configurable Ringer support
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
6
New and Changed Information
New Information for Firmware Release 12.0(1)

Updated SectionRevision
Security Enhancements for Your Phone Network, on
page 81
Enhanced Security
Updates to Cisco IP Phone Web Page, on page 222
New presentation of phone feature configuration in
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Phone
Feature Configuration, on page 135
General changes
New Information for Firmware Release 11.5(1)
Table 10: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide revisions for Firmware Release 11.5(1).
Updated SectionRevision
Set Up Additional Line Keys, on page 189
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode, on page
190
Enhanced line mode is supported.
Set Up Do Not Disturb, on page 162Do Not Disturb (DND) was updated for new display.
Phone Overview, on page 27Opus codec is supported.
Enable FIPS Mode, on page 88FIPS Mode was added.
Set Up Wireless LAN from Phone, on page 50WLAN setup was updated.
Set Up a Wi-Fi Profile using Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, on page 53
WLAN Profile for Cisco IP Phone 8861 and 8865 is
supported.
Set Up a Wi-Fi Group using Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, on page 55
Set the Number of WLAN Authentication Attempts,
on page 52
Set WLAN Authentication Attempts is supported.
Enable WLAN Prompt Mode, on page 53Enable WLAN Prompt Mode is supported.
Customize the Dial Tone, on page 112Customize Dial Tone is supported.
Display Network Information Screen, on page 213Display Network Info Screen is supported.
New Information for Firmware Release 11.0
All new features have been added to Telephone Features, on page 116.
All references into Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation have been updated to support all
Cisco Unified Communications Manager releases.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
7
New and Changed Information
New Information for Firmware Release 11.5(1)

Table 11: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Administration Guide Revisions for Firmware Release 11.0
Updated SectionRevision
• VPN Configuration, on page 188
• Configure Network Settings, on page 55
• Set Up Energy Efficient Ethernet for Switch and
PC Port, on page 166
• Video Transmit Resolution Setup, on page 193
• Enhanced Survivable Remote Site Telephony,
on page 75
Updated for clarification and to address deficiencies
• Control Debug Information from Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, on page 257.
Updated for improved Sectional phone debug option
support
• WLAN Security, on page 91.
• Set Up Authentication Mode, on page 94
• Wireless Security Credentials, on page 94
Updated for improved EAP-TLS + SCEP,
PEAP-GTC, and X.509 digital certificates support
• Problem Report Tool, on page 172.
• Configure a Customer Support Upload URL, on
page 173.
Updated for improved Problem Report Tool(PRT)
support
• Application Dial Rules, on page 75Added for Application Dial Rule support
• Set the Label for a Line, on page 174.Added for Line Text Label
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
8
New and Changed Information
New Information for Firmware Release 11.0

CHAPTER 2
Technical Details
• Physical and Operating Environment Specifications, on page 11
• Cable Specifications, on page 12
• Phone Power Requirements, on page 14
• Network Protocols, on page 16
• VLAN Interaction, on page 19
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager Interaction, on page 20
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express Interaction, on page 20
• Voice Messaging System Interaction, on page 21
• Phone Startup Overview, on page 21
• External Devices, on page 23
• USB Port Information, on page 23
• Phone Configuration Files, on page 24
• Phone Behavior During Times of Network Congestion, on page 24
• Phone Behavior on a Network with Two Network Routers, on page 25
• Application Programming Interface, on page 25
Physical and Operating Environment Specifications
The following table shows the physical and operating environment specifications for the Cisco IP Phone 8800
Series.
Table 12: Physical and Operating Specifications
Value or rangeSpecification
32° to 104°F (0° to 40°C)Operating temperature
Operating: 10% to 90% (non-condensing)
Non-operating: 10% to 95% (non-condensing)
Operating relative humidity
14° to 140°F (–10° to 60°C)Storage temperature
9.02 in. (229.1 mm)Height
10.13 in. (257.34 mm)Width
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
11

Value or rangeSpecification
1.57 in. (40 mm)Depth
2.62 lb (1.19 kg)Weight
100-240 VAC, 50-60 Hz, 0.5 A when using the AC adapter
48 VDC, 0.2 A when using the in-line power over the network cable
Power
Category 3/5/5e/6 for 10-Mbps cables with 4 pairs
Category 5/5e/6 for 100-Mbps cables with 4 pairs
Category 5e/6 for 1000-Mbps cables with 4 pairs
Cables have 4 pairs of wires for a total of 8 conductors.
Note
Cables
As supported by the Ethernet Specification, the maximum cable length between each
Cisco IP Phone and the switch is assumed to be 330 feet (100 meters).
Distance requirements
Cable Specifications
The following information lists the cable specifications:
• RJ-9 jack (4-conductor) for handset and headset connection
• RJ-45 jack for the LAN 10/100/1000BaseT connection (10/100/1000 Network port on the phone)
• RJ-45 jack for a second 10/100/1000BaseT compliant connection (10/100/1000 Computer port on the
phone)
• 3.5 mm jack for speaker connection (only Cisco IP Phone 8861)
• 48-volt power connector
• USB ports/connector: one USB port for Cisco IP Phone 8851 and two USB ports for Cisco IP Phone
8861
• 3 key expansion modules connectors which is considered as USB connector for Cisco IP Phone 8851
and 8861
Network and Computer Port Pinouts
Although both the network and computer (access) ports are used for network connectivity, they serve different
purposes and have different port pinouts.
• The network port is the 10/100/1000 SW port on the Cisco IP Phone.
• The computer (access) port is the 10/100/1000 PC port on the Cisco IP Phone.
Network Port Connector
The following table describes the network port connector pinouts.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
12
About the Cisco IP Phone
Cable Specifications

Table 13: Network Port Connector Pinouts
FunctionPin Number
BI_DA+1
BI_DA-2
BI_DB+3
BI_DC+4
BI_DC-5
BI_DB-6
BI_DD+7
BI_DD-8
BI stands for bidirectional, while DA, DB, DC, and DD stand for Data A, Data B,
Data C, and Data D respectively.
Note
Computer Port Connector
The following table describes the computer port connector pinouts.
Table 14: Computer (Access) Port Connector Pinouts
FunctionPin Number
BI_DB+1
BI_DB-2
BI_DA+3
BI_DD+4
BI_DD-5
BI_DA-6
BI_DC+7
BI_DC-8
BI stands for bidirectional, while DA, DB, DC, and DD stand for Data A, Data B, Data
C, and Data D respectively.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
13
About the Cisco IP Phone
Computer Port Connector
Phone Power Requirements
The Cisco IP Phone can be powered with external power or with Power over Ethernet (PoE). A separate power
supply provides external power. The switch can provide PoE through the phone Ethernet cable.
Cisco IP Phones 8861 and 8865 are PoE Class 4 devices and require a switch or line card with Class 4
capabilities to support extra features.
For more information on your phone's power requirements, consult your phone's data sheet.
When you install a phone that is powered with external power, connect the power supply before you connect
the Ethernet cable to the phone. When you remove a phone that is powered with external power, disconnect
the Ethernet cable from the phone before you disconnect the power supply.
Table 15: Guidelines for Cisco IP Phone Power
GuidelinesPower type
The Cisco IP Phone uses the CP-PWR-CUBE-4 power supply.External power: Provided through
the CP-PWR-CUBE-4= external
power supply
Cisco IP Phones 8851, 8851NR, 8861, 8865, and 8865NR support 802.3at PoE for accessory
use. For more information, consult your phone's data sheet.
The switch requires a backup power supply for uninterruptible operation of the phone
Make sure that the CatOS or IOS version that runs on your switch supports your intended phone
deployment. See the documentation for your switch for operating system version information.
PoE power—Provided by a switch
through the Ethernet cable attached
to the phone.
Cisco IP Phones 8865 and 8865NR supports UPoE.Universal Power over Ethernet
(UPoE)
The documents in the following table provide more information on the following topics:
• Cisco switches that work with Cisco IP Phones
• Cisco IOS releases that support bidirectional power negotiation
• Other requirements and restrictions about power
Table 16: Additional Information
URLDocument topics
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/enterprise-networks/
power-over-ethernet-solutions/index.html
PoE Solutions
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/enterprise-networks/upoe/index.htmlUPoE
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/switches/index.htmlCisco Catalyst Switches
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/routers/index.htmlIntegrated Service Routers
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/ios-nx-os-software/index.htmlCisco IOS Software
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
14
About the Cisco IP Phone
Phone Power Requirements

Power Outage
Your access to emergency service through the phone requires that the phone receive power. If a power
interruption occurs, service or emergency calling service dialing does not function until power is restored. If
a power failure or disruption occurs, you may need to reset or reconfigure the equipment before you can use
service or emergency calling service dialing.
Power Reduction
You can reduce the amount of energy that the Cisco IP Phone consumes by using Power Save or EnergyWise
(Power Save Plus) mode.
Power Save
In Power Save mode, the backlight on the screen is not lit when the phone is not in use. The phone
remains in Power Save mode for the scheduled duration or until the user lifts the handset or presses any
button.
Power Save Plus (EnergyWise)
The Cisco IP Phone supports Cisco EnergyWise (Power Save Plus) mode. When your network contains
an EnergyWise (EW) controller (for example, a Cisco switch with the EnergyWise feature enabled), you
can configure these phones to sleep (power down) and wake (power up) on a schedule to further reduce
power consumption.
Set up each phone to enable or disable the EnergyWise settings. If EnergyWise is enabled, configure a
sleep and wake time, as well as other parameters. These parameters are sent to the phone as part of the
phone configuration XML file.
Power Negotiation Over LLDP
The phone and the switch negotiate the power that the phone consumes. Cisco IP Phone operates at multiple
power settings, which lowers power consumption when less power is available.
After a phone reboots, the switch locks to one protocol (CDP or LLDP) for power negotiation. The switch
locks to the first protocol (containing a power Threshold Limit Value [TLV]) that the phone transmits. If the
system administrator disables that protocol on the phone, the phone cannot power up any accessories because
the switch does not respond to power requests in the other protocol.
Cisco recommends that Power Negotiation always be enabled (default) when connecting to a switch that
supports power negotiation.
If Power Negotiation is disabled, the switch may disconnect power to the phone. If the switch does not support
power negotiation, disable the Power Negotiation feature before you power up accessories over PoE. When
the Power Negotiation feature is disabled, the phone can power the accessories up to the maximum that the
IEEE 802.3af-2003 standard allows.
• When CDP and Power Negotiation are disabled, the phone can power the accessories up to 15.4W.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
15
About the Cisco IP Phone
Power Outage

Network Protocols
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series support several industry-standard and Cisco network protocols required for voice
communication. The following table provides an overview of the network protocols that the phones support.
Table 17: Supported Network Protocols on the Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series
Usage notesPurposeNetwork protocol
Cisco IP Phones 8845, 8865, and 8851 support
Bluetooth 4.1.
Cisco IP Phone 8861 support Bluetooth 4.0.
Cisco IP Phone 8811, 8841, 8851NR, and 8865NR
do not support Bluetooth.
Bluetooth is a wireless personal area network
(WPAN) protocol that specifies how devices
communicate over short distances.
Bluetooth
—BootP enables a network device, such as the Cisco
IP Phone, to discover certain startup information,
such as the IP address.
Bootstrap Protocol
(BootP)
The Cisco IP Phone uses CAST as an interface
between CUVA and Cisco Unified Communications
Manager using the Cisco IP Phone as a SIP proxy.
The CAST protocol allows your phones and
associated applications to communicate with the
remote IP Phones without requiring changes to the
signaling components.
Cisco Audio Session
Tunnel (CAST)
The Cisco IP Phones use CDP to communicate
information such as auxiliary VLAN ID, per port
power management details, and Quality of Service
(QoS) configuration information with the Cisco
Catalyst switch.
CDP is a device-discovery protocol that runs on all
Cisco-manufactured equipment.
Using CDP, a device can advertise its existence to
other devices and receive information about other
devices in the network.
Cisco Discovery Protocol
(CDP)
CPPDP is used by the Peer Firmware Sharing
feature.
CPPDP is a Cisco proprietary protocol used to form
a peer-to-peer hierarchy of devices. This hierarchy
is used to distribute firmware files from peer devices
to their neighboring devices.
Cisco Peer-to-Peer
Distribution Protocol
(CPPDP)
DHCP is enabled by default. If disabled, you must
manually configure the IP address, subnet mask,
gateway, and a TFTP server on each phone locally.
We recommend that you use DHCP custom option
150. With this method, you configure the TFTP
server IP address as the option value. For more
information, see the documentation for your
particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
If you cannot use option 150, you may
try using DHCP option 66.
Note
DHCP dynamically allocates and assigns an IP
address to network devices.
DHCP enables you to connect an IP phone into the
network and the phone to become operational
without the need to manually assign an IP address
or to configure additional network parameters.
Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol
(DHCP)
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
16
About the Cisco IP Phone
Network Protocols

Usage notesPurposeNetwork protocol
Cisco IP Phones use HTTP for XML services and
for troubleshooting purposes.
HTTP is the standard way of transferring information
and moving documents across the Internet and the
web.
Hypertext Transfer
Protocol (HTTP)
Web applications with both HTTP and HTTPS
support have two URLs configured. Cisco IP Phones
that support HTTPS choose the HTTPS URL.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is a
combination of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol with
the SSL/TLS protocol to provide encryption and
secure identification of servers.
Hypertext Transfer
Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
The Cisco IP Phone implements the IEEE 802.1X
standard by providing support for the following
authentication methods: EAP-FAST, and EAP-TLS.
When 802.1X authentication is enabled on the
phone, you should disable the PC port and voice
VLAN.
The IEEE 802.1X standard defines a
client-server-based access control and authentication
protocol that restricts unauthorized clients from
connecting to a LAN through publicly accessible
ports.
Until the client is authenticated, 802.1X access
control allows only Extensible Authentication
Protocol over LAN (EAPOL) traffic through the
port to which the client is connected. After
authentication is successful, normal traffic can pass
through the port.
IEEE 802.1X
The 802.11 interface is a deployment option for
cases when Ethernet cabling is unavailable or
undesirable.
Only Cisco IP Phone 8861 and 8865 support WLAN.
The IEEE 802.11 standard specifies how devices
communication over a wireless local area network
(WLAN).
802.11n operates at the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band
and 802.11ac operates at the 5 GHz band.
IEEE 802.11n/802.11ac
To communicate using IP, network devices must
have an assigned IP address, subnet, and gateway.
IP addresses, subnets, and gateway identifications
are automatically assigned if you are using the Cisco
IPPhone with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP). If you are not using DHCP, you must
manually assign these properties to each phone
locally.
The Cisco IP Phones support IPv6 addresses. For
more information, see the documentation for your
particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
IP is a messaging protocol that addresses and sends
packets across the network.
Internet Protocol (IP)
The Cisco IPPhone supports LLDP on the PC port.LLDP is a standardized network discovery protocol
(similar to CDP) that is supported on some Cisco
and third-party devices.
Link Layer Discovery
Protocol (LLDP)
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
17
About the Cisco IP Phone
Network Protocols

Usage notesPurposeNetwork protocol
The Cisco IPPhone supports LLDP-MED on the SW
port to communicate information such as:
• Voice VLAN configuration
• Device discovery
• Power management
• Inventory management
LLDP-MED is an extension of the LLDP standard
for voice products.
Link Layer Discovery
Protocol-Media Endpoint
Devices (LLDP-MED)
Cisco IP Phones use the RTP protocol to send and
receive real-time voice traffic from other phones and
gateways.
RTP is a standard protocol for transporting real-time
data, such as interactive voice, over data networks.
Real-Time Transport
Protocol (RTP)
RTCP is enabled by default.RTCP works in conjunction with RTP to provide
QoS data (such as jitter, latency, and round-trip
delay) on RTP streams.
Real-Time Control
Protocol (RTCP)
SDP capabilities, such as codec types, DTMF
detection, and comfort noise, are normally
configured on a global basis by Cisco Unified
Communications Manager or Media Gateway in
operation. Some SIP endpoints may allow
configuration of these parameters on the endpoint
itself.
SDP is the portion of the SIP protocol that
determines which parameters are available during a
connection between two endpoints. Conferences are
established by using only the SDP capabilities that
all endpoints in the conference support.
Session Description
Protocol (SDP)
Like other VoIP protocols, SIP addresses the
functions of signaling and session management
within a packet telephony network. Signaling allows
transportation of call information across network
boundaries. Session management provides the ability
to control the attributes of an end-to-end call.
Cisco IP Phones support the SIP protocol when the
phones are operating in IPv6-only, IPv4-only, or in
both IPv4 and IPv6.
SIP is the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
standard for multimedia conferencing over IP. SIP
is an ASCII-based application-layer control protocol
(defined in RFC 3261) that can be used to establish,
maintain, and terminate calls between two or more
endpoints.
Session Initiation
Protocol (SIP)
Cisco IP Phones use TCP to connect to Cisco
Unified Communications Manager and to access
XML services.
TCP is a connection-oriented transport protocol.Transmission Control
Protocol (TCP)
Upon security implementation, Cisco IP Phones use
the TLS protocol when securely registering with
Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
TLS is a standard protocol for securing and
authenticating communications.
Transport Layer Security
(TLS)
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
18
About the Cisco IP Phone
Network Protocols

Usage notesPurposeNetwork protocol
TFTP requires a TFTP server in your network that
the DHCP server can automatically identify. If you
want a phone to use a TFTP server other than the
one that the DHCP server specifies, you must
manually assign the IP address of the TFTP server
by using the Network Configuration menu on the
phone.
For more information, see the documentation for
your particular Cisco Unified Communications
Manager release.
TFTP allows you to transfer files over the network.
On the Cisco IPPhone, TFTP enables you to obtain
a configuration file specific to the phone type.
Trivial File Transfer
Protocol (TFTP)
UDP is used only for RTP streams. SIP signaling
on the phones do not support UDP.
UDP is a connectionless messaging protocol for
delivery of data packets.
User Datagram Protocol
(UDP)
For more information about LLDP-MED support, see the LLDP-MED and Cisco Discovery Protocol white
paper:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk652/tk701/technologies_white_paper0900aecd804cd46d.shtml
Related Topics
802.1X Authentication, on page 106
Configure Network Settings
Phone Startup Verification, on page 62
VLAN Interaction, on page 19
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Interaction, on page 20
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express Interaction, on page 20
Set Up the Audio and Video Port Range, on page 177
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
VLAN Interaction
The Cisco IP Phone contains an internal Ethernet switch, enabling forwarding of packets to the phone, and
to the computer (access) port and the network port on the back of the phone.
If a computer is connected to the computer (access) port, the computer and the phone share the same physical
link to the switch and share the same port on the switch. This shared physical link has the following implications
for the VLAN configuration on the network:
• The current VLANs might be configured on an IP subnet basis. However, additional IP addresses might
not be available to assign the phone to the same subnet as other devices that connect to the same port.
• Data traffic present on the VLAN supporting phones might reduce the quality of VoIP traffic.
• Network security may indicate a need to isolate the VLAN voice traffic from the VLAN data traffic.
You can resolve these issues by isolating the voice traffic onto a separate VLAN. The switch port to which
the phone connects would be configured for separate VLANs for carrying:
• Voice traffic to and from the IP phone (auxiliary VLAN on the Cisco Catalyst 6000 series, for example)
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
19
About the Cisco IP Phone
VLAN Interaction

• Data traffic to and from the PC that connects to the switch through the computer (access) port of the IP
phone (native VLAN)
Isolating the phones on a separate, auxiliary VLAN increases the quality of the voice traffic and allows a large
number of phones to be added to an existing network that does not have enough IP addresses for each phone.
For more information, see the documentation that is included with a Cisco switch. You can also access switch
information at this URL:
http://cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/index.html
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Interaction
Cisco Unified Communications Manager is an open, industry-standard call processing system. Cisco Unified
Communications Manager software sets up and tears down calls between phones, integrating traditional PBX
functionality with the corporate IP network. Cisco Unified Communications Manager manages the components
of the telephony system, such as the phones, the access gateways, and the resources necessary for features
such as call conferencing and route planning. Cisco Unified Communications Manager also provides:
• Firmware for phones
• Certificate Trust List (CTL) and Identity Trust List (ITL) files using the TFTP and HTTP services
• Phone registration
• Call preservation, so that a media session continues if signaling is lost between the primary
Communications Manager and a phone
For information about configuring Cisco Unified Communications Manager to work with the phones described
in this chapter, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
If the phone model that you want to configure does not appear in the Phone Type drop-down list in Cisco
Unified Communications Manager Administration, install the latest device package for your version of Cisco
Unified Communications Manager from Cisco.com.
Note
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express Interaction
When your phone works with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (Unified CME), it must
go into CME mode.
When a user invokes the conference feature, the tag allows the phone to use either a local or network hardware
conference bridge.
The phones do not support the following actions:
• Transfer—Only supported in the connected call transfer scenario.
• Conference—Only supported in the connected call transfer scenario.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
20
About the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Interaction

• Join—Supported using the Conference button or hookflash access.
• Hold—Supported using the Hold button.
• Barge and Merge—Not supported.
• Direct Transfer—Not supported.
• Select—Not supported.
The users cannot create conference and transfer calls across different lines.
Unified CME supports intercom calls, also known as whisper paging. But the page is rejected by the phone
during calls.
Both Session line mode and Enhanced line mode are supported in CME mode.
Voice Messaging System Interaction
Cisco Unified Communications Manager lets you integrate with different voice messaging systems, including
the Cisco Unity Connection voice messaging system. Because you can integrate with various systems, you
must provide users with information about how to use your specific system.
To enable the ability for a user to transfer to voicemail, set up a *xxxxx dialing pattern and configure it as
Call Forward All to Voicemail. For more information, see the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
documentation.
Provide the following information to each user:
• How to access the voice messaging system account.
Make sure that you have used the Cisco Unified Communications Manager to configure the Messages
button on the Cisco IP Phone.
• Initial password for accessing the voice messaging system.
Configure a default voice messaging system password for all users.
• How the phone indicates that voice messages are waiting.
Use Cisco Unified Communications Manager to set up a message waiting indicator (MWI) method.
Phone Startup Overview
When connecting to the VoIP network, the Cisco IP Phones goes through a standard startup process. Depending
on your specific network configuration, only some of these steps may occur on your Cisco IP Phone.
1. Obtain power from the switch. If a phone is not using external power, the switch provides inline power
through the Ethernet cable that is attached to the phone.
2. (For the Cisco IP Phone 8861 and 8865 in a wireless LAN only) Scan for an access point. The Cisco
IP Phone 8861 and 8865 scans the RF coverage area with the radio. The phone searches the network
profiles and scans for access points that contain a matching SSID and authentication type. The phone
associates with the access point with the highest RSSI that matches with the network profile.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
21
About the Cisco IP Phone
Voice Messaging System Interaction

3. (For the Cisco IP Phone 8861 and 8865 in a wireless LAN only) Authenticate with the access point.
The Cisco IP Phone begins the authentication process. The following table describes the authentication
process:
DescriptionKey management optionsAuthentication type
Any device can authenticate to the access point.
For added security, static WEP encryption might
optionally be used.
NoneOpen
The phone encrypts the challenge text by using
the WEP key and the access point must verify
the WEP key that was used to encrypt the
challenge text before network access is available.
NoneShared Key
The RADIUS server authenticates the username
and password before network access is available.
NonePEAP or EAP-FAST
4. Load the stored phone image. At startup, the phone runs a bootstrap loader that loads a phone firmware
image that is stored in flash memory. Using this image, the phone initializes the software and hardware.
5. Configure the VLAN. If the Cisco IP Phone is connected to a Cisco Catalyst switch, the switch next
informs the phone of the voice VLAN that is defined on the switch. The phone needs to know the VLAN
membership before it can proceed with the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) request for
an IP address.
6. Obtain an IP address. If the Cisco IP Phone is using DHCP to obtain an IP address, the phone queries
the DHCP server to obtain one. If you are not using DHCP in your network, you must assign static IP
addresses to each phone locally.
7. Request the CTL file. The TFTP server stores the CTL file. This file contains the certificates that are
necessary for establishing a secure connection between the phone and Cisco Unified Communications
Manager.
For more information, the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
8. Request the ITL file. The phone requests the ITL file after it requests the CTL file. The ITL file contains
the certificates of the entities that the phone can trust. The certificates are used to authenticate a secure
connection with the servers or to authenticate a digital signature signed by the servers. Cisco Unified
Communications Manager 8.5 and later supports the ITL file.
9. Access a TFTP server. In addition to assigning an IP address, the DHCP server directs the Cisco IP
Phone to a TFTP Server. If the phone has a statically defined IP address, you must configure the TFTP
server locally on the phone; the phone then contacts the TFTP server directly.
You can also assign an alternate TFTP server to use instead of the one that DHCP assigns.
Note
10. Request the configuration file. The TFTP server has configuration files, which define parameters for
connecting to Cisco Unified Communications Manager and other information for the phone.
11. Contact Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The configuration file defines how the Cisco IP
Phone communicates with Cisco Unified Communications Manager and provides a phone with the load
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
22
About the Cisco IP Phone
Phone Startup Overview

ID. After it obtains the file from the TFTP server, the phone attempts to make a connection to the highest
priority Cisco Unified Communications Manager on the list.
If the security profile of the phone is configured for secure signaling (encrypted or authenticated) and
the Cisco Unified Communications Manager is set to secure mode, the phone makes a TLS connection.
Otherwise, the phone makes a nonsecure TCP connection.
If the phone was manually added to the database, Cisco Unified Communications Manager identifies
the phone. If the phone was not manually added to the database and autoregistration is enabled in Cisco
Unified Communications Manager, the phone attempts to autoregister itself in the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager database.
Autoregistration is disabled when you configure the CTL client. In this case, you must add the phone to the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager database manually.
Note
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
External Devices
We recommend that you use good-quality external devices that are shielded against unwanted radio frequency
(RF) and audio frequency (AF) signals. External devices include headsets, cables, and connectors.
Depending on the quality of these devices and their proximity to other devices, such as mobile phones or
two-way radios, some audio noise may still occur. In these cases, we recommend that you take one or more
of these actions:
• Move the external device away from the source of the RF or AF signals.
• Route the external device cables away from the source of the RF or AF signals.
• Use shielded cables for the external device, or use cables with a better shield and connector.
• Shorten the length of the external device cable.
• Apply ferrites or other such devices on the cables for the external device.
Cisco cannot guarantee the performance of external devices, cables, and connectors.
In European Union countries, use only external speakers, microphones, and headsets that are fully compliant
with the EMC Directive [89/336/EC].
Caution
USB Port Information
The Cisco IP Phones 8851, 8851NR, 8861, 8865, and 8865NR support a maximum of five devices that connect
to each USB port. Each device that connects to the phone is included in the maximum device count. For
example, your phone can support five USB devices on the side port and five more standard USB devices on
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
23
About the Cisco IP Phone
External Devices

the back port. Many third-party USB products count as multiple USB devices; for example, a device containing
a USB hub and headset can count as two USB devices. For more information, see the USB device
documentation.
• Unpowered hubs are not supported, and powered hubs with more than four ports are not supported.
• USB headsets that connect to the phone through a USB hub are not supported.
Note
Each key expansion module connects to the phone counts as a USB device. If three key expansion modules
are connected to the phone, these count as three USB devices.
Phone Configuration Files
Configuration files for a phone are stored on the TFTP server and define parameters for connecting to Cisco
Unified Communications Manager. In general, any time you make a change in Cisco Unified Communications
Manager that requires the phone to be reset, a change is automatically made to the phone configuration file.
Configuration files also contain information about which image load the phone should be running. If this
image load differs from the one currently loaded on a phone, the phone contacts the TFTP server to request
the required load files.
If you configure security-related settings in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, the
phone configuration file will contain sensitive information. To ensure the privacy of a configuration file, you
must configure it for encryption. For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release. A phone requests a configuration file whenever it resets and
registers with Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
A phone accesses a default configuration file named XmlDefault.cnf.xml from the TFTP server when the
following conditions exist:
• You have enabled autoregistration in Cisco Unified Communications Manager
• The phone has not been added to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database
• The phone is registering for the first time
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Phone Behavior During Times of Network Congestion
Anything that degrades network performance can affect phone audio and video quality, and in some cases,
can cause a call to drop. Sources of network degradation can include, but are not limited to, the following
activities:
• Administrative tasks, such as an internal port scan or security scan.
• Attacks that occur on your network, such as a Denial of Service attack.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
24
About the Cisco IP Phone
Phone Configuration Files

Phone Behavior on a Network with Two Network Routers
The Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series uses a firewall to provide protection against cyber intrusions, such as a
man-in-the-middle attack. This firewall cannot be disabled. But it could stop traffic on a phone, if you configure
your network with two network routers in the same subnet and with IP redirect.
The phone firewall stops traffic because this network setup is similar to a man-in-the-middle attack. The phone
receives redirect packets for different destination IPs in a different subnet from the phone. The phone is on a
network with more than one router, and the default router sends traffic to a second router.
Look at the phone logs if you suspect the firewall is stopping traffic. Look for an error code 1 notification
from the operating system when it tried to establish a connection. One of the signatures is
sip_tcp_create_connection: socket connect failed cpr_errno: 1.
A network with two network routers in the same subnet and with IP redirect is not a common configuration.
If you are using this network setup, consider using only one router on a subnet. But if you require two network
routers on the same subnet, disable IP Redirect on the router and reboot the phone.
Application Programming Interface
Cisco supports phone API utilization by 3rd party applications that have been tested and certified through
Cisco by the 3rd party application developer. Any phone issues related to uncertified application interaction
must be addressed by the 3rd party and will not be addressed by Cisco.
For support model of Cisco certified 3rd party applications/solutions, please refer to Cisco Solution Partner
Program website for details.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
25
About the Cisco IP Phone
Phone Behavior on a Network with Two Network Routers

Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
26
About the Cisco IP Phone
Application Programming Interface

CHAPTER 3
Cisco IP Phone Hardware
• Phone Overview, on page 27
• Cisco IP Phone 8811, on page 29
• Cisco IP Phones 8841 and 8845, on page 30
• Cisco IP Phones 8851 and 8851NR, on page 31
• Cisco IP Phones 8861, 8865, and 8865NR, on page 33
• Buttons and Hardware, on page 34
• Protect Your Video Phone Camera, on page 36
Phone Overview
The Cisco IP Phones 8800 Series provides voice communication over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The
Cisco IP Phone functions much like any digital business phone, allowing you to make phone calls and to
access features such as mute, hold, transfer, and more. In addition, because the phone connects to your data
network, it offers enhanced IP telephony features, including access to network information and services, and
customizable features and services.
The Cisco IP Phone 8811 has a grayscale LCD screen. The Cisco IP Phones 8841, 8845, 8851, 8851NR, 8861,
8865, and 8865NR have a 24-bit color LCD screen.
When adding features to the phone line keys, you are limited by the number of line keys available. You cannot
add more features than the number of line keys on your phone.
The Cisco IP Phones have the following features:
• Programmable feature buttons that support up to 5 lines in Session Line Mode or up to 10 lines with
Enhanced Line Mode
• Full video capabilities (Cisco IP Phones 8845, 8865, and 8865NR only)
• Gigabit Ethernet connectivity
• Bluetooth support for wireless headsets (Cisco IP Phone 8845, 8851, 8861, and 8865 only. This feature
is not supported on Cisco IP Phone 8811, 8841, 8851NR, and 8865NR.)
• Support for an external microphone and speakers (Cisco IP Phone 8861, 8865, and 8865NR only)
• Network connectivity by Wi-Fi (Cisco IP Phone 8861 and 8865 only. Wi-Fi is not supported on Cisco
IP Phone 8865NR.)
• USB ports:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
27

• One USB port for Cisco IP Phone 8851 and 8851NR
• Two USB ports for Cisco IP Phone 8861, 8865, and 8865NR
The Cisco IP Phone 8845, 8865, and 8865NR support video calls with a built-in video camera. Use this feature
to collaborate with friends and co-workers or to hold face-to-face meetings over the phone.
You should save the box and packaging for the Cisco IP Phone 8845, 8865, and 8865NR. The cameras on
these phones are fragile. If you move the phone, we recommend that you pack the phone into the original box
to protect the camera. For more information, see Protect Your Video Phone Camera, on page 36.
Note
A video call includes the following features:
• PIP — Select from four positions: Right bottom, Right top, Left top, and Left bottom. You can also turn
PIP off.
• Swap — Toggles the views in the PIP view. The Swap softkey is disabled when PIP is off.
• Self-view Video — Select Self-view Video to view your image as it appears on video.
• Video UI and Conference/Transfer Initiation — Select to begin a conference.
For additional information on Video Calls, see Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series User Guide for Cisco Unified
Communications Manager and the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
Like other devices, a Cisco IP Phone must be configured and managed. These phones encode and decode the
following codecs:
• G.711 a-law
• G.711 mu-law
• G.722
• G722.2 AMR-WB
• G.729a/G.729ab
• G.726
• iLBC
• Opus
• iSAC
Using a cell, mobile, or GSM phone, or two-way radio in close proximity to a Cisco IP Phone might cause
interference. For more information, see the manufacturer’s documentation of the interfering device.
Caution
Cisco IP Phones provide traditional telephony functionality, such as call forwarding and transferring, redialing,
speed dialing, conference calling, and voice messaging system access. Cisco IP Phones also provide a variety
of other features.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
28
About the Cisco IP Phone
Phone Overview

As with other network devices, you must configure Cisco IP Phones to prepare them to access Cisco Unified
Communications Manager and the rest of the IP network. By using DHCP, you have fewer settings to configure
on a phone. If your network requires it, however, you can manually configure information such as: an IP
address, TFTP server, and subnet information.
Cisco IP Phones can interact with other services and devices on your IP network to provide enhanced
functionality. For example, you can integrate Cisco Unified Communications Manager with the corporate
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol 3 (LDAP3) standard directory to enable users to search for coworker
contact information directly from their IP phones. You can also use XML to enable users to access information
such as weather, stocks, quote of the day, and other web-based information.
Finally, because the Cisco IP Phone is a network device, you can obtain detailed status information from it
directly. This information can assist you with troubleshooting any problems users might encounter when using
their IP phones. You can also obtain statistics about an active call or firmware versions on the phone.
To function in the IP telephony network, the Cisco IP Phone must connect to a network device, such as a
Cisco Catalyst switch. You must also register the Cisco IP Phone with a Cisco Unified Communications
Manager system before sending and receiving calls.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Cisco IP Phone 8811
The following section describe the Cisco IP Phone 8811 attributes.
Phone Connections
Connect your phone to your organization's IP telephony network as shown in the following diagram.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
29
About the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco IP Phone 8811

Access port (10/100/1000 PC)
connection.
5DC adapter port (DC48V).1
Auxiliary port.6AC-to-DC power supply (optional).2
Handset connection.7AC power wall plug (optional).3
Analog headset connection (optional).8Network port (10/100/1000 SW)
connection. IEEE 802.3at power
enabled.
4
The Cisco IP Phone 8811 does not support a key expansion module.
Note
Cisco IP Phones 8841 and 8845
The following section describe the attributes of the Cisco IP Phones 8841 and 8845.
Phone Connections
Connect your phone to the corporate IP telephony network, using the following diagram.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
30
About the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco IP Phones 8841 and 8845

Access port (10/100/1000 PC) connection.5DC adaptor port (DC48V).1
Auxiliary port.6AC-to-DC power supply (optional).2
Handset connection.7AC power wall plug (optional).3
Analog headset connection (optional).8Network port (10/100/1000 SW) connection.
IEEE 802.3at power enabled.
4
The Cisco IP Phone 8841 and 8845 does not support a key expansion module.
Note
Cisco IP Phones 8851 and 8851NR
The following section describe the attributes of the Cisco IP Phones 8851 and 8851NR.
The Cisco IP Phone 8851NR does not support Bluetooth. Otherwise, the Cisco IP Phone 8851 and Cisco IP
Phone 8851NR support the same features.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
31
About the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco IP Phones 8851 and 8851NR

Phone Connections
Connect your phone to the corporate IP telephony network as shown in the following diagram.
Auxiliary port.6DC adaptor port (DC48V).1
Handset connection.7AC-to-DC power supply (optional).2
Analog headset connection (optional).8AC power wall plug (optional).3
USB port9Network port (10/100/1000 SW) connection.
IEEE 802.3at power enabled.
4
Access port (10/100/1000 PC) connection.5
Each USB port supports the connection of up to five supported and nonsupported devices. Each device
connected to the phone is included in the maximum device count. For example, your phone can support five
USB devices (such as two key expansion modules, one headset, one hub, and one other standard USB device)
on the side port. Many third-party USB products count as multiple USB devices, for example, a device
containing USB hub and headset can count as two USB devices. For more information, see the USB device
documentation.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
32
About the Cisco IP Phone
Phone Connections

Cisco IP Phones 8861, 8865, and 8865NR
The following section describe the attributes of the Cisco IP Phones 8861, 8865, and 8865NR.
Phone Connections
Connect your phone to the corporate IP telephony network as shown in the following diagram.
Handset connection.7DC adaptor port (DC48V).1
Analog headset connection (optional).8AC-to-DC power supply (optional).2
USB port9AC power wall plug (optional).3
Audio In/Out ports10Network port (10/100/1000 SW) connection.
IEEE 802.3at power enabled.
4
USB port11Access port (10/100/1000 PC) connection.5
Auxiliary port.6
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
33
About the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco IP Phones 8861, 8865, and 8865NR

Each USB port supports the connection of up to five supported and nonsupported devices. Each device
connected to the phone is included in the maximum device count. For example, your phone can support five
USB devices (such as three key expansion modules, one hub, and one other standard USB device) on the side
port and five additional standard USB devices on the back port. Many third-party USB products count as
multiple USB devices, for example, a device containing USB hub and headset can count as two USB devices.
For more information, see the USB device documentation.
Note
Buttons and Hardware
The Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series has two distinct hardware types:
• Cisco IP Phones 8811, 8841, 8851, 8851NR, and 8861—do not have a camera.
• Cisco IP Phones 8845, 8865, and 8865NR—have a built-in camera.
The following figure shows the Cisco IP Phone 8845.
Figure 1: Cisco IP Phone 8845 Buttons and Hardware
The following table describes the Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Buttons.
Table 18: Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Buttons
Indicates whether you have an incoming call (flashing red) or a
new voice message (steady red).
Handset and Handset light strip1
Use the camera for video calls.Camera
Cisco IP Phone 8845, 8865, and
8865NR only
2
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
34
About the Cisco IP Phone
Buttons and Hardware

Access your phone lines, features, and call sessions.
When adding features to the phone line keys, you are limited by
the number of line keys available. You cannot add more features
than the number of line keys on your phone.
For more information, see the Softkey, Line, and Feature Buttons
section in the "Cisco IP Phone Hardware" chapter.
Programmable feature buttons
and line buttons
3
Access to functions and services.
For more information, see the Softkey, Line, and Feature Buttons
section in the "Cisco IP Phone Hardware" chapter.
Softkey buttons4
Back Return to the previous screen or menu.
Navigation cluster Navigation ring and Selectbutton—Scroll
through menus, highlight items and select the highlighted item.
Release End a connected call or session.
Back, Navigation cluster, and
Release
5
Hold/Resume Place an active call on hold and resume the
held call.
Conference Create a conference call.
Transfer Transfer a call.
Hold/Resume, Conference,
and Transfer
6
Speakerphone Toggle the speakerphone on or off. When
the speakerphone is on, the button is lit.
Mute Toggle the microphone on or off. When the
microphone is muted, the button is lit.
Headset Toggle the headset on. When the headset is on,
the button islit. To leave headset mode, you pick up the handset
or select Speakerphone .
Speakerphone, Mute, and
Headset
7
Contacts Access personal and corporate directories.
Applications Access recent calls, user preferences, phone
settings, and phone model information.
Messages Autodial your voice messaging system.
Contacts, Applications, and
Messages
8
Adjust the handset, headset, and speakerphone volume
(off hook) and the ringer volume (on hook).
Volume button9
Softkey, Line, and Feature Buttons
You can interact with the features on your phone in several ways:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
35
About the Cisco IP Phone
Softkey, Line, and Feature Buttons

• Softkeys, located below the screen, give you access to the function displayed on the screen above the
softkey. The softkeys change depending on what you are doing at the time. The More ... softkey shows
you that more functions are available.
• Feature and line buttons, located on either side of the screen, give you access to phone features and phone
lines.
• Feature buttons—Used for features such as Speed dial or Call pickup, and to view your status on
another line.
• Line buttons—Used to answer a call or resume a held call. When not used for an active call, used
to initiate phone functions, such as the missed calls display.
Feature and line buttons illuminate to indicate status.
Normal Line Mode: Feature Buttons
Enhanced Line Mode
Normal Line Mode: Line ButtonsLED Color and State
Active call or two-way intercom
call, privacy in use
Active call or two-way intercom
call, held call, privacy in use
Green, steady LED
Held callNot applicable
Green, flashing LED
One-way intercom call, logged into
a Hunt Group
Incoming call, reverting call,
one-way intercom call, logged into
a Hunt Group
Amber, steady LED
Incoming call, reverting callNot applicable
Amber, flashing LED
Remote line in use, Do Not Disturb
active
Remote line in use, Remote line on
hold, Do Not Disturb active
Red, steady LED
Remote line on holdNot applicable
Red, flashing LED
Your administrator can set up some functions as softkeys or as feature buttons. You can also access some
functions with softkeys or the associated hard button.
Protect Your Video Phone Camera
The camera on your video phone is fragile and could break during transportation of the phone.
Before you begin
You need one of these:
• Original phone box and the packing material
• Packaging material, such as foam or bubble wrap
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
36
About the Cisco IP Phone
Protect Your Video Phone Camera

Procedure
Step 1 If you have the original box:
a) Place the foam on the camera in such a way that the lens is well-protected.
b) Place the phone in its original box.
Step 2 If you do not have the box, carefully wrap the phone with foam or bubble wrap to protect the camera. Ensure
that the foam protects and surrounds the camera so that nothing can press against the camera from any direction
or the camera may be damaged in transport.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
37
About the Cisco IP Phone
Protect Your Video Phone Camera

Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
38
About the Cisco IP Phone
Protect Your Video Phone Camera

CHAPTER 4
Cisco IP Phone Installation
• Verify the Network Setup, on page 41
• Activation Code Onboarding for On-premises Phones, on page 42
• Activation Code Onboarding and Mobile and Remote Access, on page 43
• Enable Autoregistration for Phones, on page 43
• Install Cisco IP Phone, on page 45
• Set Up Phone from Setup Menus, on page 47
• Enable the Wireless LAN on the Phone, on page 49
• Configure Network Settings, on page 55
• Phone Startup Verification, on page 62
• Configure Phone Services for Users, on page 62
• Change a User's Phone Model, on page 63
Verify the Network Setup
As they deploy a new IP telephony system, system administrators and network administrators must complete
several initial configuration tasks to prepare the network for IP telephony service. For information and a
checklist for setting up and configuring a Cisco IP telephony network, see the documentation for your particular
Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
For the phone to operate successfully as an endpoint in your network, your network must meet specific
requirements. One requirement is the appropriate bandwidth. The phones require more bandwidth than the
recommended 32 kbps when they register to Cisco Unified Communications Manager. Consider this higher
bandwidth requirement when you configure your QoS bandwidth. For more information, refer to Cisco
Collaboration System 12.x Solution Reference Network Designs (SRND) or later ( https://www.cisco.com/c/
en/us/td/docs/voice_ip_comm/cucm/srnd/collab12/collab12.html ).
The phone displays the date and time from Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The time displayed on
the phone can differ from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager time by up to 10 seconds.
Note
Procedure
Step 1 Configure a VoIP Network to meet the following requirements:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
41

• VoIP is configured on your routers and gateways.
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager is installed in your network and is configured to handle call
processing.
Step 2 Set up the network to support one of the following:
• DHCP support
• Manual assignment of IP address, gateway, and subnet mask
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Activation Code Onboarding for On-premises Phones
You can use Activation Code Onboarding to quickly set up new phones without autoregistration. With this
approach, you control the phone onboarding process using the one of the following:
• Cisco Unified Communications Bulk Administration Tool (BAT)
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration interface
• Administrative XML Web Service (AXL)
Enable this feature from the Device Information section of the Phone Configuration page. Select Require
Activation Code for Onboarding if you want this feature to apply to a single on-premises phone.
Users must enter an activation code before their phones can register. Activation Code Onboarding can be
applied to individual phones, a group of phones, or across an entire network.
This is an easy way for users to onboard their phones because they only enter a 16-digit activation code. Codes
are entered either manually or with a QR code if a phone has a video camera. We recommend that you use a
secure method to give users this information. But if a user is assigned to a phone, then this information is
available on the Self Care Portal. The audit log records when a user accesses the code from the portal.
Activation codes can only be used once, and they expire after 1 week by default. If a code expires, you will
have to provide the user with a new one.
You will find this approach an easy way to keep your network secure because a phone cannot register until
the Manufacturing Installed Certificate (MIC) and activation code are verified. This method is also a convenient
way to bulk onboard phones because it doesn't use the Tool for Auto-registered Phone Support (TAPS) or
autoregistration. The rate of onboarding is one phone per second or about 3600 phones per hour. Phones can
be added with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administrative, with Administrative XML Web
Service (AXL), or with BAT.
Existing phones reset after they are configured for Activation Code Onboarding. They don't register until the
activation code is entered and the phone MIC is verified. Inform current users that you are moving towards
Activation Code Onboarding before you implement it.
For more information, see Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager and IM and
Presence Service, Release 12.0(1) or later.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
42
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Activation Code Onboarding for On-premises Phones

Activation Code Onboarding and Mobile and Remote Access
You can use Activation Code Onboarding with Mobile and Remote Access when deploying Cisco IP phones
for remote users. This feature is a secure way to deploy off-premises phones when autoregistration is not
required. But you can configure a phone for autoregistration when on-premises, and activation codes when
off-premises. This feature is similar to Activation Code Onboarding for on-premises phones, but it makes
activation code available for off-premises phones also.
Activation Code Onboarding for Mobile and Remote Access requires Cisco Unified Communications Manager
12.5(1)SU1 or later, and Cisco Expressway X12.5 or later. Smart Licensing should be enabled also.
You enable this feature from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, but note the
following:
• Enable this feature from the Device Information section of the Phone Configuration page.
• Select Require Activation Code for Onboarding if you want this feature to apply just to a single
on-premises phone.
• Select Allow Activation Code via MRA and Require Activation Code for Onboarding if you want
to use Activation Onboarding for a single off-premises phone. If the phone is on-premises, it changes to
Mobile and Remote Access mode and uses the Expressway. If the phone cannot reach the Expressway,
it does not register until it is off premises.
For more information, see the following documents:
• Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager and IM and Presence Service, Release
12.0(1)
• Mobile and Remote Access Through Cisco Expressway for Cisco Expressway X12.5 or later
Enable Autoregistration for Phones
The Cisco IP Phone requires Cisco Unified Communications Manager to handle call processing. See the
documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release or the context-sensitive
help in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration to ensure that Cisco Unified
Communications Manager is set up properly to manage the phone and to properly route and process calls.
Before you install the Cisco IP Phone, you must choose a method for adding phones to the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager database.
By enabling autoregistration before you install the phones, you can:
• Add phones without first gathering MAC addresses from the phones.
• Automatically add a Cisco IP Phone to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database when you
physically connect the phone to your IP telephony network. During autoregistration, Cisco Unified
Communications Manager assigns the next available sequential directory number to the phone.
• Quickly enter phones into the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database and modify any settings,
such as the directory numbers, from Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
43
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Activation Code Onboarding and Mobile and Remote Access

• Move autoregistered phones to new locations and assign them to different device pools without affecting
their directory numbers.
Autoregistration is disabled by default. In some cases, you might not want to use autoregistration; for example,
if you want to assign a specific directory number to the phone, or if you want to use a secure connection with
Cisco Unified Communications Manager. For information about enabling autoregistration, see the
documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release. When you configure the
cluster for mixed mode through the Cisco CTL client, autoregistration is automatically disabled, however you
can enable it. When you configure the cluster for nonsecure mode through the Cisco CTL client, autoregistration
is not enabled automatically.
You can add phones with autoregistration and TAPS, the Tool for AutoRegistered Phones Support, without
first gathering MAC addresses from phones.
TAPS works with the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) to update a batch of phones that were already added
to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database with dummy MAC addresses. Use TAPS to update
MAC addresses and to download predefined configurations for phones.
Cisco recommends that you use autoregistration and TAPS to add fewer than 100 phones to your network.
To add more than 100 phones to your network, use the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT).
To implement TAPS, you or the end user dials a TAPS directory number and follows voice prompts. After
the process is complete, the phone contains the directory number and other settings, and the phone is updated
in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration with the correct MAC address.
Verify that autoregistration is enabled and is properly configured in Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration before you connect any Cisco IP Phone to the network. For information about enabling and
configuring autoregistration, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
Autoregistration must be enabled in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration for TAPS to
function.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, click System > Cisco Unified CM.
Step 2 Click Find and select the required server.
Step 3 In Auto-registration Information, configure these fields.
• Universal Device Template
• Universal Line Template
• Starting Directory Number
• Ending Directory Number
Step 4 Uncheck the Auto-registration Disabled on this Cisco Unified Communications Manager check box.
Step 5 Click Save.
Step 6 Click Apply Config.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
44
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Enable Autoregistration for Phones

Install Cisco IP Phone
After the phone connects to the network, the phone startup process begins, and the phone registers with Cisco
Unified Communications Manager. To finish installing the phone, configure the network settings on the phone
depending on whether you enable or disable DHCP service.
If you used autoregistration, you need to update the specific configuration information for the phone such as
associating the phone with a user, changing the button table, or directory number.
Before using external devices, read External Devices, on page 23.
Note
For information about installing accessories, see Cisco IP Phone 7800 and 8800 Series Accessories Guide
for Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
If you only have one LAN cable at your desk, you can plug your phone into the LAN with the SW port and
then connect your computer into the PC port. For more information, see Share a Network Connection with
Your Phone and Computer, on page 46.
You can also daisy chain two phones together. Connect the PC port of the first phone to the SW port of the
second phone.
Do not connect the SW and PC ports into the LAN.
Caution
Procedure
Step 1 Choose the power source for the phone:
• Power over Ethernet (PoE)
• External power supply
For more information, see Phone Power Requirements, on page 14.
Step 2 Connect the handset to the handset port and press the cable into the channel in the phone.
The wideband-capable handset is designed especially for use with a Cisco IP Phone. The handset includes a
light strip that indicates incoming calls and waiting voice messages.
Failure to press the cable into the channel in the phone can damage the printed circuit board. The
cable channel reduces the strain on the connector and the printed circuit board.
Caution
Step 3 Connect a headset or wireless headset. You can add a headset later if you do not connect one now.
Press the cable into the cable channel.
Failure to press the cable into the channel in the phone can damage the printed circuit board inside
the phone. The cable channel reduces the strain on the connector and the printed circuit board.
Caution
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
45
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Install Cisco IP Phone

Step 4 Connect a straight-through Ethernet cable from the switch to the network port labeled 10/100/1000 SW on
the Cisco IP Phone. Each Cisco IP Phone ships with one Ethernet cable in the box.
Use Category 3, 5, 5e, or 6 cabling for 10 Mbps connections; Category 5, 5e, or 6 for 100Mbps connections;
and Category 5e or 6 for 1000 Mbps connections. For more information, see Network and Computer Port
Pinouts, on page 12 for guidelines.
Step 5 Connect a straight-through Ethernet cable from another network device, such as a desktop computer, to the
computer port on the Cisco IP Phone. You can connect another network device later if you do not connect
one now.
Use Category 3, 5, 5e, or 6 cabling for 10 Mbps connections; Category 5, 5e, or 6 for 100Mbps connections;
and Category 5e or 6 for 1000 Mbps connections. For more information, see Network and Computer Port
Pinouts, on page 12 for guidelines.
Step 6 If the phone is on a desk, adjust the footstand. With a wall-mounted phone, you might need to adjust the
handset rest to ensure that the receiver cannot slip out of the cradle.
Step 7 Monitor the phone startup process. This step adds primary and secondary directory numbers and features that
are associated with directory numbers to the phone, and verifies that the phone is configured properly.
Step 8 If you are configuring the network settings on the phone, you can set up an IP address for the phone by either
using DHCP or manually entering an IP address.
See Configure Network Settings, on page 55 and Network Setup, on page 225.
Step 9 Upgrade the phone to the current firmware image.
Firmware upgrades over the WLAN interface may take longer than upgrading over the wired interface,
depending on the quality and bandwidth of the wireless connection. Some upgrades may take more than one
hour.
Step 10 Make calls with the Cisco IP Phone to verify that the phone and features work correctly.
See the Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series User Guide.
Step 11 Provide information to end users about how to use their phones and how to configure their phone options.
This step ensures that users have adequate information to successfully use their Cisco IP Phones.
Share a Network Connection with Your Phone and Computer
Both your phone and your computer must connect to your network to function. If you only have one Ethernet
port, then your devices can share the network connection.
Before you begin
Your administrator must enable the PC port in Cisco Unified Communications Manager before you can use
it.
Procedure
Step 1 Connect the phone SW port to the LAN with an Ethernet cable.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
46
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Share a Network Connection with Your Phone and Computer

Step 2 Connect your computer to the phone PC port with an Ethernet cable.
Set Up Phone from Setup Menus
The Cisco IP Phone includes the following configuration menus:
• Network Setup: Provides options for viewing and configuring network settings such as IPv4-only,
IPv6-only, WLAN, and Ethernet.
• Ethernet Setup: The menu items in this submenu provide configuration options to configure the Cisco
IP Phone over an ethernet network.
• WiFi Client Setup: The menu items in this submenu provide configuration options to configure the Cisco
IP Phone with the wireless local area network (WLAN). Wi-Fi is only supported on Cisco IP Phone 8861
and 8865.
The phone PC port is disabled when Wi-Fi is enabled on your phone.
Note
• IPv4 Setup and IPv6 Setup: These submenus of the Ethernet Setup menu and of the WiFi Client Setup
menu provide additional network options.
• Security Setup: Provides options for viewing and configuring security settings such as security mode,
the trust list and 802.1X authentication.
Before you can change option settings on the Network Setup menu, you must unlock options for editing.
You can control whether a phone has access to the Settings menu or to options on this menu by using the
Settings Access field in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration Phone Configuration
window. The Settings Access field accepts these values:
• Enabled: Allows access to the Settings menu.
• Disabled: Prevents access to the Settings menu.
• Restricted: Allows access to the User Preferences menu and allows volume changes to be saved. Prevents
access to other options on the Settings menu.
If you cannot access an option on the Administrator Settings menu, check the Settings Access field.
Note
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Select Admin settings.
Step 3 Select Network setup or Security setup.
Step 4 Enter your user ID and password, if required, and click Sign-In.
Step 5 Perform one of these actions to display the desired menu:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
47
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set Up Phone from Setup Menus

• Use the navigation arrows to select the desired menu and then press Select.
• Use the keypad on the phone to enter the number that corresponds to the menu.
Step 6 To display a submenu, repeat step 5.
Step 7 To exit a menu, press Exit or the back arrow .
Apply a Phone Password
You can apply a password to the phone. If you do, no changes can be made to the administrative options on
the phone without password entry on the Admin Settings phone screen.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, navigate to the Common Phone Profile
Configuration window (Device > Device Settings > Common Phone Profile).
Step 2 Enter a password in the Local Phone Unlock Password option.
Step 3 Apply the password to the common phone profile that the phone uses.
Text and Menu Entry from Phone
When you edit the value of an option setting, follow these guidelines:
• Use the arrows on the navigation pad to highlight the field that you wish to edit, then press Select in the
navigation pad to activate the field. After the field is activated, you can enter values.
• Use the keys on the keypad to enter numbers and letters.
• To enter letters by using the keypad, use a corresponding number key. Press the key one or more times
to display a particular letter. For example, press the 2 key once for “a,” twice quickly for “b,” and three
times quickly for “c.” After you pause, the cursor automatically advances to allow you to enter the next
letter.
• Press the arrow softkey if you make a mistake. This softkey deletes the character to the left of the
cursor.
• Press Cancel before pressing Save to discard any changes that you made.
• To enter an IP address, you enter values into four segments already divided for you. When you have
finished entering the leftmost digits before the first period, use the right arrow key to move to the next
segment. The period that follows the leftmost digits is automatically inserted.
• To enter a colon for an IPv6 address, press * on the keypad.
The Cisco IP Phone provides several methods to reset or restore option settings, if necessary.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
48
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Apply a Phone Password

Related Topics
Basic Reset, on page 259
Apply a Phone Password, on page 48
Enable the Wireless LAN on the Phone
Before you set up a wireless LAN, check to see that your phone supports wireless use. The Cisco IP Phone
8861 and 8865 support a wireless LAN deployment. The Cisco IP Phone 8865NR does not support a wireless
LAN.
Ensure that the Wi-Fi coverage in the location where the wireless LAN is deployed is suitable for transmitting
voice packets.
If you have enabled the Wi-Fi connectivity for voice and you're using EAP-FAST or PEAP security mode,
authenticate the Wi-Fi network with the WLAN Sign in application. WEP, PSK, and open security modes
authenticate on the Wi-Fi network.
A fast-secure roaming method is recommended for Wi-Fi users.
The phone PC port is disabled when Wi-Fi is enabled on your phone.
Note
For complete configuration information, see the Cisco IP Phone 8800 Wireless LAN Deployment Guide at
this location:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/collaboration-endpoints/unified-ip-phone-8800-series/
products-implementation-design-guides-list.html
The Cisco IP Phone 8800 Wireless LAN Deployment Guide includes the following configuration information:
• Wireless network configuration
• Wireless network configuration in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration
• Wireless network configuration on the Cisco IP Phone
Before you begin
Make sure that Wi-Fi is enabled on the phone, and the Ethernet cable is disconnected.
Procedure
Step 1 To enable the application, press Applications .
Step 2 Go to Admin settings > Network setup > Wi-Fi Client setup > Network name.
You see a list of available wireless access points to which you can connect.
Step 3 Enable the Wireless network.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
49
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Enable the Wireless LAN on the Phone

Set Up the Wireless LAN from Cisco Unified Communications Manager
In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, you must enable a parameter called “Wi-Fi” for
the wireless Cisco IP Phone.
In the Phone Configuration window in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration (Device >
Phone), use the wired-line MAC address when you configure the MAC address. Cisco Unified Communications
Manager registration does not use the wireless MAC address.
Note
Perform the following procedure in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration.
Procedure
Step 1 To enable the wireless LAN on a specific phone, perform the following steps:
a) Select Device > Phone.
b) Locate the required phone.
c) Select the Enabled setting for the Wi-Fi parameter in the Product Specific Configuration Layout section.
d) Check the Override Common Settings check box.
Step 2 To enable wireless LAN for a group of phones,
a) Select Device > Device Settings > Common Phone Profile.
b) Select the Enabled setting for the Wi-Fi parameter.
To ensure that the configuration in this step works, uncheck the Override Common Settings
check box mentioned in Step 1d.
Note
c) Check the Override Common Settings check box.
d) Associate the phones with that common phone profile using Device > Phone.
Step 3 To enable wireless LAN for all WLAN-capable phones in your network,
a) Select System > Enterprise Phone Configuration.
b) Select the Enabled setting for the Wi-Fi parameter.
To ensure that the configuration in this step works, uncheck the Override Common Settings
check box mentioned in Step 1d and Step 2c.
Note
c) Check the Override Common Settings check box.
Set Up Wireless LAN from Phone
Before the Cisco IP Phone can connect to the WLAN, you must configure the network profile for the phone
with the appropriate WLAN settings. You can use the Network setup menu on the phone to access the Wi-Fi
client setup submenu and set up the WLAN configuration.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
50
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set Up the Wireless LAN from Cisco Unified Communications Manager

The phone PC port is disabled when Wi-Fi is enabled on your phone.
Note
The Wi-Fi client setup option does not appear in the Network setup menu when Wi-Fi is disabled on the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Note
For additional information, see Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series WLAN Deployment Guide, located here:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/collaboration-endpoints/unified-ip-phone-8800-series/
products-implementation-design-guides-list.html.
The User Modifiable field in the wireless LAN profile controls that ability of the user to configure security
modes on the phone. When a user cannot change some of the fields, the fields display in gray.
Before you begin
Configure the wireless LAN from Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Select Admin settings > Network setup > Wi-Fi client setup.
Step 3 Set up the wireless configuration as described in the following table.
Table 19: WiFi Client Setup Menu Options
To changeDescriptionOption
See Configure Network Settings, on page 55.Specifies the Service Set Identifier, a unique identifier
for accessing wireless access points. Displays list of
available wireless access points.
Network name
Scroll to IPv4 Setup and press Select.In the IPv4 Setup configuration submenu, you can do
the following:
• Enable or disable the phone to use the IP address
that the DHCP server assigns.
• Manually set the IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default
Routers, DNS Server, and Alternate TFTP servers.
For more information about the IPv4 address fields, see
IPv4 Fields, on page 57.
IPv4-only Setup
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
51
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set Up Wireless LAN from Phone

To changeDescriptionOption
Scroll to IPv6 Setup and press Select.In the IPv6 Setup configuration submenu, you can do
the following:
• Enable or disable the phone to use the IPv6 address
that is either assigned by DHCPv6 server or
acquired by SLAAC through an IPv6-enabled
router.
• Manually set the IPv6 Address, Prefix Length,
Default Routers, DNS Server, and Alternate TFTP
servers.
For more information about the IPv6 address fields, see
IPv6 Fields, on page 59.
IPv6-only Setup
Display only. Cannot configure.Unique Media Access Control (MAC) address of the
phone.
MAC Address
See Configure Network Settings, on page 55.Name of the Domain Name System (DNS) domain in
which the phone resides.
Domain Name
Step 4 Press Save to make changes or press Revert to discard the connection.
Set the Number of WLAN Authentication Attempts
An authentication request is a confirmation of the user's sign-in credentials. It occurs whenever a phone that
has already joined a Wi-Fi network tries to reconnect to the Wi-Fi server. Examples include when a Wi-Fi
session times out or a Wi-Fi connection is lost and then reacquired.
You can configure the number of times a Wi-Fi phone sends an authentication request to the Wi-Fi server.
The default number of attempts is 2, but you can set this parameter from 1 to 3. If a phone fails the
authentication, then the user is prompted to sign in again.
You can apply WLAN Authentication Attempts to individual phones, to a pool of phones, or to all the Wi-Fi
phones in your network.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone and locate the phone.
Step 2 Navigate to the Product Specific Configuration area and set the WLAN Authentication Attempts field.
Step 3 Select Save.
Step 4 Select Apply Config.
Step 5 Restart the phone.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
52
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set the Number of WLAN Authentication Attempts

Enable WLAN Prompt Mode
Enable WLAN Profile 1 Prompt Mode if you want a user to sign into the Wi-Fi network when their phone
powers-up or resets.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate the phone that you need to set up.
Step 3 Navigate to the Product Specific Configuration area and set the WLAN Profile 1 Prompt Mode field to
Enable.
Step 4 Select Save.
Step 5 Select Apply Config.
Step 6 Restart the phone.
Set Up a Wi-Fi Profile using Cisco Unified Communications Manager
You can configure a Wi-Fi profile and then assign the profile to the phones that support Wi-Fi. The profile
contains the parameters required for phones to connect to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager with
Wi-Fi. When you create and use a Wi-Fi profile, you or your users do not need to configure the wireless
network for individual phones.
Wi-Fi profiles are supported on Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 10.5(2) or later. EAP-FAST,
PEAP-GTC, and PEAP-MSCHAPv2 are supported in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 10.0
and later. EAP-TLS is supported in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 11.0 and later.
A Wi-Fi profile enables you to prevent or limit changes to the Wi-Fi configuration on the phone by the user.
We recommend that you use a secure profile with TFTP encryption enabled to protect keys and passwords
when you use a Wi-Fi profile.
When you set up the phones to use EAP-FAST, PEAP-MSCHAPv2, or PEAP-GTC authentication, your users
need individual user ids and passwords to sign into the phone.
The phones only support one server certificate which can be installed either with SCEP or the manual install
method but not both methods. The phones don't support the TFTP method of certificate installation.
Phones that use Mobile and Remote Access through Expressway to connect to the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager cannot use the Wi-Fi profile. Because you do not have the SSID, authentication
mode, and login credentials of the user's phone, you cannot configure a wireless LAN profile for their phone.
Note
Procedure
Step 1 In the Cisco Unified Communications Administration, select Device > Device Settings > Wireless LAN
Profile.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
53
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Enable WLAN Prompt Mode

Step 2 Click Add New.
Step 3 In the Wireless LAN Profile Information section, set the parameters:
• Name—Enter a unique name for the Wi-Fi profile. This name displays on the phone.
• Description—Enter a description for the Wi-Fi profile to help you differentiate this profile from other
Wi-Fi profiles.
• User Modifiable—Select an option:
• Allowed—Indicates that the user can make changes to the Wi-Fi settings from their phone. This
option is selected by default.
• Disallowed—Indicates that the user cannot make any changes to the Wi-Fi settings on their phone.
• Restricted—Indicates that the user can change the Wi-Fi username and password on their phone.
But users are not allowed to make changes to other Wi-Fi settings on the phone.
Step 4 In the Wireless Settings section, set the parameters:
• SSID (Network Name)—Enter the network name available in the user environment to which the phone
can be connected. This name is displayed under the available network list on the phone and the phone
can connect to this wireless network.
• Frequency Band—Available options are Auto, 2.4 GHz, and 5 GHz. This field determines the frequency
band that the wireless connection uses. If you select Auto, the phone attempts to use the 5 GHz band
first and only uses the 2.4 GHz band when the 5 GHz is not available.
Step 5 In the Authentications Settings section, set the Authentication Method to one of these authentication
methods: EAP-FAST, EAP-TLS, PEAP-MSCHAPv2, PEAP-GTC, PSK, WEP, and None.
After you set this field, you may see extra fields that you need to set.
• User certificate—Required for EAP-TLS authentication. Select Manufacturing installed or User
installed. The phone requires a certificate to be installed, either automatically from the SCEP or manually
from the administration page on the phone.
• PSK passphrase—Required for PSK authentication. Enter the 8- 63 character ASCII or 64 HEX character
pass phrase.
• WEP Key—Required for WEP authentication. Enter the 40/102 or 64/128 ASCII or HEX WEP key.
• 40/104 ASCII is 5 characters.
• 64/128 ASCII is 13 characters.
• 40/104 HEX is 10 characters.
• 64/128 HEX is 26 characters.
• Provide Shared Credentials: Required for EAP-FAST, PEAP-MSCHAPv2, and PEAP-GTC
authentication.
• If the user manages the username and password, leave the Username and Password fields blank.
• If all your users share the same username and password, you can input the information in the
Username and Password fields.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
54
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set Up a Wi-Fi Profile using Cisco Unified Communications Manager

• Enter a description in the Password Description field.
If you need to assign each user a unique username and password, you need to create a profile
for each user.
Note
The Network Access Profile field is not supported by the Cisco IP Phone 8861 and 8865.
Note
Step 6 Click Save.
What to do next
Apply the WLAN Profile Group to a device pool (System > Device Pool) or directly to the phone (Device >
Phone).
Set Up a Wi-Fi Group using Cisco Unified Communications Manager
You can create a wireless LAN profile group and add any wireless LAN profile to this group. The profile
group can then be assigned to the phone when you set up the phone.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Administration, select Device > Device Settings > Wireless LAN Profile
Group.
You can also define a wireless LAN profile group from System > Device Pool.
Step 2 Click Add New.
Step 3 In the Wireless LAN Profile Group Information section, enter a group name and description.
Step 4 In the Profiles for this Wireless LAN Profile Group section, select an available profile from the Available
Profiles list and move the selected profile to the Selected Profiles list.
When more that one wireless LAN profile is selected, the phone uses only the first wireless LAN profile.
Step 5 Click Save.
Configure Network Settings
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 To access the Network Settings menu, select Admin settings > Ethernet setup.
Step 3 Set the fields as described in Ethernet Setup Fields, on page 56.
Step 4 After you have set the fields, select Apply and Save.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
55
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set Up a Wi-Fi Group using Cisco Unified Communications Manager

Step 5 Reboot the phone.
Ethernet Setup Fields
The Network Setup menu contains fields and submenus for IPv4 and IPv6. To change some of the fields, first
disable DHCP.
Establishing a VPN connection overwrites the Ethernet data fields.
Table 20: Ethernet Setup Menu Options
DescriptionTypeEntry
See the IPv4 Fields section.
This option displays only when the phone is configured in IPv4-only mode or in IPv4 and IPv6 mode.
MenuIPv4 setup
See the “IPv6 Fields” section.MenuIPv6 setup
Unique Media Access Control (MAC) address of the phone.
Display only. Cannot configure.
StringMAC Address
Name of the Domain Name System (DNS) domain in which the phone resides.
To change this field, turn off DHCP.
StringDomain Name
Auxiliary Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) configured on a Cisco Catalyst switch of which the
phone is a member.
This setting is blank if the auxiliary VLAN or the Administrative VLAN are configured.
If the phone has not received an auxiliary VLAN, this option indicates the Administrative VLAN.
The phone doesn't inherit the Operational VLAN from Admin VLAN if Cisco Discovery Protocol
or Link Level Discovery Protocol Media Endpoint Discovery is enabled.
To assign a VLAN ID manually, use the Admin VLAN ID option.
Operational VLAN
ID
Auxiliary VLAN of which the phone is a member.
Used only if the phone does not receive an auxiliary VLAN from the switch; otherwise, this value is
ignored.
Admin VLAN ID
Allows the phone to interoperate with third-party switches that do not support a voice VLAN. The
Admin VLAN ID option must be set before you can change this option.
PC VLAN
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
56
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Ethernet Setup Fields

DescriptionTypeEntry
Speed and duplex of the network port. Valid values specify:
• Auto Negotiate (default)
• 1000 Full:1000-BaseT/full duplex
• 100 Half: 100-BaseT/half duplex
• 100 Full: 100-BaseT/full duplex
• 10 Half: 10-BaseT/half duplex
• 10 Full: 10-BaseT/full duplex
If the phone is connected to a switch, configure the switch port to the same speed as the phone, or
configure both to autonegotiate.
Unlock network configuration options if you want to edit this setting. If you change the setting of
this option, you must change the PC Port Configuration option to the same setting.
Auto Negotiate
1000 Full
100 Half
10 Half
10 Full
SW port setup
Speed and duplex of the Computer (access) port. Valid values:
• Auto Negotiate (default)
• 1000 Full: 1000-BaseT/full duplex
• 100 Half: 100-BaseT/half duplex
• 100 Full: 100-BaseT/full duplex
• 10 Half: 10-BaseT/half duplex
• 10 Full: 10-BaseT/full duplex
If the phone is connected to a switch, configure the port on the switch to the same speed as the phone,
or configure both to autonegotiate.
Unlock network configuration options if you want to change this field. If you change the setting, you
must change the SW Port Configuration option to the same setting.
To configure the setting on multiple phones simultaneously, enable Remote Port Configuration in
the Enterprise Phone Configuration window (System > Enterprise Phone Configuration).
If the ports are configured for Remote Port Configuration in Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration, the data cannot be changed on the phone.
Auto Negotiate
1000 Full
100 Half
10 Half
10 Full
PC port setup
IPv4 Fields
Table 21: IPv4 Setup Menu Options
DescriptionEntry
Indicates whether the phone has DHCP enabled or disabled.
When DHCP is enabled, the DHCP server assigns the phone an IP address. When DHCP is disabled,
the administrator must manually assign an IP address to the phone.
For more information, see Set Up Phone to Use DHCP, on page 60 and Set Up Phone to Not Use
DHCP, on page 61.
DHCP Enabled
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
57
Cisco IP Phone Installation
IPv4 Fields

DescriptionEntry
Internet Protocol (IP) address of the phone.
If you assign an IP address with this option, you must also assign a subnet mask and default router.
See the Subnet Mask and Default Router options in this table.
IP Address
Subnet mask used by the phone.Subnet Mask
Default router used by the phone.Default Router
Primary Domain Name System (DNS) server (DNS Server 1) and optional backup DNS servers
(DNS Server 2 and 3) that the phone uses.
DNS Server 1
DNS Server 2
DNS Server 3
Indicates whether the phone is using an alternate TFTP server.Alternate TFTP
Primary Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server that the phone uses. If you are not using
DHCP in your network and you want to change this server, you must use the TFTP Server 1 option.
If you set the Alternate TFTP option to On, you must enter a nonzero value for the TFTP Server
1 option.
If neither the primary TFTP server nor the backup TFTP server is listed in the CTL or ITL file on
the phone, you must unlock the file before you can save changes to the TFTP Server 1 option. In
this case, the phone deletes the file when you save changes to the TFTP Server 1 option. A new
CTL or ITL file downloads from the new TFTP Server 1 address.
When the phone looks for the TFTP server, the phone gives precedence to manually assigned TFTP
servers, regardless of the protocol. If your configuration includes both IPv6 and IPv4 TFTP servers,
the phone prioritizes the order that it looks for the TFTP server by giving priority to manually
assigned IPv6 TFTP servers and IPv4 TFTP servers. The phone looks for the TFTP server in this
order:
1. Any manually assigned IPv4 TFTP servers
2. Any manually assigned IPv6 servers
3. DHCP assigned TFTP servers
4. DHCPv6 assigned TFTP servers
For information about the CTL and ITL files, see the Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Security Guide.
Note
TFTP Server 1
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
58
Cisco IP Phone Installation
IPv4 Fields

DescriptionEntry
Optional backup TFTP server that the phone uses if the primary TFTP server is unavailable.
If neither the primary TFTP server nor the backup TFTP server is listed in the CTL or ITL file on
the phone, you must unlock either of the files before you can save changes to the TFTP Server 2
option. In this case, the phone deletes either of the files when you save changes to the TFTP Server
2 option. A new CTL or ITL file downloads from the new TFTP Server 2 address.
If you forget to unlock the CTL or ITL file, you can change the TFTP Server 2 address in either
file, then erase them by pressing Erase from the Security Configuration menu. A new CTL or ITL
file downloads from the new TFTP Server 2 address.
When the phone looks for the TFTP server, it gives precedence to manually assigned TFTP servers,
regardless of the protocol. If your configuration includes both IPv6 and IPv4 TFTP servers, the
phone prioritizes the order that it looks for the TFTP server by giving priority to manually assigned
IPv6 TFTP servers and IPv4 TFTP servers. The phone looks for the TFTP server in the following
order:
1. Any manually assigned IPv4 TFTP servers
2. Any manually assigned IPv6 servers
3. DHCP assigned TFTP servers
4. DHCPv6 assigned TFTP servers
For information about the CTL or ITL file, see Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Security Guide.
Note
TFTP Server 2
Indicates whether the phone received the IP address from a BOOTP server rather than from a
DHCP server.
BOOTP Server
Releases the IP address that DHCP assigned.
This field is editable if DHCP is enabled. If you wish to remove the phone from the VLAN and
release the IP address for reassignment, set this option to Yes and press Apply.
DHCP Address Released
IPv6 Fields
Before IPv6 setup options can be configured on your device, IPv6 must be enabled and configured in Cisco
Unified Communication Administration. The following device configuration fields apply to IPv6 configuration:
• IP Addressing Mode
• IP Addressing Mode Preference for Signalling
If IPv6 is enabled in the Unified cluster, the default setting for IP addressing mode is IPv4 and IPv6. In this
addressing mode, the phone acquires and uses one IPv4 address and one IPv6 address. It can use the IPv4 and
the IPv6 address as required for media. The phone uses either the IPv4 or IPv6 address for call control signaling.
For more details about IPv6 deployment, see the IPv6 Deployment Guide for Cisco Collaboration Systems
Release 12.0.
You set up IPv6 from one of the following menus:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
59
Cisco IP Phone Installation
IPv6 Fields

• When Wi-Fi is disabled: Ethernet Setup > IPv6 setup
• When Wi-Fi is enabled: Wi-Fi Client Setup > IPv6 setup
Use the phone keypad to enter or edit an IPv6 address. To enter a colon, press the asterisk (*) on the keypad.
To enter hexadecimal digits a, b, and c, press 2 on the keypad, scroll to select the required digit, and press
Enter. To enter hexadecimal digits d, e, and f, press 3 on the keypad, scroll to select the required digit, and
press Enter.
The following table describes the IPv6 related information found in the IPv6 menu.
Table 22: IPv6 Setup Menu Options
DescriptionDefault valueEntry
Indicates the method that the phone uses to get the IPv6-only address.
When DHCPv6 is enabled, the phone gets the IPv6 address either from DHCPv6 server or from SLAAC by RA sent by
the IPv6-enabled router. And if DHCPv6 is disabled, the phone will not have any stateful (from DHCPv6 server) or
stateless (from SLAAC) IPv6 address.
YesDHCPv6 Enabled
Displays the current IPv6-only address of the phone or allows the user to enter a new IPv6 address.
A valid IPv6 address is 128 bits in length, including the subnet prefix. Two address formats are supported:
• Eight sets of hexadecimal digits separated by colons X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X
• Compressed format to collapse a single run of consecutive zero groups into a single group represented by a double
colon.
If the IP address is assigned with this option, you must also assign the IPv6 prefix length and the default router.
::IPv6 Address
Displays the current prefix length for the subnet or allows the user to enter a new prefix length.
The subnet prefix length is a decimal value from 1 to 128.
0IPv6 Prefix Length
Displays the default router used by the phone or allows the user to enter a new IPv6-only default router.::IPv6 Default Router
Displays the primary DNSv6 server used by the phone or allows the user to enter a new server.::IPv6 DNS Server 1
Displays the secondary DNSv6 server used by the phone or allows the user to set a new secondary DNSv6 server.::IPv6 DNS Server 2
Allows the user to enable the use of an alternate (secondary) IPv6 TFTP server.NoIPv6 Alternate TFTP
Displays the primary IPv6 TFTP server used by the phone or allows the user to set a new primary TFTP server.::IPv6 TFTP Server 1
(Optional) Displays the secondary IPv6 TFTP server used if the primary IPv6 TFTP server is unavailable or allows the
user to set a new secondary TFTP server.
::IPv6 TFTP Server 2
Allows the user to release IPv6-related information.NoIPv6 Address Released
Set Up Phone to Use DHCP
To enable DHCP and allow the DHCP server to automatically assign an IP address to the Cisco IP Phone and
direct the phone to a TFTP server, perform these steps:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
60
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set Up Phone to Use DHCP

Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Choose Admin settings > Network setup > Ethernet setup > IPv4 Setup.
Step 3 To enable DHCP, set DHCP Enabled to Yes. DHCP is enabled by default.
Step 4 To use an alternate TFTP server, set Alternate TFTP Server to Yes, and enter the IP address for the TFTP
Server.
Consult with the network administrator to determine whether you need to assign an alternative
TFTP server instead of using the TFTP server that DHCP assigns.
Note
Step 5 Press Apply,
Set Up Phone to Not Use DHCP
When not using DHCP, you must configure the IP address, subnet mask, TFTP server, and default router
locally on the phone.
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Choose Admin settings > Network setup > Ethernet Setup > IPv4 Setup.
Step 3 To disable DHCP and manually set an IP address:
a) Set DHCP Enabled to No.
b) Enter the static IP address for phone.
c) Enter the subnet mask.
d) Enter the default router IP addresses.
e) Set Alternate TFTP Server to Yes, and enter the IP address for TFTP Server 1.
Step 4 Press Apply.
Load Server
Load Server is used to optimize installation time for phone firmware upgrades and offload the WAN by storing
images locally, which negates the need to traverse the WAN link for each phone upgrade.
You can set the Load Server to another TFTP server IP address or name (other than the TFTP Server 1 or
TFTP Server 2) from which the phone firmware can be retrieved for phone upgrades. When the Load Server
option is set, the phone contacts the designated server for the firmware upgrade.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
61
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set Up Phone to Not Use DHCP

A Load Server option allows you to specify an alternate TFTP server for phone upgrades only. The phone
continues to use TFTP Server 1 or TFTP Server 2 to obtain configuration files. The Load Server option does
not provide management of the process and of the files, such as file transfer, compression, or deletion.
Note
The Load Server is configured from the Enterprise Phone Configuration window. From Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Phone >Enterprise Phone Configuration.
Phone Startup Verification
After the Cisco IP Phone has power connected to it, the phone begins the startup diagnostic process by cycling
through the following steps.
1. The Feature and Session buttons flash amber and then green in sequence during the various stages of
bootup as the phone checks the hardware.
2. The main screen displays Registering to Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
If the phone completes these stages successfully, it has started up properly and the Select button stays lit until
it is selected.
Configure Phone Services for Users
You can give users access to Cisco IP Phone Services on the IP phone. You can also assign a button to different
phone services. These services comprise XML applications and Cisco-signed Java midlets that enable the
display of interactive content with text and graphics on the phone. The IP phone manages each service as a
separate application. Examples of services include local movie times, stock quotes, and weather reports.
Before a user can access any service:
• You must use Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration to configure services that are not
present by default.
• The user must subscribe to services by using the Cisco Unified Communications Self Care Portal. This
web-based application provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for limited, end-user configuration of
IP phone applications. However, a user cannot subscribe to any service that you configure as an enterprise
subscription.
For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
Before you set up services, gather the URLs for the sites that you want to set up and verify that users can
access those sites from your corporate IP telephony network. This activity is not applicable for the default
services that Cisco provides.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Device Settings > Phone
Services
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
62
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Phone Startup Verification

Step 2 Verify that your users can access the Cisco Unified Communications Self Care Portal, from which they can
select and subscribe to configured services.
See Self Care Portal Management, on page 77 for a summary of the information that you must provide to
end users.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Change a User's Phone Model
You or your user can change a user's phone model. The change can be required for a number of reasons, for
example:
• You have updated your Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM) to a software version
that doesn't support the phone model.
• The user wants a different phone model from their current model.
• The phone requires repair or replacement.
The Unified CM identifies the old phone and uses the old phone's MAC address to identify the old phone
configuration. The Unified CM copies the old phone configuration into the entry for the new phone. The new
phone then has the same configuration as the old phone.
If you change an old phone with SCCP firmware to a model in the Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series, the new phone
is configured for Session Line Mode.
If the old phone has a key expansion model configured, the Unified CM copies the expansion module
information to the new phone at the same time. When the user connects a compatible key expansion module
to the new phone, the new expansion module gets the migrated expansion module information.
If the old phone has a key expansion model configured and the new phone doesn't support an expansion
module, the Unified CM doesn't copy the expansion module information.
Limitation: If the old phone has more lines or line buttons than the new phone, the new phone doesn't have
the extra lines or line buttons configured.
The phone reboots when the configuration is complete.
Before you begin
Set up your Cisco Unified Communications Manager according to the instructions in the Feature Configuration
Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
You need a new, unused phone that comes preinstalled with Firmware Release 12.8(1) or later.
Procedure
Step 1 Power off the old phone.
Step 2 Power on the new phone.
Step 3 On the new phone, select Replace an existing phone.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
63
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Change a User's Phone Model

Step 4 Enter the primary extension of the old phone.
Step 5 If the old phone had a PIN assigned, enter the PIN.
Step 6 Press Submit.
Step 7 If there is more than one device for the user, select the device to replace and press Continue.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
64
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Change a User's Phone Model

CHAPTER 5
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Phone
Setup
• Set Up Cisco IP Phone, on page 65
• Determine the Phone MAC Address, on page 68
• Phone Addition Methods, on page 68
• Add Users to Cisco Unified Communications Manager, on page 70
• Add a User to an End User Group, on page 71
• Associate Phones with Users , on page 72
• Survivable Remote Site Telephony, on page 72
• Enhanced Survivable Remote Site Telephony, on page 75
• Application Dial Rules, on page 75
Set Up Cisco IP Phone
If autoregistration is not enabled and the phone does not exist in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
database, you must configure the Cisco IP Phone in Cisco Unified Communications Manager manually. Some
tasks in this procedure are optional, depending on your system and user needs.
For more information about Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, see the documentation
for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Perform the configuration steps in the following procedure using Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration.
Procedure
Step 1 Gather the following information about the phone:
• Phone model
• MAC address
• Physical location of the phone
• Name or user ID of phone user
• Device pool
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
65

• Partition, calling search space, and location information
• Number of lines and associated directory numbers (DNs) to assign to the phone
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager user to associate with the phone
• Phone usage information that affects phone button template, phone features, IP Phone services, or phone
applications
The information provides a list of configuration requirements for setting up phones and identifies preliminary
configuration that you need to perform before configuring individual phones, such as phone button templates.
Step 2 Verify that you have sufficient unit licenses for your phone.
Step 3 Customize phone button templates (if required) by changing the number of line buttons, speed-dial buttons
or service URL buttons. Select Device > Device Settings > Phone Button Template to create and update
the templates.
You can add a Privacy, All Calls, or Mobility button to meet user needs.
For more information, see Phone Button Templates, on page 185.
Step 4 Define the Device Pools. Select System > Device Pool.
Device Pools define common characteristics for devices, such as region, date/time group, softkey template,
and MLPP information.
Step 5 Define the Common Phone Profile. Select Device > Device settings > Common Phone Profile.
Common phone profiles provide data that the Cisco TFTP server requires, as well as common phone settings,
such as Do Not Disturb and feature control options.
Step 6 Define a Calling Search Space. In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, click Call
Routing > Class of Control > Calling Search Space.
A Calling Search Space is a collection of partitions that are searched to determine how a dialed number is
routed. The calling search space for the device and the calling search space for the directory number are used
together. The directory number CSS takes precedence over the device CSS.
Step 7 Configure a security profile for the device type and protocol. Select System > Security > Phone Security
Profile.
Step 8 Add and configure the phone by completing the required fields in the Phone Configuration window. An
asterisk (*) next to the field name indicates a required field; for example, MAC address and device pool.
This step adds the device with the default settings to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database.
For information about product-specific configuration fields, see the “?” Button Help in the Phone Configuration
window.
If you want to add both the phone and user to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
database at the same time, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Note
Step 9 Add and configure directory numbers (lines) on the phone by completing the required fields in the Directory
Number Configuration window. An asterisk (*) next to the field name indicates a required field; for example,
directory number and presence group.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
66
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set Up Cisco IP Phone

This step adds primary and secondary directory numbers and features associated with directory numbers to
the phone.
If you do not configure the primary directory number, the user sees the message Unprovisioned
on the phone.
Note
Step 10 Configure speed-dial buttons and assign speed-dial numbers.
Users can change speed-dial settings on their phones by using Cisco Unified Communications Self Care Portal.
Step 11 Configure Cisco Unified IP Phone services and assign services (optional) to provide IP Phone services.
Users can add or change services on their phones by using the Cisco Unified Communications Self Care
Portal.
Users can subscribe to the IP Phone service only if the Enterprise Subscription check box is
unchecked when the IP Phone service is first configured in Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Administration.
Note
Some Cisco-provided default services are classified as enterprise subscriptions, so the user cannot
add them through the Self Care Portal. Such services are on the phone by default, and they can
only be removed from the phone if you disable them in Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration.
Note
Step 12 Assign services to programmable buttons (optional) to provide access to an IP Phone service or URL.
Step 13 Add user information by configuring required fields. An asterisk (*) next to the field name indicates a required
field; for example, User ID and last name. This step adds user information to the global directory for Cisco
Unified Communications Manager.
Assign a password (for Self Care Portal) and PIN (for Cisco Extension Mobility and Personal
Directory).
Note
If your company uses a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory to store
information about users, you can install and configure Cisco Unified Communications to use
your existing LDAP directory.
Note
If you want to add both the phone and user to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
database at the same time, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Note
Step 14 Associate a user to a user group. This step assigns users a common list of roles and permissions that apply to
all users in a user group. Administrators can manage user groups, roles, and permissions to control the level
of access (and, therefore, the level of security) for system users. For example, you must add users to the
standard Cisco CCM End Users group so users can access Cisco Unified Communications Manager Self Care
Portal.
Step 15 Associate a user with a phone (optional). This step provides users with control over their phone such a
forwarding calls or adding speed-dial numbers or services.
Some phones, such as those in conference rooms, do not have an associated user.
Step 16 If you are not already in the End User Configuration window, choose User Management > End User to
perform some final configuration tasks. Use the Search fields and Find to locate the user (for example, John
Doe), then click on the user ID to get to the End User Configuration window for the user.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
67
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Set Up Cisco IP Phone

Step 17 In the Directory Number Associations area of the screen, set the primary extension from the drop-down list.
Step 18 In the Mobility Information area, check the Enable Mobility box.
Step 19 In the Permissions Information area, use the User Group buttons to add this user to any user groups.
For example, you may want to add the user to a group that is defined as a Standard CCM End User Group.
Step 20 To view all configured user groups, choose User Management > User Group.
Step 21 In the Extension Mobility area, check the Enable Extension Mobility Cross Cluster box if the user is allowed
for Extension Mobility Cross Cluster service.
Step 22 Select Save.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Determine the Phone MAC Address
To add phones to Cisco Unified Communications Manager, you must determine the MAC address of a phone.
Procedure
Perform one of the following actions:
• On the phone, press Applications , select Phone Information and look at the MAC Address field.
• Look at the MAC label on the back of the phone.
• Display the web page for the phone and click Device Information.
Phone Addition Methods
After you install the Cisco IP Phone, you can choose one of the following options to add phones to the Cisco
Unified Communications Manager database.
• Add phones individually with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration
• Add multiple phones with the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT)
• Autoregistration
• BAT and the Tool for Auto-Registered Phones Support (TAPS)
Before you add phones individually or with BAT, you need the MAC address of the phone. For more
information, see Determine the Phone MAC Address, on page 68.
For more information about the Bulk Administration Tool, see the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
68
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Determine the Phone MAC Address

Add Phones Individually
Collect the MAC address and phone information for the phone that you will add to the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Phone.
Step 2 Click Add New.
Step 3 Select the phone type.
Step 4 Select Next.
Step 5 Complete the information about the phone including the MAC Address.
For complete instructions and conceptual information about Cisco Unified Communications Manager, see
the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Step 6 Select Save.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Add Phones with a BAT Phone Template
The Cisco Unified Communications Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) enables you to perform batch operations,
including registration of multiple phones.
To add phones using BAT only (not in conjunction with TAPS), you must obtain the appropriate MAC address
for each phone.
For more information about using BAT, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Administration, choose Bulk Administration > Phones > Phone
Template.
Step 2 Click Add New.
Step 3 Choose a Phone Type and click Next.
Step 4 Enter the details of phone-specific parameters, such as Device Pool, Phone Button Template, and Device
Security Profile.
Step 5 Click Save.
Step 6 Select Device > Phone > Add New to add a phone using the BAT phone template.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
69
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Add Phones Individually

Add Users to Cisco Unified Communications Manager
You can display and maintain information about the users registered in Cisco Unified Communications
Manager. Cisco Unified Communications Manager also allows each user to perform these tasks:
• Access the corporate directory and other customized directories from a Cisco IP Phone.
• Create a personal directory.
• Set up speed dial and call forwarding numbers.
• Subscribe to services that are accessible from a Cisco IP Phone.
Procedure
Step 1 To add users individually, see Add a User Directly to Cisco Unified Communications Manager, on page 71.
Step 2 To add users in batches, use the Bulk Administration Tool. This method also enables you to set an identical
default password for all users.
For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Add a User from an External LDAP Directory
If you added a user to an LDAP Directory (a non-Cisco Unified Communications Server directory), you can
immediately synchronize the LDAP directory to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager on which you
are adding the user and the user phone.
If you do not synchronize the LDAP Directory to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager immediately,
the LDAP Directory Synchronization Schedule on the LDAP Directory window determines when the next
autosynchronization is scheduled. Synchronization must occur before you can associate a new user to a device.
Note
Procedure
Step 1 Sign into Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration.
Step 2 Select System > LDAP > LDAP Directory.
Step 3 Use Find to locate your LDAP directory.
Step 4 Click on the LDAP directory name.
Step 5 Click Perform Full Sync Now.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
70
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Add Users to Cisco Unified Communications Manager

Add a User Directly to Cisco Unified Communications Manager
If you are not using a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory, you can add a user directly
with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration by following these steps.
If LDAP is synchronized, you cannot add a user with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration.
Note
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose User Management > End User.
Step 2 Click Add New.
Step 3 In the User Information pane, enter the following:
• User ID: Enter the end user identification name. Cisco Unified Communications Manager does not permit
modifying the user ID after it is created. You may use the following special characters: =, +, <, >, #,;, \,,
“”, and blank spaces. Example: johndoe
• Password and Confirm Password: Enter five or more alphanumeric or special characters for the end user
password. You may use the following special characters: =, +, <, >, #, ;, \, , “”, and blank spaces.
• Last Name: Enter the end user last name. You may use the following special characters: =, +, <, >, #, ;,
\, , “”, and blank spaces. Example: doe
• Telephone Number: Enter the primary directory number for the end user. End users can have multiple
lines on their phones. Example: 26640 (John Doe’s internal company telephone number)
Step 4 Click Save.
Add a User to an End User Group
To add a user to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Standard End User group, perform these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose User Management > User Settings >
Access Control Group.
The Find and List Users window displays.
Step 2 Enter the appropriate search criteria and click Find.
Step 3 Select the Standard CCM End Users link. The User Group Configuration window for the Standard CCM
End Users appears.
Step 4 Select Add End Users to Group. The Find and List Users window appears.
Step 5 Use the Find User drop-down list boxes to find the users that you want to add and click Find.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
71
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Add a User Directly to Cisco Unified Communications Manager

A list of users that matches your search criteria appears.
Step 6 In the list of records that appear, click the check box next to the users that you want to add to this user group.
If the list is long, use the links at the bottom to see more results.
The list of search results does not display users that already belong to the user group.
Note
Step 7 Choose Add Selected.
Associate Phones with Users
You associate phones with users from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager End User window.
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose User Management > End User.
The Find and List Users window appears.
Step 2 Enter the appropriate search criteria and click Find.
Step 3 In the list of records that appear, select the link for the user.
Step 4 Select Device Association.
The User Device Association window appears.
Step 5 Enter the appropriate search criteria and click Find.
Step 6 Choose the device that you want to associate with the user by checking the box to the left of the device.
Step 7 Choose Save Selected/Changes to associate the device with the user.
Step 8 From the Related Links drop-down list in the upper, right corner of the window, select Back to User, and
click Go.
The End User Configuration window appears and the associated devices that you chose display in the Controlled
Devices pane.
Step 9 Choose Save Selected/Changes.
Survivable Remote Site Telephony
Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) ensures that basic phone functions remain accessible when WAN
connectivity is lost. In this scenario, the phone can keep an in-progress call active, and the user can access a
subset of the features available. When failover occurs, the user receives an alert message on the phone.
For more information about supported firmware and Survivable Remote Site Telephony, see Cisco Unified
Survivable Remote Site Telephony Compatibility Information page on Cisco.com
(http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/unified-communications/unified-survivable-remote-site-telephony/products-device-support-tables-list.html).
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
72
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Associate Phones with Users

The following table describes the availability of features during failover.
Table 23: SRST feature support
NotesSupportedFeature
YesNew Call
YesEnd Call
YesRedial
YesAnswer
YesHold
YesResume
YesConference
The Active Calls softkey does not display.NoConference to Active Calls (Join)
NoConference List
YesTransfer
NoTransfer to Active Calls (Direct
Transfer)
YesAuto Answer
YesCall Waiting
YesCaller ID
YesAudible Message Waiting Indicator
YesAll Calls Programmable Line Key
YesAnswer Programmable Line Key
Conference is the only feature supported
due to other feature limitations.
YesUnified Session Presentation
Voicemail will not be synchronized with
other users in the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager cluster.
YesVoicemail
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
73
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Survivable Remote Site Telephony

NotesSupportedFeature
Forward state is only available on the phone
that sets the forward because there are no
shared line appearances in SRST mode. The
Call Forward All settings are not preserved
on failover to SRST from the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, or from SRST
fail-back to the Communications Manager.
Any original Call Forward All still active
on the Communications Manager should be
indicated when the device reconnects to the
Communications Manager after failover.
YesCall Forward All
YesSpeed Dial
YesService IRL Programmable Line
Key
The iDivert softkey does not display.NoTo Voicemail (iDivert)
Lines are supported but cannot be shared.PartialLine Filters
The Park softkey does not display.NoPark Monitoring
The Barge softkey does not display.NoBarge
Message count badges do not appear on the
phone screen.
Only the Message Waiting icon displays.
NoEnhanced Message Waiting
Indication
The softkey does not display.NoDirected Call Park
BLF feature key works like Speed Dial
keys.
PartialBLF
Calls remain on hold indefinitely.NoHold Reversion
Calls appear as Local Hold calls.NoRemote Hold
The Meet Me softkey does not display.NoMeet Me
The softkey causes no action.NoPickUp
The softkey causes no action.NoGroup PickUp
The softkey causes no action.NoOther PickUp
The softkey causes no action.NoMalicious Call ID
The softkey causes no action.NoQRT
The softkey causes no action.NoHunt Group
The softkey causes no action.NoIntercom
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
74
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Survivable Remote Site Telephony

NotesSupportedFeature
The softkey causes no action.NoMobility
The softkey causes no action.NoPrivacy
The Call Back softkey does not display.NoCall Back
Video conference is not supported.YesVideo
Video conference is not supported.YesVideo
NoShared Line
YesBLF Speed Dial
Enhanced Survivable Remote Site Telephony
Enhanced Survivable Remote Site Telephony (E-SRST) ensures that additional phone features are available
remain accessible when WAN connectivity is lost. In addition to the features supported by Survivable Remote
Site Telephony(SRST), E-SRST supports the following:
• Shared-Line
• Busy-Lamp-Field (BLF)
• Video Calls
For more information about supported firmware and Survivable Remote Site Telephony, see Cisco Unified
Survivable Remote Site Telephony Compatibility Information page on Cisco.com
(http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/unified-communications/unified-survivable-remote-site-telephony/products-device-support-tables-list.html).
Application Dial Rules
Application Dial Rules are used to convert numbers for shared mobile contacts to network dialable numbers.
Application Dial Rules do not apply when the user is dialing a number manually, or if the number is edited
before the user places the call.
Application Dial Rules are set in Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
For additional information about dial rules, see System Conf iguration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications
Manager, “Configure Dial Rules” chapter.
Configure Application Dial Rules
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, go to Call Routing > Dial Rules > Application
Dial Rules.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
75
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Enhanced Survivable Remote Site Telephony

Step 2 Choose Add New to create a new application dial rule, or choose an existing application dial rule to edit it.
Step 3 Fill in the following fields:
• Name This field comprises a unique name for the dial rule that can contain up to 20 alphanumeric
characters and any combination of spaces, periods (.), hyphens (-), and underscore characters (_).
• Description This field comprises a brief description that you enter for the dial rule.
• Number Begins With This field comprises the initial digits of the directory numbers to which you want
to apply this application dial rule.
• Number of Digits This required field comprises the initial digits of the directory numbers to which you
want to apply this application dial rule.
• Total Digits to be Removed This required field comprises the number of digits that you want Cisco
Unified Communications Manager to remove from directory numbers that apply to this dial rule.
• Prefix With PatternThis required field comprises the pattern to prepend to directory numbers that apply
to this application dial rule.
• Application Dial Rule Priority This field displays when you enter the Prefix With Pattern information.
The field allows you to set the priority order of the application dial rules.
Step 4 Restart Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
76
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Configure Application Dial Rules

CHAPTER 6
Self Care Portal Management
• Self Care Portal Overview, on page 77
• Set Up User Access to the Self Care Portal, on page 77
• Customize the Self Care Portal Display, on page 78
Self Care Portal Overview
From the Cisco Unified Communications Self Care Portal, users can customize and control phone features
and settings.
As the administrator, you control access to the Self Care Portal. You must also provide information to your
users so that they can access the Self Care Portal.
Before a user can access the Cisco Unified Communications Self Care Portal, you must use Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Administration to add the user to a standard Cisco Unified Communications
Manager End User group.
You must provide end users with the following information about the Self Care Portal:
• The URL to access the application. This URL is:
https://<server_name:portnumber>/ucmuser/, where server_name is the host on which
the web server is installed, and portnumber is the port number on that host.
• A user ID and default password to access the application.
• An overview of the tasks that users can accomplish with the portal.
These settings correspond to the values that you entered when you added the user to Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Set Up User Access to the Self Care Portal
Before a user can access the Self Care Portal, you need to authorize the access.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
77

Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select User Management > End User.
Step 2 Search for the user.
Step 3 Click the user ID link.
Step 4 Ensure that the user has a password and PIN configured.
Step 5 In the Permission Information section, ensure that the Groups list includes Standard CCM End Users.
Step 6 Select Save.
Customize the Self Care Portal Display
Most options display on the Self Care Portal. However, you must set the following options by using Enterprise
Parameters Configuration settings in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration:
• Show Ring Settings
• Show Line Label Settings
The settings apply to all Self Care Portal pages at your site.
Note
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select System > Enterprise Parameters.
Step 2 In the Self Care Portal area, set the Self Care Portal Default Server field.
Step 3 Enable or disable the parameters that the users can access in the portal.
Step 4 Select Save.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
78
Cisco IP Phone Installation
Customize the Self Care Portal Display

CHAPTER 7
Cisco IP Phone Security
• Security Enhancements for Your Phone Network, on page 81
• Supported Security Features, on page 82
Security Enhancements for Your Phone Network
You can enable Cisco Unified Communications Manager 11.5(1) or later version to operate in an enhanced
security environment. With these enhancements, your phone network operates under a set of strict security
and risk management controls to protect you and your users.
The enhanced security environment includes the following features:
• Contact search authentication.
• TCP as the default protocol for remote audit logging.
• FIPS mode.
• An improved credentials policy.
• Support for the SHA-2 family of hashes for digital signatures.
• Support for a RSA key size of 512 and 4096 bits.
Your Cisco IP Phone can only store a limited number of Identity Trust List (ITL) files. ITL files cannot exceed
64K limit on phone so limit the number of files that the Cisco Unified Communications Manager sends to the
phone.
Note
SIP OAuth Support
SIP OAuth mode allows you to use OAuth refresh tokens for phone authentication.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM) verifies the token presented by the phone and serves
the configuration files only to authorized ones. OAuth token validation during SIP registration is completed
when OAuth-based authorization is enabled on Unified CM cluster and Cisco IP phones.
Cisco IP phones support SIP OAuth authentication on Proxy Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) and Cisco
Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST).
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
81

• SIP OAuth on TFTP requirements:
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 14.0(1)SU1 or later
• Cisco IP Phone Firmware Release 14.1(1) or later
Proxy TFTP and OAuth for Proxy TFTP aren't supported on Mobile Remote
Access (MRA).
Note
• SIP OAuth on SRST requirements:
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager 14.0(1)SU1 or later
• Cisco IP Phone Firmware Release 14.2(1) or later
• Cisco SRST Software Release: IOS XE 17.8.1a or later
• Cisco SRST Hardware Models: ISR1100, ISR43xx, ISR44xx, Catalyst 8200, or Catalyst 8300
platform
For information about how to configure SIP OAuth, see SIP OAuth Mode in SecurityGuide for CiscoUnified
Communications Manager.
Where to Find More Information about Phone Security
For additional information about security, see the following:
• Security Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager (https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/
voice_ip_comm/cucm/security/14SU2/cucm_b_security-guide-14su2.html)
• Cisco Unified SCCP and SIP SRST System Administration Guide (https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/
docs/voice_ip_comm/cusrst/admin/sccp_sip_srst/configuration/guide/SCCP_and_SIP_SRST_Admin_
Guide/srst_roadmap.html)
• System Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Release 14.0(1) or later
(https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/unified-communications/
unified-communications-manager-callmanager/products-installation-and-configuration-guides-list.html).
• Cisco IP Phone 7800 and 8800 Series Security Overview (https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/
collaboration-endpoints/unified-ip-phone-8800-series/white-paper-listing.html)
Supported Security Features
Security features protect against several threats, including threats to the identity of the phone and to data.
These features establish and maintain authenticated communication streams between the phone and the Cisco
Unified Communications Manager server, and ensure that the phone uses only digitally signed files.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 8.5(1) and later includes Security by Default, which provides
the following security features for Cisco IP Phones without running the CTL client:
• Signing of the phone configuration files
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
82
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Supported Security Features

• Phone configuration file encryption
• HTTPS with Tomcat and other Web services
Secure signaling and media features still require you to run the CTL client and use hardware eTokens.
Note
Implementing security in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager system prevents identity theft of the
phone and Cisco Unified Communications Manager server, prevents data tampering, and prevents call signaling
and media stream tampering.
To alleviate these threats, the Cisco IP telephony network establishes and maintains secure (encrypted)
communication streams between a phone and the server, digitally signs files before they are transferred to a
phone, and encrypts media streams and call signaling between Cisco IP Phones.
A Locally Significant Certificate (LSC) installs on phones after you perform the necessary tasks that are
associated with the Certificate Authority Proxy Function (CAPF). You can use Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Administration to configure an LSC, as described in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Security Guide. Alternatively, you can initiate the installation of an LSC from the Security Setup menu on
the phone. This menu also lets you update or remove an LSC.
A LSC cannot be used as the user certificate for EAP-TLS with WLAN authentication.
The phones use the phone security profile, which defines whether the device is nonsecure or secure. For
information about applying the security profile to the phone, see the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
If you configure security-related settings in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, the
phone configuration file contains sensitive information. To ensure the privacy of a configuration file, you
must configure it for encryption. For detailed information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
The Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series complies with Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS). To function
correctly, FIPS mode requires a key size of 2048 bits or greater. If the certificate is not 2048 bits or greater,
the phone will not register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Phone failed to
If the phone has an LSC, you need to update the LSC key size to 2048 bits or greater before enabling FIPS.
The following table provides an overview of the security features that the phones support. For more information,
see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
For view the current security settings on a phone, including Security mode, Trust list, and 802.1X
Authentication, press Applications and choose Admin Settings > Security setup.
Table 24: Overview of Security Features
DescriptionFeature
Signed binary files (with the extension.sbn) prevent tampering with the firmware image
before the image is loaded on a phone.
Tampering with the image causes a phone to fail the authentication process and reject
the new image.
Image authentication
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
83
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Supported Security Features

DescriptionFeature
Encrypted binary files (with the extension.sebn) prevent tampering with the firmware
image before the image is loaded on a phone.
Tampering with the image causes a phone to fail the authentication process and reject
the new image.
Image encryption
Each Cisco IP Phone requires a unique certificate for device authentication. Phones
include a manufacturing installed certificate (MIC), but for additional security, you can
specify certificate installation in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration
using the Certificate Authority Proxy Function (CAPF). Alternatively, you can install
a Locally Significant Certificate (LSC) from the Security Configuration menu on the
phone.
Customer site certificate installation
Occurs between the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server and the phone
when each entity accepts the certificate of the other entity. Determines whether a secure
connection between the phone and a Cisco Unified Communications Manager should
occur; and, if necessary, creates a secure signaling path between the entities by using
TLS protocol. Cisco Unified Communications Manager does not register phones unless
it can authenticate them.
Device authentication
Validates digitally signed files that the phone downloads. The phone validates the
signature to make sure that file tampering did not occur after file creation. Files that fail
authentication are not written to Flash memory on the phone. The phone rejects such
files without further processing.
File authentication
Encryption prevents sensitive information from being revealed while the file is in transit
to the phone. In addition, the phone validates the signature to make sure that file
tampering did not occur after file creation. Files that fail authentication are not written
to Flash memory on the phone. The phone rejects such files without further processing.
File encryption
Uses the TLS protocol to validate that no tampering to signaling packets has occurred
during transmission.
Signaling authentication
Each Cisco IP Phone contains a unique manufacturing installed certificate (MIC), which
is used for device authentication. The MIC provides permanent unique proof of identity
for the phone and allows Cisco Unified Communications Manager to authenticate the
phone.
Manufacturing installed certificate
Uses SRTP to ensure that media streams between supported devices prove secure and
that only the intended device receives and reads the data. Includes creating a media
primary key pair for the devices, delivering the keys to the devices, and securing the
delivery of the keys while the keys are in transport.
Media encryption
Implements parts of the certificate generation procedure that are too processing-intensive
for the phone, and interacts with the phone for key generation and certificate installation.
The CAPF can be configured to request certificates from customer-specified certificate
authorities on behalf of the phone, or it can be configured to generate certificates locally.
CAPF (Certificate Authority Proxy
Function)
Defines whether the phone is nonsecure, authenticated, encrypted, or protected. Other
entries in this table describe security features.
Security profile
Lets you ensure the privacy of phone configuration files.Encrypted configuration files
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
84
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Supported Security Features

DescriptionFeature
For security purposes, you can prevent access to the web pages for a phone (which
display a variety of operational statistics for the phone) and Self Care Portal.
Optional web server disabling for a phone
Additional security options, which you control from Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Administration:
• Disabling PC port
• Disabling Gratuitous ARP (GARP)
• Disabling PC Voice VLAN access
• Disabling access to the Setting menus, or providing restricted access that allows
access to the Preferences menu and saving volume changes only
• Disabling access to web pages for a phone
• Disabling Bluetooth Accessory Port
• Restricting TLS ciphers
Phone hardening
The Cisco IP Phone can use 802.1X authentication to request and gain access to the
network. See 802.1X Authentication, on page 106 for more information.
802.1X Authentication
After you configure a Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) reference for security
and then reset the dependent devices in Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration, the TFTP server adds the SRST certificate to the phone cnf.xml file
and sends the file to the phone. A secure phone then uses a TLS connection to interact
with the SRST-enabled router.
Secure SIP Failover for SRST
Ensures that all SIP signaling messages that are sent between the device and the Cisco
Unified Communications Manager server are encrypted.
Signaling encryption
When the Trust List updates on the phone, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
receives an alarm to indicate the success or failure of the update. See the following table
for more information.
Trust List update alarm
When connected to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release 10.5(2) and later,
the phones support AES 256 encryption support for TLS and SIP for signaling and
media encryption. This enables phones to initiate and support TLS 1.2 connections using
AES-256 based ciphers that conform to SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm) standards and
are Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) compliant. The ciphers include:
• For TLS connections:
• TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
• TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
• For sRTP:
• AEAD_AES_256_GCM
• AEAD_AES_128_GCM
For more information, see the Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation.
AES 256 Encryption
As part of Common Criteria (CC) certification, Cisco Unified Communications
Manageradded ECDSA certificates in version 11.0. This affects all Voice Operating
System (VOS) products from version CUCM 11.5 and later.
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm
(ECDSA) certificates
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
85
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Supported Security Features

The following table contains the Trust List update alarm messages and meaning. For more information, see
the Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation
Table 25: Trust List Update Alarm Messages
DescriptionCode and Message
Received new CTL and/or ITL1 - TL_SUCCESS
Received new CTL, no existing TL2 - CTL_INITIAL_SUCCESS
Received new ITL, no existing TL3 - ITL_INITIAL_SUCCESS
Received new CTL and ITL, no existing TL4 - TL_INITIAL_SUCCESS
Update to new CTL failed, but have previous TL5 - TL_FAILED_OLD_CTL
Update to new TL failed, and have no old TL6 - TL_FAILED_NO_TL
Generic failure7 - TL_FAILED
Update to new ITL failed, but have previous TL8 - TL_FAILED_OLD_ITL
Update to new TL failed, but have previous TL9 - TL_FAILED_OLD_TL
The Security Setup menu provides information about various security settings. The menu also provides access
to the Trust List menu and indicates whether the CTL or ITL file is installed on the phone.
The following table describes the options in the Security Setup menu.
Table 26: Security Setup Menu
To ChangeDescriptionOption
From Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration, choose Device > Phone. The setting
appears in the Protocol Specific Information portion
of the Phone Configuration window.
Displays the security mode that is set for the phone.Security Mode
For information about how to manage the LSC for
your phone, see the documentation for your
particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
Indicates whether a locally significant certificate
that is used for security features is installed on the
phone (Yes) or is not installed on the phone (No).
LSC
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
86
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Supported Security Features

To ChangeDescriptionOption
For more information, see Set Up a Locally
Significant Certificate, on page 87.
The Trust List provides submenus for the CTL, ITL,
and Signed Configuration files.
The CTL File submenu displays the contents of the
CTL file. The ITL File submenu displays contents
of the ITL file.
The Trust List menu also displays the following
information:
• CTL Signature: the SHA1 hash of the CTL file
• Unified CM/TFTP Server: the name of the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager and
TFTP Server that the phone uses. Displays a
certificate icon if a certificate is installed for
this server.
• CAPF Server: the name of the CAPF server
that the phone uses. Displays a certificate icon
if a certificate is installed for this server.
• SRST Router: the IP address of the trusted
SRST router that the phone can use. Displays
a certificate icon if a certificate is installed for
this server.
Trust List
See 802.1X Authentication, on page 106.Allows you to enable 802.1X authentication for this
phone.
802.1X Authentication
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Set Up a Locally Significant Certificate
This task applies to setting up a LSC with the authentication string method.
Before you begin
Make sure that the appropriate Cisco Unified Communications Manager and the Certificate Authority Proxy
Function (CAPF) security configurations are complete:
• The CTL or ITL file has a CAPF certificate.
• In Cisco Unified Communications Operating System Administration, verify that the CAPF certificate is
installed.
• The CAPF is running and configured.
For more information about these settings, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
87
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up a Locally Significant Certificate

Procedure
Step 1 Obtain the CAPF authentication code that was set when the CAPF was configured.
Step 2 From the phone, press Applications .
Step 3 Choose Admin Settings > Security Setup.
You can control access to the Settings menu by using the Settings Access field in the Cisco
Unified Communications Manager Administration Phone Configuration window.
Note
Step 4 Choose LSC and press Select or Update.
The phone prompts for an authentication string.
Step 5 Enter the authentication code and press Submit.
The phone begins to install, update, or remove the LSC, depending on how the CAPF is configured. During
the procedure, a series of messages appears in the LSC option field in the Security Configuration menu, so
you can monitor progress. When the procedure is complete, Installed or Not Installed displays on the phone.
The LSC install, update, or removal process can take a long time to complete.
When the phone installation procedure is successful, the Installed message displays. If the phone displays
Not Installed, then the authorization string may be incorrect or the phone upgrade may not be enabled.
If the CAPF operation deletes the LSC, the phone displays Not Installed to indicate that the operation
succeeded. The CAPF server logs the error messages. See the CAPF server documentation to locate the logs
and to understand the meaning of the error messages.
Enable FIPS Mode
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone and locate the phone.
Step 2 Navigate to the Product Specific Configuration area.
Step 3 Set the FIPS Mode field to Enabled.
Step 4 Select Apply Config.
Step 5 Select Save.
Step 6 Restart the phone.
Phone Call Security
When security is implemented for a phone, you can identify secure phone calls by icons on the phone screen.
You can also determine whether the connected phone is secure and protected if a security tone plays at the
beginning of the call.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
88
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Enable FIPS Mode

In a secure call, all call signaling and media streams are encrypted. A secure call offers a high level of security,
providing integrity and privacy to the call. When a call in progress is encrypted, the call progress icon to the
right of the call duration timer in the phone screen changes to the following icon: .
If the call is routed through non-IP call legs, for example, PSTN, the call may be nonsecure even though it is
encrypted within the IP network and has a lock icon associated with it.
Note
In a secure call, a security tone plays at the beginning of a call to indicate that the other connected phone is
also receiving and transmitting secure audio. If your call connects to a nonsecure phone, the security tone
does not play.
Secure calling is supported for connections between two phones only. Some features, such as conference
calling and shared lines, are not available when secure calling is configured.
Note
When a phone is configured as secure (encrypted and trusted) in Cisco Unified Communications Manager, it
can be given a “protected” status. After that, if desired, the protected phone can be configured to play an
indication tone at the beginning of a call:
• Protected Device: To change the status of a secure phone to protected, check the Protected Device check
box in the Phone Configuration window in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration
(Device > Phone).
• Play Secure Indication Tone: To enable the protected phone to play a secure or nonsecure indication
tone, set the Play Secure Indication Tone setting to True. By default, Play Secure Indication Tone is set
to False. You set this option in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration (System >
Service Parameters). Select the server and then the Unified Communications Manager service. In the
Service Parameter Configuration window, select the option in the Feature - Secure Tone area. The default
is False.
Secure Conference Call Identification
You can initiate a secure conference call and monitor the security level of participants. A secure conference
call is established by using this process:
1. A user initiates the conference from a secure phone.
2. Cisco Unified Communications Manager assigns a secure conference bridge to the call.
3. As participants are added, Cisco Unified Communications Manager verifies the security mode of each
phone and maintains the secure level for the conference.
4. The phone displays the security level of the conference call. A secure conference displays the secure icon
to the right of Conference on the phone screen.
Secure calling is supported between two phones. For protected phones, some features, such as conference
calling, shared lines, and Extension Mobility, are not available when secure calling is configured.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
89
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Secure Conference Call Identification

The following table provides information about changes to conference security levels depending on the initiator
phone security level, the security levels of participants, and the availability of secure conference bridges.
Table 27: Security Restrictions with Conference Calls
Results of ActionSecurity Level of ParticipantsFeature UsedInitiator Phone
Security Level
Nonsecure conference bridge
Nonsecure conference
SecureConferenceNonsecure
Secure conference bridge
Nonsecure conference
At least one member is nonsecure.ConferenceSecure
Secure conference bridge
Secure encrypted level conference
SecureConferenceSecure
Initiator receives message Does not meet
Security Level, call rejected.
Minimum security level is
encrypted.
Meet MeNonsecure
Secure conference bridge
Conference accepts all calls.
Minimum security level is
nonsecure.
Meet MeSecure
Secure Phone Call Identification
A secure call is established when your phone, and the phone on the other end, is configured for secure calling.
The other phone can be in the same Cisco IP network, or on a network outside the IP network. Secured calls
can only be made between two phones. Conference calls should support secure call after secure conference
bridge set up.
A secured call is established using this process:
1. A user initiates the call from a secured phone (secured security mode).
2. The phone displays the secure icon on the phone screen. This icon indicates that the phone is configured
for secure calls, but this does not mean that the other connected phone is also secured.
3. The user hears a security tone if the call connects to another secured phone, indicating that both ends of
the conversation are encrypted and secured. If the call connects to a nonsecure phone, the user does not
hear the security tone.
Secure calling is supported between two phones. For protected phones, some features, such as conference
calling, shared lines, and Extension Mobility, are not available when secure calling is configured.
Note
Only protected phones play these secure or nonsecure indication tones. Nonprotected phones never play tones.
If the overall call status changes during the call, the indication tone changes and the protected phone plays
the appropriate tone.
A protected phone plays a tone or not under these circumstances:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
90
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Secure Phone Call Identification

• When the Play Secure Indication Tone option is enabled:
• When end-to-end secure media is established and the call status is secure, the phone plays the secure
indication tone (three long beeps with pauses).
• When end-to-end nonsecure media is established and the call status is nonsecure, the phone plays
the nonsecure indicationtone (six short beeps with brief pauses).
If the Play Secure Indication Tone option is disabled, no tone plays.
Provide Encryption for Barge
Cisco Unified Communications Manager checks the phone security status when conferences are established
and changes the security indication for the conference or blocks the completion of the call to maintain integrity
and security in the system.
A user cannot barge into an encrypted call if the phone that is used to barge is not configured for encryption.
When barge fails in this case, a reorder (fast busy) tone plays on the phone that the barge was initiated.
If the initiator phone is configured for encryption, the barge initiator can barge into a nonsecure call from the
encrypted phone. After the barge occurs, Cisco Unified Communications Manager classifies the call as
nonsecure.
If the initiator phone is configured for encryption, the barge initiator can barge into an encrypted call, and the
phone indicates that the call is encrypted.
WLAN Security
Because all WLAN devices that are within range can receive all other WLAN traffic, securing voice
communications is critical in WLANs. To ensure that intruders do not manipulate nor intercept voice traffic,
the Cisco SAFE Security architecture supports the Cisco IP Phone and Cisco Aironet APs. For more information
about security in networks, see
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns744/networking_solutions_program_home.html.
The Cisco Wireless IP telephony solution provides wireless network security that prevents unauthorized
sign-ins and compromised communications by using the following authentication methods that the wireless
Cisco IP Phone supports:
• Open Authentication: Any wireless device can request authentication in an open system. The AP that
receives the request may grant authentication to any requestor or only to requestors that are found on a
list of users. Communication between the wireless device and AP could be nonencrypted or devices can
use Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) keys to provide security. Devices that use WEP only attempt to
authenticate with an AP that is using WEP.
• Extensible Authentication Protocol-Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling (EAP-FAST)
Authentication: This client server security architecture encrypts EAP transactions within a Transport
Level Security (TLS) tunnel between the AP and the RADIUS server, such as the Cisco Access Control
Server (ACS).
The TLS tunnel uses Protected Access Credentials (PACs) for authentication between the client (phone)
and the RADIUS server. The server sends an Authority ID (AID) to the client (phone), which in turn
selects the appropriate PAC. The client (phone) returns a PAC-Opaque to the RADIUS server. The server
decrypts the PAC with the primary key. Both endpoints now contain the PAC key and a TLS tunnel is
created. EAP-FAST supports automatic PAC provisioning, but you must enable it on the RADIUS server.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
91
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Provide Encryption for Barge

In the Cisco ACS, by default, the PAC expires in one week. If the phone has an
expired PAC, authentication with the RADIUS server takes longer while the
phone gets a new PAC. To avoid PAC provisioning delays, set the PAC expiration
period to 90 days or longer on the ACS or RADIUS server.
Note
• Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) Authentication: EAP-TLS
requires a client certificate for authentication and network access. For wired EAP-TLS, the client certificate
can be either the phone’s MIC or an LSC. LSC is the recommended client authentication certificate for
wired EAP-TLS.
• Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP): Cisco proprietary password-based mutual
authentication scheme between the client (phone) and a RADIUS server. Cisco IP Phone can use PEAP
for authentication with the wireless network. Both PEAP-MSCHAPV2 and PEAP-GTC authentication
methods are supported.
The following authentication schemes use the RADIUS server to manage authentication keys:
• WPA/WPA2: Uses RADIUS server information to generate unique keys for authentication. Because
these keys are generated at the centralized RADIUS server, WPA/WPA2 provides more security than
WPA preshared keys that are stored on the AP and phone.
• Fast Secure Roaming: Uses RADIUS server and a wireless domain server (WDS) information to manage
and authenticate keys. The WDS creates a cache of security credentials for CCKM-enabled client devices
for fast and secure reauthentication. The Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series supports 802.11r (FT). Both 11r
(FT) and CCKM are supported to allow for fast secure roaming. But Cisco strongly recommends to
utilize the 802.11r (FT) over air method.
With WPA/WPA2 and CCKM, encryption keys are not entered on the phone, but are automatically derived
between the AP and phone. But the EAP username and password that are used for authentication must be
entered on each phone.
To ensure that voice traffic is secure, the Cisco IP Phone supports WEP, TKIP, and Advanced Encryption
Standards (AES) for encryption. When these mechanisms are used for encryption, both the signalling SIP
packets and voice Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) packets are encrypted between the AP and the Cisco
IP Phone.
WEP
With WEP use in the wireless network, authentication happens at the AP by using open or shared-key
authentication. The WEP key that is setup on the phone must match the WEP key that is configured at
the AP for successful connections. The Cisco IP Phone supports WEP keys that use 40-bit encryption
or a 128-bit encryption and remain static on the phone and AP.
EAP and CCKM authentication can use WEP keys for encryption. The RADIUS server manages the
WEP key and passes a unique key to the AP after authentication for encrypting all voice packets;
consequently, these WEP keys can change with each authentication.
TKIP
WPA and CCKM use TKIP encryption that has several improvements over WEP. TKIP provides
per-packet key ciphering and longer initialization vectors (IVs) that strengthen encryption. In addition,
a message integrity check (MIC) ensures that encrypted packets are not being altered. TKIP removes the
predictability of WEP that helps intruders decipher the WEP key.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
92
Cisco IP Phone Administration
WLAN Security

AES
An encryption method used for WPA2 authentication. This national standard for encryption uses a
symmetrical algorithm that has the same key for encryption and decryption. AES uses Cipher Blocking
Chain (CBC) encryption of 128 bits in size, which supports key sizes of 128, 192 and 256 bits, as a
minimum. The Cisco IP Phone supports a key size of 256 bits.
The Cisco IP Phone does not support Cisco Key Integrity Protocol (CKIP) with CMIC.
Note
Authentication and encryption schemes are set up within the wireless LAN. VLANs are configured in the
network and on the APs and specify different combinations of authentication and encryption. An SSID
associates with a VLAN and the particular authentication and encryption scheme. In order for wireless client
devices to authenticate successfully, you must configure the same SSIDs with their authentication and encryption
schemes on the APs and on the Cisco IP Phone.
Some authentication schemes require specific types of encryption. With Open authentication, you can use
static WEP for encryption for added security. But if you are using Shared Key authentication, you must set
static WEP for encryption, and you must configure a WEP key on the phone.
• When you use WPA pre-shared key or WPA2 pre-shared key, the pre-shared key must be statically set
on the phone. These keys must match the keys that are on the AP.
• The Cisco IP Phone does not support auto EAP negotiation; to use EAP-FAST mode, you must specify
it.
Note
The following table provides a list of authentication and encryption schemes that are configured on the Cisco
Aironet APs that the Cisco IP Phone supports. The table shows the network configuration option for the phone
that corresponds to the AP configuration.
Table 28: Authentication and Encryption Schemes
AP ConfigurationCisco IP Phone
Configuration
Fast RoamingEncryptionKey ManagementSecuritySecurity Mode
N/ANoneNoneNoneNone
N/AWEPStaticStatic WEPWEP
NoneTKIPWPAPSKPSK
FTAESWPA2
CCKMWEP
802.1xEAP-FASTEAP-FAST
CCKMTKIPWPA
FT, CCKMAESWPA2
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
93
Cisco IP Phone Administration
WLAN Security

AP ConfigurationCisco IP Phone
Configuration
CCKMWEP
802.1xEAP-TLSEAP-TLS
CCKMTKIPWPA
FT, CCKMAESWPA2
CCKMWEP
802.1xPEAP-MSCHAPV2PEAP-MSCHAPV2
CCKMTKIPWPA
FT, CCKMAESWPA2
CCKMWEP
802.1xPEAP-GTCPEAP-GTC
CCKMTKIPWPA
FT, CCKMAESWPA2
For more information about configuring authentication and encryption schemes on APs, see the Cisco Aironet
Configuration Guide for your model and release under the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/psa/configure.html?mode=prod&level0=278875243
Set Up Authentication Mode
To select the Authentication Mode for this profile, follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 Choose the network profile that you want to configure.
Step 2 Choose the authentication mode.
Depending on what you selected, you must configure additional options in Wireless Security or
Wireless Encryption. See WLAN Security, on page 91 for more information.
Note
Step 3 Click Save to make the change.
Wireless Security Credentials
When your network uses EAP-FAST and PEAP for user authentication, you must configure both the username
and password if required on the Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) and the phone.
If you use domains within your network, you must enter the username with the domain name, in the format:
domain\username.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
94
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Authentication Mode

The following actions could result in the existing Wi-Fi password being cleared:
• Entering an invalid user id or password
• Installing an invalid or expired Root CA when the EAP type is set to PEAP-MSCHAPV2 or PEAP-GTC
• Disabling the EAP type on the RADIUS server used by the phone before changing a phone to the new
EAP type
To change EAP types, do the following in the stated order:
• Enable the new EAP types on the RADIUS.
• Change the EAP type on a phone to the new EAP type.
Keep the current EAP type configured on the phone until the new EAP type is enabled on the RADIUS server.
Once the new EP type is enabled on the RADIUS server, then you can change the phone’s EAP type. Once
all phones have been changed to the new EAP type, you can disable the previous EAP type if you want.
Set Up Username and Password
To enter or change the username or password for the network profile, you must use the same username and
the same password string that are configured in the RADIUS server. The maximum length of the username
or password entry is 64 characters.
To set up the username and password in Wireless Security Credentials, follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 Choose the network profile.
Step 2 In the Username field, enter the network username for this profile.
Step 3 In the Password field, enter the network password string for this profile.
Step 4 Click Save to make the change.
Pre-Shared Key Setup
Use the following sections to guide you as you set up pre-shared keys.
Pre-Shared Key Formats
The Cisco IP Phone supports ASCII and hexadecimal formats. You must use one of these formats when setting
up a WPA Pre-shared key:
Hexadecimal
For hexadecimal keys, you enter 64 hex digits (0-9 and A-F); for example,
AB123456789CD01234567890EFAB123456789CD01234567890EF3456789C
ASCII
For ASCII keys, you enter a character string that uses 0-9, A-Z (upper and lower case), including symbols
and is from 8 to 63 characters in length; for example, GREG12356789ZXYW
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
95
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Username and Password

Set Up PSK
To set up a PSK in the Wireless Credentials area, follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 Choose the network profile that enables the WPA Pre-shared key or WPA2 Pre-shared key.
Step 2 In the Key Type area, enter the appropriate key.
Step 3 Enter an ASCII string or hexadecimal digits in the Passphrase/Pre-shared key field.
Step 4 Click Save to make the change.
Wireless Encryption
If your wireless network uses WEP encryption, and you set the Authentication Mode as Open + WEP, you
must enter an ASCII or hexadecimal WEP Key.
The WEP Keys for the phone must match the WEP Keys assigned to the access point. Cisco IP Phone and
Cisco Aironet Access Points support both 40-bit and 128-bit encryption keys.
WEP Key Formats
You must use one of these formats when setting up a WEP key:
Hexadecimal
For hexadecimal keys, you use one of the following key sizes:
40-bit
You enter a 10-digit encryption key string that uses the hex digits (0-9 and A-F); for example,
ABCD123456.
128-bit
You enter a 26-digit encryption key string that uses the hex digits (0-9 and A-F); for example,
AB123456789CD01234567890EF.
ASCII
For ASCII keys, you enter a character string that uses 0-9, A-Z (upper and lower case), and all symbols,
with one of the following key sizes:
40-bit
You enter a 5-character string; for example, GREG5.
128-bit
You enter a 13-character string; for example, GREGSSECRET13.
Set Up WEP Keys
To set up WEP keys, follow these steps.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
96
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up PSK

Procedure
Step 1 Choose the network profile that uses Open+WEP or Shared+WEP.
Step 2 In the Key Type area, enter the appropriate key.
Step 3 In the Key Size area, choose one of these character string lengths:
• 40
• 128
Step 4 In the Encryption Key field, enter the appropriate key string based on the selected Key Type and Key Size.
See WEP Key Formats, on page 96.
Step 5 Click Save to make the change.
Export CA certificate from ACS using Microsoft Certificate Services
Export the root CA certificate from the ACS server. For additional information, see the CA or RADIUS
documentation.
Manufacturing Installed Certificate
Cisco has included a Manufacturing Installed Certificate (MIC) in the phone at the factory.
During EAP-TLS authentication, the ACS server needs to verify the trust of the phone and the phone needs
to verify the trust of the ACS server.
To verify the MIC, the Manufacturing Root Certificate and Manufacturing Certificate Authority (CA) Certificate
must be exported from a Cisco IP Phone and installed on the Cisco ACS server. These two certificates are
part of the trusted certificate chain used to verify the MIC by the Cisco ACS server.
To verify the Cisco ACS certificate, a trusted subordinate certificate (if any) and root certificate (created from
a CA) on the Cisco ACS server must be exported and installed on the phone. These certificates are part of the
trusted certificate chain used to verify the trust of the certificate from the ACS server.
User-Installed Certificate
To use a user-installed certificate, a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is generated, and sent to the CA for
approval. A user certificate can also be generated by the CA without a CSR.
During EAP-TLS authentication, the ACS server verifies the trust of the phone and the phone verifies the
trust of the ACS server.
To verify the authenticity of the user-installed certificate, you must install a trusted subordinate certificate (if
any) and root certificate from the CA that approved the user certificate on the Cisco ACS server. These
certificates are part of the trusted certificate chain used to verify the trust of the user installed certificate.
To verify the Cisco ACS certificate, you export a trusted subordinate certificate (if any) and root certificate
(created from a CA) on the Cisco ACS server and the exported certificates are installed on the phone. These
certificates are part of the trusted certificate chain used to verify the trust of the certificate from the ACS
server.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
97
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Export CA certificate from ACS using Microsoft Certificate Services

Install EAP-TLS Authentication Certificates
To install authentication certificates for EAP-TLS, perform the following steps.
Procedure
Step 1 From the phone web page, set the Cisco Unified Communications Manager date and time on the phone.
Step 2 If using the Manufacturing Installed Certificate (MIC):
a) From the phone web page, export the CA root certificate and manufacturing CA certificate.
b) From Internet Explorer, install certificates on the CiscoACS server and edit the trust list.
c) Import the root CA to the phone.
For more information, see:
• Export and Install Certificates on ACS, on page 99
• Export CA certificate from ISE using Microsoft Certificate Services, on page 99
Step 3 Using the ACS configuration tool, set up the user account.
For more information, see:
• Set Up ACS User Account and Install Certificate, on page 101
• User Guide for Cisco Secure ACS for Windows(http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/security/
secure-access-control-system/products-user-guide-list.html)
Set Date and Time
EAP-TLS uses certificate-based authentication that requires the internal clock on the Cisco IP Phone to be
set correctly. The date and time on the phone might change when it is registered to CiscoUnified
Communications Manager.
If a new server authentication certificate is being requested and the local time is behind the Greenwich Mean
Time (GMT), the authentication certificate validation might fail. Cisco recommends that you set the local
date and time ahead of the GMT.
Note
To set the phone to the correct local date and time, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Select Date & Time from the left navigation pane.
Step 2 If the setting in the Current Phone Date & Time field is different from the Local Date & Time field, click Set
Phone to Local Date & Time.
Step 3 Click Phone Restart, and then click OK.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
98
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Install EAP-TLS Authentication Certificates

Export and Install Certificates on ACS
To use the MIC, export the Manufacturing Root Certificate and Manufacturing CA Certificate and install it
on the Cisco ACS server.
To export the manufacturing root certificate and manufacturing CA certificate to the ACS server, follow these
steps.
Procedure
Step 1 From the phone web page, choose Certificates.
Step 2 Click Export next to the Manufacturing Root Certificate.
Step 3 Save the certificate and copy it to the ACS server.
Step 4 Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for the Manufacturing CA certificate.
Step 5 From the ACS Server System Configuration page, enter the file path for each certificate and install the
certificates.
For more information about using the ACS configuration tool, see the ACS online help or the
User Guide for Cisco Secure ACS for Windows(http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/security/
secure-access-control-system/products-user-guide-list.html).
Note
Step 6 Use the Edit the Certificate Trust List (CTL) page to add the certificates to be trusted by ACS.
ACS Certificate Export Methods
Depending on the type of certificate you export from the ACS, use one of the following methods:
• To export the CA certificate from the ACS server that signed the user-installed certificate or ACS
certificate, see Export CA certificate from ISE using Microsoft Certificate Services, on page 99.
• To export the CA certificate from the ACS server that uses a self-signed certificate, see Export CA
Certificate from ACS Using Internet Explorer, on page 100.
Export CA certificate from ISE using Microsoft Certificate Services
Use this method to export the CA certificate from the ISE server that signed the user-installed certificate or
ISE certificate.
To export the CA certificate using the Microsoft Certificate Services web page, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 From the Microsoft Certificate Services web page, select Download a CA certificate, certificate chain or
CRL.
Step 2 At the next page, highlight the current CA certificate in the text box, choose DER under Encoding Method,
then click Download CA certificate.
Step 3 Save the CA certificate.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
99
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Export and Install Certificates on ACS

Export CA Certificate from ACS Using Internet Explorer
Use this method to export the CA certificate from the ACS server that uses a self-signed certificate.
To export certificates from the ACS server using Internet Explorer, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 From Internet Explorer, choose Tools > Internet Options, then click the Content tab.
Step 2 Under Certificates, click Certificates, then click the Trusted Root Certification Authorities tab.
Step 3 Highlight the root certificate and click Export. The Certificate Export Wizard appears.
Step 4 Click Next.
Step 5 At the next window, select DER encoded binary X.509 (.CER), and click Next.
Step 6 Specify a name for the certificate and click Next.
Step 7 Save the CA certificate to be installed on the phone.
Request and Import User-Installed Certificate
To request and install the certificate on the phone, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 From the phone web page, choose the network profile using EAP-TLS, and select User Installed in the
EAP-TLS Certificate field.
Step 2 Click Certificates.
On the User Certificate Installation page, the Common Name field should match the user name in the ACS
server.
You can edit the Common Name field if you wish. Make sure that it matches the username in
the ACS server. See Set Up ACS User Account and Install Certificate, on page 101.
Note
Step 3 Enter the information to be displayed on the certificate, and click Submit to generate the Certificate Signing
Request (CSR).
Install Authentication Server Root Certificate
To install the Authentication Server Root Certificate on the phone, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Export the Authentication Server Root Certificate from the ACS. See ACS Certificate Export Methods, on
page 99.
Step 2 Go to the phone web page and choose Certificates.
Step 3 Click Import next to the Authentication Server Root certificate.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
100
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Export CA Certificate from ACS Using Internet Explorer

Step 4 Restart the phone.
Set Up ACS User Account and Install Certificate
To set up the user account name and install the MIC root certificate for the phone on the ACS, follow these
steps.
For more information about using the ACS configuration tool, see the ACS online help or the User Guide for
Cisco Secure ACS for Windows .
Note
Procedure
Step 1 From the ACS configuration tool User Setup page, create a phone user account name if it is not already set
up.
Typically, the user name includes the phone MAC address at the end. No password is necessary for EAP-TLS.
Make sure the user name matches the Common Name field in the User Certificate Installation
page. See Request and Import User-Installed Certificate, on page 100.
Note
Step 2 On the System Configuration page, in the EAP-TLS section, enable these fields:
• Allow EAP-TLS
• Certificate CN comparison
Step 3 On the ACS Certification Authority Setup page, add the Manufacturing Root Certificate and Manufacturing
CA Certificate to the ACS server.
Step 4 Enable both the Manufacturing Root Certificate and Manufacturing CA Certificate in the ACS Certificate
Trust List.
PEAP Setup
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) uses server-side public key certificates to authenticate
clients by creating an encrypted SSL/TLS tunnel between the client and the authentication server.
Cisco IP Phone 8865 only supports one server certificate which can be installed either via SCEP or the manual
install method but not both. The phone does not support the TFTP method of certificate installation.
The authentication server validation can be enabled by importing the authentication server certificate.
Note
Before You Begin
Before you configure PEAP authentication for the phone, make sure these CiscoSecure ACS requirements
are met:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
101
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up ACS User Account and Install Certificate

• The ACS root certificate must be installed.
• A certificate can also be installed to enable Server Validation for PEAP. But if a server certificate is
installed then server validation is enabled.
• The Allow EAP-MSCHAPv2 setting must be enabled.
• User account and password must be configured.
• For password authentication, you can use the local ACS database or an external one (such as Windows
or LDAP).
Enable PEAP Authentication
Procedure
Step 1 From the phone configuration web page, choose PEAP as the authentication mode.
Step 2 Enter a user name and password.
Wireless LAN Security
Cisco phones that support Wi-Fi have more security requirements and require extra configuration. These extra
steps include installing certificates and setting up security on the phones and on the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
For additional information, see Security Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Page
Cisco phones that support Wi-Fi have special web pages that are different from the pages for other phones.
You use these special web pages for phone security configuration when Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol
(SCEP) is not available. Use these pages to manually install security certificates on a phone, to download a
security certificate, or to manually configure the phone date and time.
These web pages also show the same information that you see on other phone web pages, including device
information, network setup, logs, and statistical information.
Related Topics
Cisco IP Phone Web Page, on page 222
Configure the Administration Page for Phone
The administration web page is enabled when the phone ships from the factory and the password is set to
Cisco. But if a phone registers with Cisco Unified Communications Manager, the administration web page
must be enabled and a new password configured.
Enable this web page and set the sign-in credentials before you use the web page for the first time after the
phone has registered.
Once enabled, the administration web page is accessible at HTTPS port 8443 (https://x.x.x.x:8443,
where x.x.x.x is a phone IP address).
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
102
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Enable PEAP Authentication

Before you begin
Decide on a password before you enable the administration web page. The password can be any combination
of letters or numbers, but it must be between 8 and 127 characters in length.
Your username is permanently set to admin.
Procedure
Step 1 From the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate your phone.
Step 3 In the Product Specific Configuration Layout section, set Web Admin to Enabled.
Step 4 In the Admin Password field, enter a password.
Step 5 Select Save and click OK.
Step 6 Select Apply Config and click OK.
Step 7 Restart the phone.
Access the Phone Administration Web Page
When you want to access the administration web pages, you need to specify the administration port.
Procedure
Step 1 Obtain the IP address of the phone:
• In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone, and locate the phone.
Phones that register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager display the IP address on the Find
and List Phones window and at the top of the Phone Configuration window.
• On the phone, press Applications , choose Phone Information, and then scroll to the IPv4 address
field.
Step 2 Open a web browser and enter the following URL, where IP_address is the IP address of the Cisco IP Phone:
https://<IP_address>:8443
Step 3 Enter the password in the Password field.
Step 4 Click Submit.
Install a User Certificate from the Phone Administration Web Page
You can manually install a user certificate on the phone if Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) is
not available.
The preinstalled Manufacturing Installed Certificate (MIC) can be used as the User Certificate for EAP-TLS.
After the User Certificate installs, you need to add it to the RADIUS server trust list.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
103
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Access the Phone Administration Web Page

Before you begin
Before you can install a User Certificate for a phone, you must have:
• A User Certificate saved on your PC. The certificate must be in PKCS #12 format.
• The certificate's extract password.
Procedure
Step 1 From the phone administration web page, select Certificates.
Step 2 Locate the User install field and click Install.
Step 3 Browse to the certificate on your PC.
Step 4 In the Extract password field, enter the certificate extract password.
Step 5 Click Upload.
Step 6 Restart the phone after the upload is complete.
Install an Authentication Server Certificate from the Phone Administration Web Page
You can manually install an Authentication Server certificate on the phone if Simple Certificate Enrollment
Protocol (SCEP) is not available.
The root CA certificate that issued the RADIUS server certificate must be installed for EAP-TLS.
Before you begin
Before you can install a certificate on a phone, you must have an Authentication Server Certificate saved on
your PC. The certificate must be encoded in PEM (Base-64) or DER.
Procedure
Step 1 From the phone administration web page, select Certificates.
Step 2 Locate the Authentication server CA (Admin webpage) field and click Install.
Step 3 Browse to the certificate on your PC.
Step 4 Click Upload.
Step 5 Restart the phone after the upload is complete.
If you are installing more than one certificate, install all of the certificates before restarting the phone.
Manually Remove a Security Certificate from the Phone Administration Web Page
You can manually remove a security certificate from a phone if Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP)
is not available.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
104
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Install an Authentication Server Certificate from the Phone Administration Web Page

Procedure
Step 1 From the phone administration web page, select Certificates.
Step 2 Locate the certificate on the Certificates page.
Step 3 Click Delete.
Step 4 Restart the phone after the deletion process completes.
Manually Set the Phone Date and Time
With certificate-based authentication, the phone must display the correct date and time. An authentication
server checks the phone date and time against the certificate expiry date. If the phone and the server dates and
times don't match, the phone stops working.
Use this procedure to manually set the date and time on the phone if the phone is not receiving the correct
information from your network.
Procedure
Step 1 From the phone administration web page, scroll to Date & Time.
Step 2 Perform one of the following options:
• Click Set Phone to Local Date & Time to synch the phone to a local server.
• In the Specify Date &Timefields, select the month, day, year, hour, minute, and second using the menus
and click Set Phone to Specific Date & Time.
SCEP Setup
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) is the standard for automatically provisioning and renewing
certificates. It avoids manual installation of certificates on your phones.
Configure the SCEP Product Specific Configuration Parameters
You must configure the following SCEP parameters on your phone web page
• RA IP address
• SHA-1 or SHA-256 fingerprint of the root CA certificate for the SCEP server
The Cisco IOS Registration Authority (RA) serves as a proxy to the SCEP server. The SCEP client on the
phone use the parameters that are downloaded from Cisco Unified Communication Manager. After you
configure the parameters, the phone sends a SCEP getcs request to the RA and the root CA certificate is
validated using the defined fingerprint.
Procedure
Step 1 From the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
105
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Manually Set the Phone Date and Time

Step 2 Locate the phone.
Step 3 Scroll to the Product Specific Configuration Layout area.
Step 4 Check the WLAN SCEP Server check box to activate the SCEP parameter.
Step 5 Check the WLAN Root CA Fingerprint (SHA256 or SHA1) check box to activate the SCEP QED parameter.
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol Server Support
If you are using a Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) server, the server can automatically maintain
your user and server certificates. On the SCEP server, configure the SCEP Registration Agent (RA) to:
• Act as a PKI trust point
• Act as a PKI RA
• Perform device authentication using a RADIUS server
For more information, see your SCEP server documentation.
802.1X Authentication
The Cisco IP Phones support 802.1X Authentication.
Cisco IP Phones and Cisco Catalyst switches traditionally use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) to identify
each other and determine parameters such as VLAN allocation and inline power requirements. CDP does not
identify locally attached workstations. Cisco IP Phones provide an EAPOL pass-through mechanism. This
mechanism allows a workstation attached to the Cisco IP Phone to pass EAPOL messages to the 802.1X
authenticator at the LAN switch. The pass-through mechanism ensures that the IP phone does not act as the
LAN switch to authenticate a data endpoint before accessing the network.
Cisco IP Phones also provide a proxy EAPOL Logoff mechanism. In the event that the locally attached PC
disconnects from the IP phone, the LAN switch does not see the physical link fail, because the link between
the LAN switch and the IP phone is maintained. To avoid compromising network integrity, the IP phone sends
an EAPOL-Logoff message to the switch on behalf of the downstream PC, which triggers the LAN switch to
clear the authentication entry for the downstream PC.
Support for 802.1X authentication requires several components:
• Cisco IP Phone: The phone initiates the request to access the network. Cisco IP Phones contain an 802.1X
supplicant. This supplicant allows network administrators to control the connectivity of IP phones to the
LAN switch ports. The current release of the phone 802.1X supplicant uses the EAP-FAST and EAP-TLS
options for network authentication.
• Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS) (or other third-party authentication server): The authentication
server and the phone must both be configured with a shared secret that authenticates the phone.
• Cisco Catalyst Switch (or other third-party switch): The switch must support 802.1X, so it can act as the
authenticator and pass the messages between the phone and the authentication server. After the exchange
completes, the switch grants or denies the phone access to the network.
You must perform the following actions to configure 802.1X.
• Configure the other components before you enable 802.1X Authentication on the phone.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
106
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol Server Support

• Configure PC Port: The 802.1X standard does not consider VLANs and thus recommends that only a
single device should be authenticated to a specific switch port. However, some switches (including Cisco
Catalyst switches) support multidomain authentication. The switch configuration determines whether
you can connect a PC to the PC port of the phone.
• Enabled: If you are using a switch that supports multidomain authentication, you can enable the PC
port and connect a PC to it. In this case, Cisco IP Phones support proxy EAPOL-Logoff to monitor
the authentication exchanges between the switch and the attached PC. For more information about
IEEE 802.1X support on the Cisco Catalyst switches, see the Cisco Catalyst switch configuration
guides at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps708/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
• Disabled: If the switch does not support multiple 802.1X-compliant devices on the same port, you
should disable the PC Port when 802.1X authentication is enabled. If you do not disable this port
and subsequently attempt to attach a PC to it, the switch denies network access to both the phone
and the PC.
• Configure Voice VLAN: Because the 802.1X standard does not account for VLANs, you should configure
this setting based on the switch support.
• Enabled: If you are using a switch that supports multidomain authentication, you can continue to
use the voice VLAN.
• Disabled: If the switch does not support multidomain authentication, disable the Voice VLAN and
consider assigning the port to the native VLAN.
Access 802.1X Authentication
You can access the 802.1X authentication settings by following these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Choose Admin settings > Security setup > 802.1X Authentication.
Step 3 Configure the Options as described in 802.1X Authentication Options, on page 107.
Step 4 To exit this menu, press Exit.
802.1X Authentication Options
The following table describes the 802.1X authentication options.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
107
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Access 802.1X Authentication

Table 29: 802.1X Authentication Settings
To changeDescriptionOption
See Set Device Authentication Field, on page
108.
Determines whether 802.1X authentication is enabled:
• Enabled: Phone uses 802.1X authentication to request
network access.
• Disabled: Default setting. The phone uses CDP to
acquire VLAN and network access.
Device Authentication
Display only. Cannot configure.State: Displays the state of 802.1x authentication:
• Disconnected: Indicates that 802.1x authentication is
not configured on the phone.
• Authenticated: Indicates that the phone is authenticated.
• Held: Indicates that the authentication process is in
progress.
Protocol: Displays the EAP method that is used for 802.1x
authentication (can be EAP-FAST or EAP-TLS).
Transaction Status
Set Device Authentication Field
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Choose Admin settings > Security setup > 802.1X Authentication
Step 3 Set the Device Authentication option:
• Yes
• No
Step 4 Press Apply.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
108
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Device Authentication Field

CHAPTER 8
Cisco IP Phone Customization
• Custom Phone Rings, on page 109
• Custom Background Images, on page 109
• Set Up Wideband Codec, on page 111
• Set Up Idle Display, on page 111
• Customize the Dial Tone, on page 112
Custom Phone Rings
The phone ships with three ring tones that are implemented in hardware: Sunshine, Chirp, Chirp1.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager also provides a default set of additional phone ring sounds that are
implemented in software as pulse code modulation (PCM) files. The PCM files, along with an XML file
(named Ringlist-wb.xml) that describes the ring list options that are available at your site, exist in the TFTP
directory on each Cisco Unified Communications Manager server.
All file names are case sensitive. If you use Ringlist-wb.xml for the file name, the phone will not apply your
changes.
Attention
For more information, see the "Custom Phone Rings and Backgrounds" chapter, Feature Configuration Guide
for Cisco Unified Communications Manager for Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 12.0(1) or
later.
Custom Background Images
You can customize a Cisco IP phone with a background image or wallpaper. Customized wallpapers are a
popular way to display corporate logos or images and many organizations use them to make their phones
stand out.
As of Firmware Release 12.7(1), you can customize your wallpaper on both your phones and your key
expansion modules. But you need one image for the phone and one image for the expansion module.
The phone analyzes the wallpaper colors, and changes the font colors and icons so you can read them. If your
wallpaper is dark, the phone changes the fonts and icons to white. If your wallpaper is light, the phone displays
the fonts and icons as black.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
109

It is best to choose a simple image such as a solid color or pattern for your background. Avoid high contrast
images.
You add customized wallpaper in one of two ways:
• Using the List file
• Using a Common Phone Profile
If you want the user to be able to select your image from various wallpapers available on the phone, then
modify the List file. But if you want to push the image to the phone, then create or modify an existing Common
Phone Profile.
Regardless of your approach, note the following:
• Your images must be in PNG format and the full sized image must be within the following dimensions:
• Thumbnail images—139 pixels (width) by 109 pixels (height)
• Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series—800 pixels by 480 pixels
• Cisco IP Phone 8851 and 8861 Key Expansion Module with a dual LCD screen—320 by 480 pixels
• Cisco IP Phone 8865 Key Expansion Module with a dual LCD screen—320 by 480 pixels
• Cisco IP Phone 8800 Key Expansion Module with a single LCD screen—272 by 480 pixels
• Upload the images, the thumbnails, and List file to your TFTP server. The directory is:
• Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series—Desktops/800x480x24
• Cisco IP Phone 8851 and 8861 Key Expansion Module with a dual LCD
screen—Desktops/320x480x24
• Cisco IP Phone 8865 Key Expansion Module with a dual LCD screen—Desktops/320x480x24
• Cisco IP Phone 8800 Key Expansion Module with a single LCD screen—Desktops/272x480x24
After the upload is done, you restart the TFTP server.
• If you don't want the user selecting their own wallpaper, then disable Enable End User Access to Phone
Background Image Setting. Save and apply the phone profile. Restart the phones so your changes take
effect.
You can apply the phone background images in bulk with the Common Phone
Profile. But bulk configuration requires you to disable Enable End User Access
to Phone Background Image Setting. For more information on bulk
configuration of background images, refer to the “Configure the Common Phone
Profile” chapter of Customized Wallpapers Best Practices Cisco IP Phone 8800
Series.)
Note
For more information on customizing wallpaper, refer to the following documentation:
• Customized Wallpapers Best Practices Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series).
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
110
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Custom Background Images

• "Custom Phone Rings and Backgrounds" chapter, Feature Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified
Communications Manager for Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 12.0(1) or later.
• “Settings” chapter in the Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series User Guide.
Set Up Wideband Codec
By default, the G.722 codec is enabled for the Cisco IP Phone. If Cisco Unified Communications Manager
is configured to use G.722 and if the far endpoint supports G.722, the call connects using the G.722 codec in
place of G.711.
This situation occurs regardless of whether the user has enabled a wideband headset or wideband handset,
but if either the headset or handset is enabled, the user may notice greater audio sensitivity during the call.
Greater sensitivity means improved audio clarity but also means that the far endpoint can hear more background
noise: noise such as rustling papers or nearby conversations. Even without a wideband headset or handset,
some users may prefer the additional sensitivity of G.722 distracting. Other users may prefer the additional
sensitivity of G.722.
The Advertise G.722 and iSAC Codec service parameter affects whether wideband support exists for all
devices that register with this Cisco Unified Communications Manager server or for a specific phone, depending
on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration window where the parameter is configured.
Procedure
Step 1 To configure wideband support for all devices:
a) From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose System> Enterprise Parameters
b) Set the Advertise G.722 and iSAC Codec field
The default value of this enterprise parameter is True, which means that all Cisco IP Phone Models that
register to this Cisco Unified Communications Manager advertise G.722 to Cisco Unified Communications
Manager. If each endpoint in the attempted call supports G.722 in the capabilities set, Cisco Unified
Communications Manager chooses that codec for the call whenever possible.
Step 2 To configure wideband support for a specific device:
a) From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Phone.
b) Set the Advertise G.722 and iSAC Codec parameter in the Product Specific Configuration area.
The default value of this product-specific parameter is to use the value that the enterprise parameter
specifies. If you want to override this on a per-phone basis, choose Enabled or Disabled
Set Up Idle Display
You can specify an idle display (text only; text file size should not exceed 1M bytes) that appears on the phone
screen. The idle display is an XML service that the phone invokes when the phone is idle (not in use) for a
designated period and no feature menu is open.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
111
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Wideband Codec

For detailed instructions about creating and displaying the idle display, see Creating Idle URL Graphics on
Cisco IP Phone at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/products_tech_note09186a00801c0764.shtml
In addition, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release for
the following information:
• Specifying the URL of the idle display XML service:
• For a single phone: Idle field in the Phone Configuration window in Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Administration.
• For multiple phones simultaneously: URL Idle field in the Enterprise Parameters Configuration
window, or the Idle field in the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT)
• Specifying the length of time that the phone is not used before the idle display XML service is invoked:
• For a single phone: Idle Timer field in the Phone configuration window in Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Administration.
• For multiple phones simultaneously: URL Idle Time field in the Enterprise Parameters Configuration
window, or the Idle Timer field in the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT)
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone
Step 2 In the Idle field, enter the URL to the idle display XML Service.
Step 3 In the Idle Timer field, enter the time that the idle phone waits before displaying the idle display XML service.
Step 4 Select Save.
Customize the Dial Tone
You can set up your phones so that users hear different dial tones for internal and external calls. Depending
upon your needs, you can choose from three dial tone options:
• Default: A different dial tone for inside and outside calls.
• Inside: The inside dial tone is used for all calls.
• Outside: The outside dial tone is used for all calls.
Always Use Dial Tone is a required field on Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select System > Service Parameters.
Step 2 Select the appropriate Server.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
112
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Customize the Dial Tone

Step 3 Select Cisco CallManager as the Service.
Step 4 Scroll to the Clusterwide Parameters pane.
Step 5 Set Always Use Dial Tone to one of the following:
• Outside
• Inside
• Default
Step 6 Select Save.
Step 7 Restart your phones.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
113
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Customize the Dial Tone

Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
114
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Customize the Dial Tone

CHAPTER 9
Phone Features and Setup
• Phone Features and Setup Overview, on page 115
• Cisco IP Phone User Support, on page 115
• Telephone Features, on page 116
• Feature Buttons and Softkeys, on page 133
• Phone Feature Configuration, on page 135
• Set Up Softkey Template, on page 183
• Phone Button Templates, on page 185
• VPN Configuration, on page 188
• Set Up Additional Line Keys, on page 189
• Set Up TLS Resumption Timer, on page 192
• Enable Intelligent Proximity, on page 193
• Video Transmit Resolution Setup, on page 193
• Headset Management on Older Versions of Cisco Unified Communications Manager, on page 195
Phone Features and Setup Overview
After you install Cisco IP Phones in your network, configure their network settings, and add them to Cisco
Unified Communications Manager, you must use the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration
application to configure telephony features, optionally modify phone templates, set up services, and assign
users.
You can modify additional settings for the Cisco IP Phone from Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration. Use this web-based application to set up phone registration criteria and calling search spaces,
to configure corporate directories and services, and to modify phone button templates, among other tasks.
When adding features to the phone line keys, you are limited by the number of line keys available. You cannot
add more features than the number of line keys on your phone.
Cisco IP Phone User Support
If you are a system administrator, you are likely the primary source of information for Cisco IP Phone users
in your network or company. It is important to provide current and thorough information to end users.
To successfully use some of the features on the Cisco IP Phone (including Services and voice message system
options), users must receive information from you or from your network team or must be able to contact you
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
115

for assistance. Make sure to provide users with the names of people to contact for assistance and with
instructions for contacting those people.
We recommend that you create a web page on your internal support site that provides end users with important
information about their Cisco IP Phones.
Consider including the following types of information on this site:
• User guides for all Cisco IP Phone models that you support
• Information on how to access the Cisco Unified Communications Self Care Portal
• List of features supported
• User guide or quick reference for your voicemail system
Telephone Features
After you add Cisco IP Phones to Cisco Unified Communications Manager, you can add functionality to the
phones. The following table includes a list of supported telephony features, many of which you can configure
by using Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration.
For information about using most of these features on the phone, see Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series User Guide.
See Feature Buttons and Softkeys, on page 133 for a list of features that can be configured as programmable
buttons and dedicated softkeys and feature buttons.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration also provides several service parameters that you
can use to configure various telephony functions. For more information on accessing and configuring service
parameters, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
For more information on the functions of a service, select the name of the parameter or the question mark
(?) help button in the Product Specific Configuration window.
Note
For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
Description and more informationFeature
Allows users to speed dial a phone number by entering an assigned index code (1-199)
on the phone keypad.
You can use Abbreviated Dialing while on-hook or off-hook.
Note
Users assign index codes from the Self Care Portal.
Abbreviated Dialing
Provides different options to control the incoming call alerts. You can disable or enable
the call alert. You can also activate or deactivate the caller ID display.
See Actionable Incoming Call Alert, Product Specific Configuration, on page 136.
Actionable Incoming Call Alert
Enhances security by supporting TLS 1.2 and new ciphers. For more information, see
Supported Security Features, on page 82.
AES 256 Encryption Support for Phones
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
116
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features
Description and more informationFeature
Allows an agent to create and update a prerecorded greeting that plays at the beginning
of a customer call, before the agent begins the conversation with the caller. The agent
can prerecord a single greeting or multiple ones as needed.
See Enable Agent Greeting, on page 163.
Agent Greeting
Always keeps the DECT connection between the headset and base even when the user
is not on a call or playing music.
This feature is supported on Cisco Headset 500 Series.
See Headset template management in Call Manager for more information.
Always On Mode
Allows users to pick up a call on any line in their call pickup group, regardless of how
the call was routed to the phone.
See call pickup in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications
Manager release.
Any Call Pickup
Convert numbers for shared mobile contacts to network dialable numbers.
See Application Dial Rules, on page 75.
Application Dial Rules
Enables users to park a call by pressing only one button using the Direct Park feature.
Administrators must configure a Busy Lamp Field (BLF) Assisted Directed Call Park
button. When users press an idle BLF Assisted Directed Call Park button for an active
call, the active call is parked at the Direct Park slot associated with the Assisted Directed
Call Park button.
See assisted directed call park in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Assisted Directed Call Park
A stutter tone from the handset, headset, or speakerphone indicates that a user has one
or more new voice messages on a line.
The stutter tone is line-specific. You hear it only when using the line with
the waiting messages.
Note
Audible Message Waiting Indicator
(AMWI)
Connects incoming calls automatically after a ring or two.
Auto Answer works with either the speakerphone or the headset.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Auto Answer
Synchronizes ports to the lowest speed between ports of a phone to eliminate packet loss.
See Automatic Port Synchronization, Product Specific Configuration, on page 136.
Automatic Port Synchronization
Allows a user to use one-touch pickup functionality for call pickup features.
See call pickup in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications
Manager release.
Auto Pickup
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
117
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Enables a user to barge into a call by establishing the three-way conference call using
the built-in conference bridge of the target phone.
See “cBarge” in this table.
Barge
Prevents users from transferring an external call to another external number.
See external call transfer information in the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
Block External to External Transfer
Enables the user to pair multiple devices to the phone. The user can then connect a mobile
device using Bluetooth and a Bluetooth headset at the same time.
Cisco IP Phone 8851NR does not support Bluetooth.
Bluetooth Multiconnection
The mute status between the IP Phone and Cisco headset is synchronized automatically
during a call.
Supported on the Cisco IP Phones 8845, 8851, 8861, and 8865, connected with Cisco
Headset 730 or Cisco Head 720 Series.
Bluetooth Mute Sync for Cisco Headset
700 Series
Allows a user to monitor the call state of a directory number associated with a speed-dial
button on the phone.
See presence information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Busy Lamp Field (BLF)
Provides enhancements to BLF speed dial. Allows you to configure a Directory Number
(DN) that a user can monitor for incoming calls. When the DN receives an incoming
call, the system alerts the monitoring user, who can then pick up the call.
See call pickup information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Busy Lamp Field (BLF) Pickup
Provides users with an audio and visual alert on the phone when a busy or unavailable
party becomes available.
See call back information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Call Back
Determines the information that will display for calling or connected lines, depending
on the parties who are involved in the call.
See routing plans and call display restriction information in the documentation for your
particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Call Display Restrictions
Allows users to redirect incoming calls to another number. Call Forward options include
Call Forward All, Call Forward Busy, Call Forward No Answer, and Call Forward No
Coverage.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release and Customize the Self Care Portal Display, on page
78.
Call Forward
Detects and prevents Call Forward All loops. When a Call Forward All loop is detected,
the Call Forward All configuration is ignored and the call rings through.
Call Forward All Loop Breakout
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
118
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Detects and prevents Call Forward All loops. When a Call Forward All loop is detected,
the Call Forward All configuration is ignored and the call rings through.
Call Forward All Loop Prevention
Prevents a user from configuring a Call Forward All destination directly on the phone
that creates a Call Forward All loop or that creates a Call Forward All chain with more
hops than the existing Forward Maximum Hop Count service parameter allows.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Call Forward Configurable Display
Allows you to override Call Forward All (CFA) in cases where the CFA target places a
call to the CFA initiator. This feature allows the CFA target to reach the CFA initiator
for important calls. The override works whether the CFA target phone number is internal
or external.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Call Forward Destination Override
Allows you to configure the information that the user sees when receiving a forwarded
call.
See Set Up Call Forward Notification, on page 164.
Call Forward Notification
Allows you to view shared line activity in the phone Call History. This feature will:
• Log missed calls for a shared line
• Log all answered and placed calls for a shared line
Call History for Shared Line
Allows users to park (temporarily store) a call and then retrieve the call by using another
phone in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager system.
You can configure the field Dedicate one line for call park in the Product Specific
Configuration Layout pane to park the call to the original line or a different line.
When the field is enabled, the parked call remains on the user's line and they can use the
Resume softkey to pick up the call. The user sees the extension number for the parked
call on the phone display.
When the field is disabled, the parked call transfers to the call park line. The user's line
returns to the idle state and they see the call park extension in a pop-up window. The
user dials the extension to pick up the call.
See call park information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Call Park
Allows users to redirect a call that is ringing on another phone within their pickup group
to their phone.
You can configure an audio and visual alert for the primary line on the phone. This alert
notifies the users that a call is ringing in their pickup group.
See call pickup information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Call Pickup
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
119
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Allows a supervisor to record an active call. The user might hear a recording audible
alert tone during a call when it is being recorded.
When a call is secured, the security status of the call is displayed as a lock icon on Cisco
IP Phones. The connected parties might also hear an audible alert tone that indicates the
call is secured and is being recorded.
When an active call is being monitored or recorded, the user can receive or
place intercom calls; however, if the user places an intercom call, the active
call is put on hold, which causes the recording session to terminate and the
monitoring session to suspend. To resume the monitoring session, the party
whose call is being monitored must resume the call.
Note
See monitoring and recording information in the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
Call Recording
Indicates (and allows users to answer) an incoming call that rings while on another call.
Incoming call information appears on the phone display.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Call Waiting
Provides Call Waiting users with the option of an audible ring instead of the standard
beep.
Options are Ring and Ring Once.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Call Waiting Ring
Caller identification such as a phone number, name, or other descriptive text appear on
the phone display.
See routing plan, call display restrictions, and directory number information in the
documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Caller ID
Allows a user to block their phone number or email address from phones that have caller
identification enabled.
See routing plan and directory number information in the documentation for your
particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Caller ID Blocking
Calling party normalization presents phone calls to the user with a dialable phone number.
Any escape codes are added to the number so that the user can easily connect to the caller
again. The dialable number is saved in the call history and can be saved in the Personal
Address Book.
Calling Party Normalization
Establishes communication between the Cisco Unified Video Advantage (CUVA) and
the Cisco IP phones to support video on the PC even if the IP phone does not have video
capability.
CAST for SIP
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
120
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Allows a user to join a nonprivate call on a shared phone line. cBarge adds a user to a
call and converts it into a conference, allowing the user and other parties to access
conference features. The conference call is created using the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager conference bridge functionality.
You must enable both the softkey and the conference bridge functionality for cBarge to
function correctly.
In Firmware Release 10.2(2) and later, the cBarge functionality is accessed using the
Barge softkey.
For more information, refer to the "Barge" chapter, Feature Configuration Guide for
Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
cBarge
Allows a user to charge a mobile device by connecting it to the USB port of the Cisco
IP Phone.
See Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series User Guide.
Charge a Mobile Device
Allows users access to their Cisco IP Phone configuration such as line appearances,
services, and speed dials from a shared Cisco IP Phone.
Cisco Extension Mobility is useful if people work from a variety of locations within your
company or if they share a workspace with coworkers.
Cisco Extension Mobility
Enables a user configured in one cluster to log into a Cisco IP Phone in another cluster.
Users from a home cluster log into a Cisco IP Phone at a visiting cluster.
Configure Cisco Extension Mobility on Cisco IP Phones before you
configure EMCC.
Note
Cisco Extension Mobility Cross Cluster
(EMCC)
Provides call routing and other call management features to help managers and assistants
handle phone calls more effectively.
See Set up Cisco IP Manager Assistant, on page 178.
Cisco IP Manager Assistant (IPMA)
Provides additional keys by adding an expansion module to the phone.
For additional information, see Cisco IP Phone 7800 and 8800 Series Accessories Guide
for Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Key Expansion
Module
Cisco IP Phone 8851/8861 Key Expansion
Module
Cisco IP Phone 8865 Key Expansion
Module
Provides support for the Cisco IP Phone 8811.Cisco IP Phone 8811 Support
Provides support for the Cisco IP Phone 8851NRCisco IP Phone 8851NR Support
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
121
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
The Cisco Unified Communication Manager Express uses a special tag in the information
sent to the phone to identify itself. This tag enables the phone to provide services to the
user that the switch supports.
See:
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express System Administrator Guide
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express Interaction, on page 20
Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Express (Unified CME) Version
Negotiation
Allows users to make video calls by using a Cisco IP Phone, a personal computer, and
a video camera.
Configure the Video Capabilities parameter in the Product Specific
Configuration Layout section in Phone Configuration.
Note
See the Cisco Unified Video Advantage documentation.
Cisco Unified Video Advantage (CUVA)
Allows users to make calls from web and desktop applications.Cisco WebDialer
Supports ringtones that are embedded in the phone firmware or downloaded from the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The feature makes the available ringtones
common with other Cisco IP Phones.
See Custom Phone Rings, on page 109.
Classic Ringtone
Allows a user to talk simultaneously with multiple parties by calling each participant
individually. Conference features include Conference and Meet Me.
Allows a noninitiator in a standard (adhoc) conference to add or remove participants;
also allows any conference participant to join together two standard conferences on the
same line.
The Advance Adhoc Conference service parameter, disabled by default in Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Administration, allows you to enable these features.
Be sure to inform your users if these features are activated.
Note
Conference
Provides a method to control EEE functions on personal computer port and switch port
by enabling or disabling EEE. The feature controls both type of ports individually. The
default value is Enabled.
See Set Up Energy Efficient Ethernet for Switch and PC Port, on page 166.
Configurable Energy Efficient Ethernet
(EEE) for PC and Switch Port
Allows users to increase or decrease the maximum number of characters the IP phone
displays for Call History and Call Screen by changing the font size.
A smaller font increases the maximum number of displayed characters, and a larger font
decreases the maximum number of displayed characters.
Configurable Font Size
A computer telephony integration (CTI) route point can designate a virtual device to
receive multiple, simultaneous calls for application-controlled redirection.
CTI Applications
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
122
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features
Description and more informationFeature
Allows a user to transfer a ringing, connected, or held call directly to a voice-messaging
system. When a call is declined, the line becomes available to make or receive new calls.
See immediate divert information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Decline All
Provides end users with the ability to record their telephone calls via a softkey.
In addition administrators may continue to record telephone calls via the CTI User
Interface.
See monitoring and recording information in the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
Device Invoked Recording
Allows a user to transfer an active call to an available directed call park number that the
user dials or speed dials. A Call Park BLF button indicates whether a directed call park
number is occupied and provides speed-dial access to the directed call park number.
If you implement Directed Call Park, avoid configuring the Park softkey.
This prevents users from confusing the two Call Park features.
Note
See call park information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Directed Call Park
Displays the battery and signal strength of the mobile phone on the IP Phone when the
mobile phone is connected to the IP Phone using Bluetooth.
Cisco IP Phone 8851NR does not support Bluetooth.
Display Battery Strength and Signal
Strength Icons
Users can customize how their phone indicates an incoming call and a new voice mail
message.
See call pickup information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Distinctive Ring
When DND is turned on, either no audible rings occur during the ringing-in state of a
call, or no audible or visual notifications of any type occur.
When enabled, the phone header turns red and Do not disturb is displayed on the phone.
If multilevel precedence and preemption (MLPP) is configured and the user receives a
precedence call, the phone will ring with a special ringtone.
See Set Up Do Not Disturb, on page 162.
Do Not Disturb (DND)
Allows a user to set up the call behavior when the headset is lift from the base or is put
down on the base.
This feature is supported on Cisco Headset 500 Series.
See Headset template management in Call Manager for more information.
Dock Event
Allows the administrator to control the Join Across Lines (JAL) and Direct Transfer
Across Lines (TAL) features.
See Join and Direct Transfer Policy, Product Specific Configuration, on page 136.
Enable/Disable JAL/TAL
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
123
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Enables an IP Phone to sleep (power down) and wake (power up) at predetermined times,
to promote energy savings.
See Schedule EnergyWise on Cisco IP Phone, on page 158.
EnergyWise
Enable Enhanced Line Mode to use the buttons on both sides of the phone screen as line
keys.
See Set Up Additional Line Keys, on page 189
Enhanced Line Mode
Improves the Secure Extension Mobility Cross Cluster (EMCC) feature by preserving
the network and security configurations on the login phone. By so doing, security policies
are maintained, network bandwidth is preserved and network failure is avoided within
the visiting cluster (VC).
Enhanced Secure Extension Mobility
Cross Cluster (EMCC)
Allows a user to enter a Fast Dial code to place a call. Fast Dial codes can be assigned
to phone numbers or Personal Address Book entries. See “Services” in this table.
See Modify Phone Button Template for PAB or Fast Dial, on page 188.
Fast Dial Service
Allows a user to answer a call that is ringing on a directory number in another group.
See call pickup information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Group Call Pickup
Allows an administrator to set the sidetone level of a wired headset.Headset Sidetone Control
Limits the amount of time that a call can be on hold before reverting back to the phone
that put the call on hold and alerting the user.
Reverting calls are distinguished from incoming calls by a single ring (or beep, depending
on the new call indicator setting for the line). This notification repeats at intervals if not
resumed.
A call that triggers Hold Reversion also displays an animated icon in the call bubble.
You can configure call focus priority to favor incoming or reverting calls.
Hold Reversion
Enables phones with a shared line to distinguish between the local and remote lines that
placed a call on hold.
Hold Status
Allows the user to move a connected call from an active state to a held state.
• No configuration required unless you want to use Music On Hold. See “Music On
Hold” in this table for information.
• See “Hold Reversion” in this table.
Hold/Resume
Enhances the file download process to the phone to use HTTP by default. If the HTTP
download fails, the phone reverts to using the TFTP download.
HTTP Download
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
124
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Provides load sharing for calls to a main directory number. A hunt group contains a series
of directory numbers that can answer the incoming calls. When the first directory number
in the hunt group is busy, the system hunts in a predetermined sequence for the next
available directory number in the group and directs the call to that phone.
You can have Caller ID (If the Caller ID is configured), Directory Number and Hunt
group Pilot Number display on the Incoming Call Alert for the hunt group call. The
hunt group number is displayed after the label "Hunt Group.
See hunt group and routing plans information in the documentation for your particular
Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Hunt Group
Allows you to set the length of time that an incoming call toast (notification) appears on
the phone screen.
See Incoming Call Toast Timer, Product Specific Configuration, on page 136.
Incoming Call Toast Timer
Enables users to pair a mobile device with the phone using Bluetooth and use the phone
to place and receive mobile calls,
See Enable Intelligent Proximity, on page 193.
Cisco IP Phone 8811, 8841, and 8851NR do not support Bluetooth or Intelligent
Proximity.
Intelligent Proximity
Allows users to place and receive intercom calls using programmable phone buttons.
You can configure intercom line buttons to:
• Directly dial a specific intercom extension.
• Initiate an intercom call and then prompt the user to enter a valid intercom number.
If your user logs into the same phone on a daily basis using their Cisco
Extension Mobility profile, assign the phone button template that contains
intercom information to their profile, and assign the phone as the default
intercom device for the intercom line.
Note
Intercom
Provides support for expanded IP addressing on Cisco IP Phones. IPv4 and IPv6
configuration is recommended and fully supported. Certain features are not supported
in a standalone configuration. Only IPv6 address are assigned.
See Configure Network Settings, on page 55.
IPv6-only Support
The Jitter Buffer feature handles jitter from 10 milliseconds (ms) to 1000 ms for audio
streams.
It runs in an adaptive mode and it dynamically adjusts to the amount of jitter.
Jitter Buffer
Allows users to combine two calls that are on one line to create a conference call and
remain on the call.
Join
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
125
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Allows the user to see the Line Status availability status of monitored line numbers in
the Call History list. The Line Status states are
• Offline
• Available
• In use
• Do not disturb
See Enable BLF for Call Lists, on page 165.
Line Status for Call Lists
Enables the display of the status of a contact in the Corporate Directory.
• Offline
• Available
• In use
• Do not disturb
See Enable BLF for Call Lists, on page 165.
Line Status in Corporate Directory
Sets a text label for a phone line instead of the directory number.
See Set the Label for a Line, on page 174.
Line Text Label
Allows users to log out of a hunt group and temporarily block calls from ringing their
phone when they are not available to take calls. Logging out of hunt groups does not
prevent nonhunt group calls from ringing their phone.
See routing plan information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Log out of hunt groups
Allows users to notify the system administrator about suspicious calls that are received.Malicious Caller Identification (MCID)
Allows a user to host a Meet Me conference in which other participants call a
predetermined number at a scheduled time.
Meet Me Conference
Defines directory numbers for message waiting on and off indicators. A directly-connected
voice-message system uses the specified directory number to set or to clear a message
waiting indication for a particular Cisco IP Phone.
See message waiting and voice mail information in the documentation for your particular
Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Message Waiting
A light on the handset that indicates that a user has one or more new voice messages.
See message waiting and voice mail information in the documentation for your particular
Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Message Waiting Indicator
Sets a minimum ringer volume level for an IP phone.Minimum Ring Volume
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
126
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Allows a user to specify whether missed calls will be logged in the missed calls directory
for a given line appearance.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Missed Call Logging
Enables users to manage business calls using a single phone number and pick up
in-progress calls on the desk phone and a remote device such as a mobile phone. Users
can restrict the group of callers according to phone number and time of day.
See Cisco Unified Mobility information in the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
Mobile Connect
Allows remote workers to easily and securely connect into the corporate network without
using a virtual private network (VPN) client tunnel.
See Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway, on page 167
Mobile and Remote Access Through
Expressway
Extends Mobile Connect capabilities by allowing users to access an interactive voice
response (IVR) system to originate a call from a remote device such as a cellular phone.
See Cisco Unified Mobility in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Mobile Voice Access
Allows a supervisor to silently monitor an active call. The supervisor cannot be heard
by either party on the call. The user might hear a monitoring audible alert tone during a
call when it is being monitored.
When a call is secured, the security status of the call is displayed as a lock icon on Cisco
IP Phones. The connected parties might also hear an audible alert tone that indicates the
call is secured and is being monitored.
When an active call is being monitored or recorded, the use can receive or
place intercom calls; however, if the user place an intercom call, the active
call will be put on hold, which causes the recording session to terminate
and the monitoring session to suspend. To resume the monitoring session,
the party whose call is being monitored must resume the call.
Note
Monitoring and Recording
Enables the user to make and receive urgent or critical calls in some specialized
environments, such as military or government offices.
See Multilevel Precedence and Preemption, on page 183.
Multilevel Precedence and Preemption
Each line can support multiple calls. By default, the phone supports two active calls per
line, and a maximum of six active calls per line. Only one call can be connected at any
time; other calls are automatically placed on hold.
The system allows you to configure maximum calls/busy trigger not more than 6/6. Any
configuration more than 6/6 is not officially supported.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Multiple Calls Per Line Appearance
Plays music while callers are on hold.Music On Hold
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
127
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Mutes the handset or headset microphone.Mute
Makes it easier for end users to identify transferred calls by displaying the original caller’s
phone number. The call appears as an Alert Call followed by the caller’s telephone
number.
No Alert Name
Allows a user to dial a number without going off hook. The user can then either pick up
the handset or press Dial.
Onhook Dialing
Allows a user to answer a call ringing on a phone in another group that is associated with
the user's group.
See call pickup information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Other Group Pickup
This feature enhances the phone interface for the Extension Mobility user by providing
friendly messages.
Phone Display Message for Extension
Mobility Users
Enables the phone to send an alarm to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager when
the Trust List (TL) is updated.
See Supported Security Features, on page 82.
Phone Trust List Notification in Cisco
Unified Communications Manager
The PLK Support for Queue Statistics feature enables the users to query the call queue
statistics for hunt pilots and the information appears on phone screen.
PLK Support for Queue Statistics
Allows the user to dial E.164 numbers prefixed with a plus (+) sign.
To dial the + sign, the user needs to press and hold the star (*) key for at least 1 second.
This applies to dialing the first digit for an on-hook (including edit mode) or off-hook
call.
Plus Dialing
Allows the phone to negotiate power using Link Level Endpoint Discovery Protocol
(LLDP) and Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP).
See Power Negotiation, Product Specific Configuration, on page 136.
Power Negotiation over LLDP
Simplifies making a call. The Recents list changes to displays only phone numbers similar
to the number being dialed.
Predictive Dialing is enabled when Enhanced Line mode is enabled. Simplified New
Call UI must be disabled for Predictive Dialing to function.
Predictive Dialing
Prevents users who share a line from adding themselves to a call and from viewing
information on their phone display about the call of the other user.
See barge and privacy information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Privacy
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
128
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager administrator can configure a phone number
that the Cisco IP Phone dials as soon as the handset goes off hook. This can be useful
for phones that are designated for calling emergency or “hotline” numbers.
The administrator can configure a delay of up to 15-seconds. This allows the user time
to place a call before the phone defaults to the hotline number. The timer is configurable
through the parameter Off Hook To First Digit Timer under Device > DeviceSettings >
SIP Profile.
For more information, refer to Feature Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
Private Line Automated Ringdown
(PLAR)
Submit phone logs or report problems to an administrator.
See Problem Report Tool, on page 172.
Problem Report Tool (PRT)
You can assign features, such as New Call, Call Back, and Forward All to line buttons.
See phone button template information in the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
Programmable Feature Buttons
Allows users to submit information about problem phone calls by pressing a button. QRT
can be configured for either of two user modes, depending upon the amount of user
interaction desired with QRT.
Quality Reporting Tool (QRT)
Allows users to see the 150 most recent individual calls and call groups. You can see the
recently dialed numbers, missed calls, and delete a call record.
Recents
Allows users to call the most recently dialed phone number by pressing a button or the
Redial softkey.
Redial
Allows you to configure the speed and duplex function of the phone Ethernet ports
remotely by using Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration. This enhances
the performance for large deployments with specific port settings.
If the ports are configured for Remote Port Configuration in Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, the data cannot be changed on the phone.
Note
See Remote Port Configuration, Product Specific Configuration, on page 136.
Remote Port Configuration
Reroutes a direct call to a user's mobile phone to the enterprise number (desk phone).
For an incoming call to remote destination (mobile phone), only remote destination rings;
desk phone does not ring. When the call is answered on their mobile phone, the desk
phone displays a Remote In Use message. During these calls, users can make use of
various features of their mobile phone.
See the Cisco Unified Mobility information in the documentation for your particular
Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Reroute Direct Calls to Remote
Destination to Enterprise Number
Improves the End Call response time by removing the Call ended message display
on the phone screen.
Remove 'Call Ended' Prompt Timer
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
129
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Identifies ring type used for a line when a phone has another active call.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release and Custom Phone Rings, on page 109.
Ringtone Setting
Ensures that held calls are not dropped by the gateway. The gateway checks the status
of the RTCP port to determine if a call is active or not. By keeping the phone port open,
the gateway will not end held calls.
RTCP Hold For SIP
Allows secure phones to place conference calls using a secured conference bridge. As
new participants are added by using Confrn, Join, or Barge softkeys or MeetMe
conferencing, the secure call icon displays as long as all participants use secure phones.
The Conference List displays the security level of each conference participant. Initiators
can remove nonsecure participants from the Conference List. Noninitiators can add or
remove conference participants if the Advanced Adhoc Conference Enabled parameter
is set.
See conference bridge and security information in the documentation for your particular
Cisco Unified Communications Manager release and Supported Security Features, on
page 82.
Secure Conference
Improves the EMCC feature by providing enhanced security for a user logging into their
phone from a remote office.
Secure EMCC
Allows you to use the Cisco IP Phone Services Configuration menu in Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Administration to define and maintain the list of phone services
to which users can subscribe.
See services information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Services
Allows users to access services from a programmable button rather than by using the
Services menu on a phone.
See services information the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Services URL button
The phones can display both the calling ID and calling number for incoming calls. The
IP phone LCD display size limits the length of the calling ID and the calling number that
display.
The Show Calling ID and Calling Number feature applies to the incoming call alert only
and does not change the function of the Call Forward and Hunt Group features.
See “Caller ID” in this table.
Show Calling ID and Calling Number
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
130
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Enables users to sign into Extension Mobility with their Cisco headsets.
When the phone is in MRA mode, the user can use the headset to sign into the phone.
This feature requires Cisco Unified Communications Manager(UCM) Release 11.5(1)SU8,
11.5(1)SU.9, 12.5(1)SU3 or later.
For more information, see Feature Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, Release 11.5(1)SU8 or later, or Release 12.5(1)SU3 or later.
With Cisco Headset 730, user can also sign into Extension Mobility with the headset
USB adapter. The required version of the headset is 1-8-0-213 or later, and the USB
adapter is 1-3-20 or later.
Simplify Extension Mobility Login with
Cisco Headsets
Enables an Android or iOS tablet user to pair the tablet to the phone using Bluetooth and
then use the phone for the audio part of a call on the tablet.
See Enable Intelligent Proximity, on page 193.
Cisco IP Phone 8851NR does not support Bluetooth.
Simplified Tablet Support
Dials a specified number that has been previously stored.Speed Dial
Allows you to enable or disable the SSH Access setting using Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Administration. Enabling the SSH server allows the phone
to accept the SSH connections. Disabling the SSH server functionality of the phone
blocks the SSH access to the phone.
See SSH Access, Product Specific Configuration, on page 136.
SSH Access
Restricts access to specified telephony features by time period.
See time period and time-of-day routing information in the documentation for your
particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Time-of-Day Routing
Updates the Cisco IP Phone with time zone changes.
See date and time information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Time Zone Update
Allows users to redirect connected calls from their phones to another number.Transfer
Transfer: The first invocation of Transfer will always initiate a new call by using the
same directory number, after putting the active call on hold.
The user can directly transfer calls using Transfer Active Call Function.
Some JTAPI/TAPI applications are not compatible with the Join and Direct Transfer
feature implementation on the Cisco IP Phone and you may need to configure the Join
and Direct Transfer Policy to disable join and direct transfer on the same line or possibly
across lines.
See directory number information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Transfer - Direct Transfer
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
131
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Trust Verification Services (TVS) enables phones to authenticate signed configurations
and authenticate other servers or peers without increasing the size of the Certificate Trust
List (CTL) or requiring the downloading of an updated CTL file to the phone. TVS is
enabled by default.
The Security Setting menu on the phone displays the TVS information.
TVS
The Cisco IP Phones support Unified Capabilities Requirements (UCR) 2013 by providing
the following functions:
• Support for Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-2
• Support for 80-bit SRTCP Tagging
As an IP Phone administrator, you must set up specific parameters in Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Administration.
UCR 2013
Alerts the user when the primary line is not configured. The user sees the message
Unprovisioned on the phone screen.
Unconfigured Primary Line Notification
Increases the size of the application window to minimize truncated strings.User Interface Updates for List, Alert, and
Visual Voicemail.
Allows a user to select the video display mode for viewing a video conference, depending
on the modes configured in the system.
See video information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Available on Cisco IP Phone 8845, 8865, and 8865NR.
Video Mode
Enables video support on the phone. The Video Capabilities parameter needs to be enabled
for video calls on Cisco Unified Communications Manager Phone Configuration window.
It is enabled by default.
Available on Cisco IP Phone 8845, 8865, and 8865NR.
Video Support
Allows users to make video calls by using their Cisco Unified IP Phone, personal
computer, and an external video camera.
The feature also allows users to make video calls with Cisco Jabber or Cisco Unified
Video Advantage products.
Video Through PC
Replaces the voicemail audio prompts with a graphical interface.
See Installation and Configuration Guide for Visual Voicemail located at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/products/ps9829/prod_installation_guides_
list.html#anchor3.
Visual Voicemail
Enables callers to leave messages if calls are unanswered.
See voice mail information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release and Set up Visual Voicemail, on page 180.
Voice Message System
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
132
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Telephone Features

Description and more informationFeature
Using SSL, provides a virtual private network (VPN) connection on the Cisco Unified
IP Phone when it is located outside a trusted network or when network traffic between
the phone and Unified Communications Manager must cross untrusted networks.
VPN
Enhances security by disabling access to all web services, such as HTTP. Users can only
access web services if you enable web access.
Web Access Disabled by Default
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Feature Buttons and Softkeys
The following table provides information about features that are available on softkeys, features that are
available on dedicated feature buttons, and features that you need to configure as programmable feature
buttons. A “Supported” entry in the table indicates that the feature is supported for the corresponding button
type or softkey. Of the two button types and softkeys, only programmable feature buttons require configuration
in Cisco IP Phone administration.
For information about configuring programmable feature buttons, see Phone Button Templates, on page 185.
Table 30: Features and Corresponding Buttons and Softkeys
SoftkeyProgrammable feature
button
Dedicated feature
button
Feature name
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedAlert Calls
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedAll Calls
SupportedSupportedNot supportedAnswer
SupportedNot supportedNot supportedcBarge
SupportedSupportedNot supportedCall Back
SupportedNot supportedNot supportedCall Forward All
SupportedSupportedNot supportedCall Park
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedCall Park Line Status
SupportedSupportedNot supportedCall Pickup (Pick Up)
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedCall Pickup Line
Status
SupportedNot supportedSupportedConference
SupportedNot supportedNot supportedDivert
SupportedSupportedNot supportedDo Not Disturb
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
133
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Feature Buttons and Softkeys

SoftkeyProgrammable feature
button
Dedicated feature
button
Feature name
SupportedSupportedNot supportedGroup Pickup (Group
Pick Up)
SupportedNot supportedSupportedHold
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedHunt Groups
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedIntercom
SupportedSupportedNot supportedMalicious Call
Identification (MCID)
SupportedSupportedNot supportedMeet Me
SupportedNot supportedNot supportedMerge
SupportedSupportedNot supportedMobile Connect
(Mobility)
Not supportedNot supportedSupportedMute
SupportedSupportedNot supportedOther Pickup
SupportedNot supportedNot supportedPLK Support for
Queue Status
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedPrivacy
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedQueue Status
SupportedSupportedNot supportedQuality Reporting
Tool (QRT)
SupportedNot supportedNot supportedRecord
SupportedSupportedNot supportedRedial
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedSpeed Dial
Not supportedSupportedNot supportedSpeed Dial Line
Status
SupportedNot supportedNot supportedSupport for Hold
Button on USB
Headsets
SupportedNot supportedSupportedTransfer
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
134
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Feature Buttons and Softkeys

Phone Feature Configuration
You can set up phones to have a variety of features, based on the needs of your users. You can apply features
to all phones, a group of phones, or to individual phones.
When you set up features, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration window displays
information that is applicable to all phones and information that is applicable to the phone model. The
information that is specific to the phone model is in the Product Specific Configuration Layout area of the
window.
For information on the fields applicable to all phone models, see the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
documentation.
When you set a field, the window that you set the field in is important because there is a precedence to the
windows. The precedence order is:
1. Individual phones (highest precedence)
2. Group of phones
3. All phones (lowest precedence)
For example, if you don't want a specific set of users to access the phone Web pages, but the rest of your users
can access the pages, you:
1. Enable access to the phone web pages for all users.
2. Disable access to the phone web pages for each individual user, or set up a user group and disable access
to the phone web pages for the group of users.
3. If a specific user in the user group did need access to the phone web pages, you could enable it for that
particular user.
Set Up Phone Features for All Phones
Procedure
Step 1 Sign in to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration as an administrator.
Step 2 Select System > Enterprise Phone Configuration.
Step 3 Set the fields you want to change.
Step 4 Check the Override Enterprise Settings check box for any changed fields.
Step 5 Click Save.
Step 6 Click Apply Config.
Step 7 Restart the phones.
This will impact all phones in your organization.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
135
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Phone Feature Configuration

Set Up Phone Features for a Group of Phones
Procedure
Step 1 Sign in to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration as an administrator.
Step 2 Select Device > Device Settings > Common Phone Profile.
Step 3 Locate the profile.
Step 4 Navigate to the Product Specific Configuration Layout pane and set the fields.
Step 5 Check the Override Enterprise Settings check box for any changed fields.
Step 6 Click Save.
Step 7 Click Apply Config.
Step 8 Restart the phones.
Set Up Phone Features for a Single Phone
Procedure
Step 1 Sign in to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration as an administrator.
Step 2 Select Device > Phone
Step 3 Locate the phone associated with the user.
Step 4 Navigate to the Product Specific Configuration Layout pane and set the fields.
Step 5 Check the Override Common Settings check box for any changed fields.
Step 6 Click Save.
Step 7 Click Apply Config.
Step 8 Restart the phone.
Product Specific Configuration
The following table describes the fields in the Product Specific Configuration Layout pane.
Table 31: Product Specific Configuration Fields
Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Turns off the speakerphone capability of the phone.UncheckedCheck boxDisable Speakerphone
Turns off the speakerphone and headset capability of the phone.UncheckedCheck boxDisable Speakerphone
and Headset
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
136
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Phone Features for a Group of Phones

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Turns off the handset capability of the phone.UncheckedCheckboxDisable Handset
Controls the ability to use the PC port to connect a computer
into the LAN.
EnabledEnabled
Disabled
PC Port
Enables, disables, or restricts access to the local phone
configuration settings in the Settings app.
• Disabled—The Settings menu does not display any
options.
• Enabled—All entries in the Settings menu are accessible.
• Restricted—Only the Phone settings menu is accessible.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Restricted
Settings Access
Indicates whether the phone will allow a device attached to the
PC port to access the Voice VLAN.
• Disabled—The PC can't send and receive data on the
Voice VLAN or from the phone.
• Enabled—The PC can send and receive data from the
Voice VLAN or from the phone. Set this field to Enabled
if an application is being run on the PC that to monitor
phone traffic. These applications could include monitoring
and recording applications, and the use of network
monitoring software for analysis purposes.
EnabledEnabled
Disabled
PC Voice VLAN
Access
Allows users to make video calls by using a Cisco IP Phone,
a personal computer, and a video camera.
8845, 8865, and
8865NR: Enabled
8811, 8851,
8851NR, 8861:
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Video Capabilities
Enables or disables access to the phone web pages through a
web browser.
If you enable this field, you may expose sensitive
information about the phone.
Caution
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Web Access
Controls the use of TLS 1.2 for a web server connection.
• Disabled—A phone configured for TLS1.0, TLS 1.1, or
TLS1.2 can function as a HTTPs server.
• Enabled—Only a phone configured for TLS1.2 can
function as a HTTPs server.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Disable TLS 1.0 and
TLS 1.1 for Web
Access
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
137
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Controls the dialing method.
• Disabled—The Cisco Unified Communications Manager
waits for the interdigit timer to expire when there is a dial
plan or route pattern overlap.
• Enabled—The entire dialed string is sent to Cisco Unified
Communications Manager once the dialing is complete.
To avoid the T.302 timer timeout, we recommend that
you enable Enbloc Dialing whenever there is a dialplan
or route pattern overlap.
Forced Authorization Codes (FAC) or Client Matter Codes
(CMC) do not support the Enbloc Dialing. If you use FAC or
CMC to manage call access and accounting, then you cannot
use this feature.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Enbloc Dialing
Defines the days that the display does not turn on automatically
at the time specified in the Display On Time field.
Choose the day or days from the drop-down list. To choose
more than one day, Ctrl+click each day that you want.
Days of the weekDays Display Not
Active
Defines the Time each day that the display turns on
automatically (except on the days specified in the Days Display
Not Active field).
Enter the time in this field in 24 hour format, where 0:00 is
midnight.
For example, to automatically turn the display on at 07:00 a.m.
(0700), enter 07:00. To turn the display on at 02:00 p.m. (1400),
enter 14:00.
If this field is blank, the display automatically turns on at 0:00.
hh:mmDisplay On Time
Defines the length of time that the display remains on after
turning on at the time specified in the Display On Time field.
For example, to keep the display on for 4 hours and 30 minutes
after it turns on automatically, enter 04:30.
If this field is blank, the phone turns off at the end of the day
(0:00).
If Display On Time is 0:00 and the display on duration is blank
(or 24:00), the display does not turn off.
hh:mmDisplay On Duration
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
138
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Defines the length of time that the phone is idle before the
display turns off. Applies only when the display was off as
scheduled and was turned on by a user (by pressing a button
on the phone or lifting the handset).
Enter the value in this field in the format hours:minutes.
For example, to turn the display off when the phone is idle for
1 hour and 30 minutes after a user turns the display on, enter
01:30.
For more information, see Set Up Idle Display, on page 111.
01:00hh:mmDisplay Idle Timeout
Turns the idle display on when there is an incoming call.EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Display On When
Incoming Call
Defines the schedule of days for which the phone powers off.
Choose the day or days from the drop-down list. To choose
more than one day, Ctrl+click each day that you want.
When Enable Power Save Plus is turned on, you receive a
message that warns about emergency (e911) concerns.
While Power Save Plus Mode (the “Mode”) is in
effect, endpoints that are configured for the mode
are disabled for emergency calling and from
receiving inbound calls. By selecting this mode,
you agree to the following: (i) You take full
responsibility for providing alternate methods for
emergency calling and receiving calls while the
mode is in effect; (ii) Cisco has no liability in
connection with your selection of the mode and
all liability in connection with enabling the mode
is your responsibility; and (iii) You fully inform
users of the effects of the mode on calls, calling
and otherwise.
Caution
To disable Power Save Plus, you must uncheck the Allow
EnergyWise Overrides check box. If the Allow EnergyWise
Overrides remains checked but no days are selected in the
Enable Power Save Plus field, Power Save Plus is not disabled.
Days of the weekEnable Power Save
Plus
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
139
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Determines when the phone automatically turns on for the days
that are in the Enable Power Save Plus field.
Enter the time in this field in 24-hour format, where 00:00 is
midnight.
For example, to automatically power up the phone at 07:00
a.m. (0700), enter 07:00. To power up the phone at 02:00 p.m.
(1400), enter 14:00.
The default value is blank, which means 00:00.
The Phone On Time must be at least 20 minutes later than the
Phone Off Time. For example, if the Phone Off Time is 07:00,
the Phone On Time must be no earlier than 07:20.
hh:mmPhone On Time
Identifies the time of day that the phone powers down for the
days that are selected in the Enable Power Save Plus field. If
the Phone On Time and the Phone Off Time fields contain the
same value, the phone does not power down.
Enter the time in this field in 24-hour format, where 00:00 is
midnight.
For example, to automatically power down the phone at 7:00
a.m. (0700), enter 7:00. To power down the phone at 2:00 p.m.
(1400), enter 14:00.
The default value is blank, which means 00:00.
The Phone On Time must be at least 20 minutes later than the
Phone Off Time. For example, if the Phone Off Time is 7:00,
the Phone On Time must be no earlier than 7:20.
hh:mmPhone Off Time
Indicates the length of time that the phone must be idle before
the phone powers down.
The timeout occurs under the following conditions:
• When the phone was in Power Save Plus mode, as
scheduled, and was taken out of Power Save Plus mode
because the phone user pressed the Select key.
• When the phone is repowered by the attached switch.
• When the Phone Off Time is reached but the phone is in
use.
6020 to 1440 minutesPhone Off Idle
Timeout
When enabled, instructs the phone to play an audible alert
starting 10 minutes before the time that the Phone Off Time
field specifies.
This check box applies only if the Enable Power Save Plus list
box has one or more days selected.
UncheckedCheck boxEnable Audible Alert
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
140
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Identifies the EnergyWise domain that the phone is in.Up to 127 charactersEnergyWise Domain
Identifies the security secret password that is used to
communicate with the endpoints in the EnergyWise domain.
Up to 127 charactersEnergyWise Secret
Determines whether you allow the EnergyWise domain
controller policy to send power level updates to the phones.
The following conditions apply:
• One or more days must be selected in the Enable Power
Save Plus field.
• The settings in Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration take effect on schedule even if EnergyWise
sends an override.
For example, assuming the Phone Off Time is set to 22:00
(10:00 p.m.), the value in the Phone On Time field is 06:00
(6:00 a.m.), and the Enable Power Save Plus has one or more
days selected.
• If EnergyWise directs the phone to turn off at 20:00 (8:00
p.m.), that directive remains in effect (assuming no phone
user intervention occurs) until the configured Phone On
Time at 6:00 a.m.
• At 6:00 a.m., the phone turns on and resumes receiving
the power level changes from the settings in Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Administration.
• To change the power level on the phone again,
EnergyWise must reissue a new power level change
command.
To disable Power Save Plus, you must uncheck the Allow
EnergyWise Overrides check box. If the Allow EnergyWise
Overrides remains checked but no days are selected in the
Enable Power Save Plus field, Power Save Plus is not disabled.
UncheckedCheck boxAllow EnergyWise
Overrides
Controls the ability of a user to join and transfer calls.
• Same line, across line enable—Users can directly transfer
or join a call on current line to another call on another
line.
• Same line enable only—Users can only directly transfer
or join the calls when both calls are on same line.
• Same line, across line disable— Users can't join or transfer
calls on the same line. The join and transfer features are
disabled and the user can't do the direct transfer or join
function.
Same line, across
line enable
Same line, across line
enable
Same line enable only
Same line, across line
disable
Join and Direct
Transfer Policy
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
141
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Indicates whether the phone forwards packets that are
transmitted and received on the network port to the access port.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Span to PC Port
Controls the playing of the tone when a user is recording a call.DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Recording Tone
Controls the volume of the recording tone to the local user.100Integer 0–100Recording Tone Local
Volume
Controls the volume of the recording tone to the remote user.50Integer 0–100Recording Tone
Remote Volume
Controls the duration of the recording tone.Integer 1–3000
milliseconds
Recording Tone
Duration
Identifies the IPv4 syslog server for phone debug output.
The format for the address is:
address:<port>@@base=<0-7>;pfs=<0-1>
String of up to 256
characters
Log Server
Controls Cisco Discovery Protocol on the SW port of the
phone.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Cisco Discovery
Protocol (CDP):
Switch Port
Controls Cisco Discovery Protocol on the PC port of the phone.EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Cisco Discovery
Protocol (CDP): PC
Port
Enables LLDP-MED on the SW port.EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Link Layer Discovery
Protocol - Media
Endpoint Discover
(LLDP-MED): Switch
Port
Enables LLDP on the PC port.EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Link Layer Discovery
Protocol (LLDP): PC
Port
Identifies the asset ID that is assigned to the phone for
inventory management.
String, up to 32
characters
LLDP Asset ID
Assigns a phone power priority to the switch, thus enabling
the switch to appropriately provide power to the phones.
UnknownUnknown
Low
High
Critical
LLDP Power Priority
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
142
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration
Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Specifies the 802.1x authentication feature status.
• User Controlled—The user can configure the 802.1x on
the phone.
• Disabled—802.1x Authentication is not used.
• Enabled—802.1x authentication is used, and you
configure the authentication for the phones.
User ControlledUser Controlled
Enabled
Disabled
802.1x Authentication
Synchronizes ports to the lowest speed between ports of a
phone to eliminate packet loss.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Automatic Port
Synchronization
Allows you to configure the speed and duplex function of the
phone SW port remotely. This enhances the performance for
large deployments with specific port settings.
If the SW ports are configured for Remote Port Configuration
in Cisco Unified Communications Manager, the data cannot
be changed on the phone.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Switch Port Remote
Configuration
Allows you to configure the speed and duplex function of the
phone PC port remotely. This enhances the performance for
large deployments with specific port settings.
If the ports are configured for Remote Port Configuration in
Cisco Unified Communications Manager, the data cannot be
changed on the phone.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
PC Port Remote
Configuration
Controls the access to the SSH daemon through port 22.
Leaving port 22 open leaves the phone vulnerable to Denial
of Service (DoS) attacks.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
SSH Access
Gives the time, in seconds, that the toast displays. The time
includes the fade-in and fade-out times for the window.
0 means that the incoming call toast is disabled.
50, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
15, 30, 60
Incoming Call Toast
Timer
Controls the ringing pattern.DefaultDefault
Japan
Ring Locale
Controls the ability to resume a TLS session without repeating
the entire TLS authentication process. If the field is set to 0,
then the TLS session resumption is disabled.
3600Integer 0–3600 secondsTLS Resumption
Timer
Enables or disables the Federal Information Processing
Standards (FIPS) mode on the phone.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
FIPS Mode
Specifies whether to record a shared line call in the call log.DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Record Call Log from
Shared Line
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
143
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Controls the minimum ring volume for the phone.
You can set a phone so that the ringer cannot be turned off.
0-Silent0-Silent
1–15
Minimum Ring
Volume
Allows the phone to find other phones of the same model on
the subnet and share updated firmware files. If the phone has
a new firmware load, it can share that load with the other
phones. If one of the other phones has a new firmware load,
the phone can download the firmware from the other phone,
instead of from the TFTP server.
Peer firmware sharing:
• Limits congestion on TFTP transfers to centralized remove
TFTP servers.
• Eliminates the need to manually control firmware
upgrades.
• Reduces phone downtime during upgrades when large
numbers of phones are reset simultaneously.
• Helps with firmware upgrades in branch or remote office
deployment scenarios that run over bandwidth-limited
WAN links.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Peer Firmware
Sharing
Identifies the alternate IPv4 server that the phone uses to obtain
firmware loads and upgrades.
The format for the address is:
address:<port>@@base=<0-7>;pfs=<0-1>
String of up to 256
characters
Load Server
Identifies the alternate IPv6 server that the phone uses to obtain
firmware loads and upgrades.
The format for the address is:
[address]:<port>@@base=<0-7>;pfs=<0-1>
String of up to 256
characters
IPv6 Load Server
Allows the user to use the wideband codec for an analog
headset.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Wideband Headset UI
Control
Enables or disables the use of a Wideband Headset on the
phone. Used in conjunction with User Control Wideband
Headset.
For more information, see Set Up Wideband Codec, on page
111.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Wideband Headset
Enables the Cisco IP Phones 8861 and 8865 to connect to the
Wi-Fi network.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Wi-Fi
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
144
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Controls the ability to use the USB port on the back of the
Cisco IP Phones 8861 and 8865.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
8861, 8865, and
8865NR: Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Back USB Port
Controls the ability to use the USB port on the side of the Cisco
IP Phones 8851, 8851NR, 8861, 8865, and 8865NR.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Side USB Port
Specifies whether the serial console is enabled or disabled.DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Console Access
Enables or disables the Bluetooth option on the phone. If
disabled, the user cannot enable Bluetooth on the phone.
Supported on the Cisco IP Phones 8845, 8851, 8861, and 8865.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Bluetooth
Enables the user to import contacts from their connected mobile
device using Bluetooth. When disabled, the user cannot import
contacts from their connected mobile device on their phone.
Supported on the Cisco IP Phones 8845, 8851, 8861, and 8865.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Allow Bluetooth
Contacts Import
Enables users to take advantage of the acoustic properties of
the phone with their mobile device or tablet. The user pairs the
mobile device or tablet to the phone using Bluetooth. When
disabled, the user cannot pair the mobile device or tablet with
their phone.
With a mobile device paired, the user can place and receive
mobile calls on the phone. With a tablet, the user can route the
audio from the tablet to the phone.
Users can pair multiple mobile devices, tablets, and a Bluetooth
headset to the phone. However, only one device and one
headset can be connected at the same time.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Allow Bluetooth
Mobile Handsfree
Mode
Indicates which Bluetooth profiles on the phone are enabled
or disabled.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
HandsfreeHandsfree
Human Interface
Device
Bluetooth Profiles
Enables or disables the ability for the phone to learn MAC
addresses from Gratuitous ARP. This capability is required to
monitor or record voice streams.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Gratuitous ARP
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
145
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Specifies if all calls presented to this phone will be shown on
the primary line or not.
The purpose of this field is to make it easier for the end user
to see all calls on all lines at a glance rather than having to
choose a line to see the calls on that line. In other words, when
multiple lines are configured on the phone, it typically makes
more sense to be able to see all the calls on all lines in one
combined display. When this feature is enabled, all calls will
be shown on the primary line, but you can still choose a specific
line to filter the display to show only the calls for that specific
line.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Show All Calls on
Primary Line
Controls the type of communication to the phone. If you select
HTTPS only, phone communication is more secure.
HTTP and HTTPS
enabled
HTTP and HTTPS
enabled
HTTPS only
HTTPS Server
Identifies the IPv6 log server.
The format for the address is:
[address]:<port>@@base=<0-7>;pfs=<0-1>
String of up to 256
characters
IPv6 Log Server
Controls the ability to send logs to the syslog server.DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Remote Log
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
146
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Specifies the predefined logging profile.
• Default—Default debug logging level
• Preset—Does not overwrite the phone local debug logging
setting
• Telephony—Logs information about Telephony or call
features
• SIP—Logs information about SIP signaling
• UI—Logs information about the phone user interface
• Network—Logs network information
• Media—Logs media information
• Upgrade—Logs upgrade information
• Accessory—Logs accessory information
• Security—Logs security information
• Wi-Fi—Logs Wi-Fi information
• VPN—Logs virtual private network information
• Energywise—Logs energy-savings information
• MobileRemoteAC—Logs Mobile and Remote Access
through Expressway information
PresetDefault
Preset
Telephony
SIP
UI
Network
Media
Upgrade
Accessory
Security
Wi-Fi
VPN
Energywise
MobileRemoteAc
Log Profile
Indicates whether the phone advertises the G.722 and iSAC
codecs to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
• Use System Default—Defers to the setting specified in
the enterprise parameter Advertise G.722 Codec.
• Disabled—Does not advertise G.722 to the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
• Enabled—Advertises G.722 to the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
For more information, see the note that follows the table.
Use System DefaultUse System Default
Disabled
Enabled
Advertise G.722 and
iSAC Codecs
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
147
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Determines the sensitivity that the phone has for detecting a
connection failure to Cisco Unified Communications Manager
(Unified CM), which is the first step before device failover to
a backup Unified CM/SRST occurs.
• Normal—Detection of a Unified CM connection failure
occurs at the standard system rate. Choose this value for
faster recognition of a Unified CM connection failure.
• Delayed—Detection of a Unified CM connection failover
occurs approximately four times slower than Normal.
Choose this value if you prefer failover to be delayed
slightly to give the connection the opportunity to
reestablish
The precise time difference between Normal and Delayed
connection failure detection depends on many variables that
are constantly changing.
This field only applies to the wired Ethernet connection.
NormalNormal
Delayed
Detect Unified CM
Connection Failure
Allows the phone to negotiate power using Link Level Endpoint
Discovery Protocol (LLDP) and Cisco Discovery Protocol
(CDP).
Power Negotiation should not be disabled when the phone is
connected to a switch that supports power negotiation. If
disabled, the switch could shut off power to the phone.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Power Negotiation
Controls whether the user hears dial tone when the Release
key is pressed.
• Disabled—User doesn't hear dial tone.
• Enabled—User hears dial tone.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Provide Dial Tone
from Release Button
Specifies the default wallpaper file. When a default wallpaper
is set, the user can't change the phone wallpaper.
String up to 64
characters
Background Image
Controls the user interface for off-hook dialing. When enabled,
the user cannot select a number from the recent calls list.
When enabled, this field provides a simplified window for the
user to place a call. The user does not see the call history
pop-up window that is displayed when the phone is taken
off-hook. The pop-up window display is considered useful, so
Simplified New Call UI is disabled by default.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Simplified New Call
UI
Specifies whether the phone will revert to All Calls after any
call ends or not if the call is on a filter other than Primary line,
All Calls, or Alerting Calls.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Revert to All Calls
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
148
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Controls the display of the Recents list.
• Disabled—The Recents list shows the call history for all
lines.
• Enabled—The Recents list shows the call history for the
selected line.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Show Call History for
Selected Line Only
Controls the type of incoming call alert that displays on the
phone screen. The purpose of this field is to reduce the number
of button presses that the end user requires to answer a call.
• Disabled—The actionable incoming call alert is disabled
and the user sees the traditional incoming call pop-up
alert.
• Show for all Incoming Call—The actionable incoming
call alert displays for all calls regardless of visibility.
• Show for Invisible Incoming Call—The actionable
incoming call alert displays for calls not shown on the
phone. This parameter behaves similarly to the incoming
call alert pop-up notification.
Show for all
Incoming Call
Disabled
Show for all Incoming
Call
Show for Invisible
Incoming Call
Actionable Incoming
Call Alert
Controls how network packets are sent. Packets can be sent in
chunks (fragments) of various sizes.
When the DF bit is set to 1 in the packet header, the network
payload does not fragment when going through network
devices, such as switches and routers. Removing fragmenting
avoids incorrect parsing on the receiving side, but results in
slightly slower speeds.
The DF bit setting does not apply to ICMP, VPN, VXC VPN,
or DHCP traffic.
00
1
DF bit
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
149
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Indicates the list of phones that are in the default filter.
When the default line filter is configured, users see a filter
named Daily schedule in Call notifications in the
Settings > Pr eferences menu of the phone. This daily schedule
filter is in addition to the preset All Calls filter.
If the default line filter is not configured, the phone checks all
provisioned lines. If configured, the phone checks the lines set
on Cisco Unified Communications Manager if the user selects
Default filter as the active filter, or if there are no custom filters.
Custom line filters enable you to filter on high-priority lines
to reduce alert activity. You can set the alerting call notification
priority on a subset of lines covered by an alert filter. The
custom filter generates either traditional pop-up alerts or
actionable alerts for incoming calls on the selected lines. For
each filter, only the covered subset of lines will generate an
alert. This feature provides a way for users with multiple lines
to reduce alert activity by filtering and displaying alerts only
from high-priority lines. The end users can configure this
themselves. Alternatively, you can program the default line
filter and push the filter down to the phone.
List of
comma-separated
phone device names
Default Line Filter
Specifies the alert state when using shared lines.
• Disabled—When there is an incoming call alerting on the
shared line, the LED/Line state icon reflects the alerting
state instead of Remote-In-Use.
• Enabled—When there is an incoming call alerting on the
shared line, the user sees the Remote-In-Use icon.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Lowest Alerting Line
State Priority
Controls the display on the Key Expansion Module.
• Disabled—The expansion module uses two-column mode.
• Enabled—The expansion module uses one-column mode.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
One Column Display
for KEM
Controls EEE on the PC port.DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Energy Efficient
Ethernet (EEE): PC
Port
Controls EEE on the switch port.DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Energy Efficient
Ethernet (EEE): SW
Port
Defines the start of the port range for video calls.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
Start Video Port
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
150
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Defines the end of the port range for video calls.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
Stop Video Port
Controls if the phone stores the users' sign-in credentials. When
disabled, the user is always sees the prompt to sign into the
Expressway server for Mobile and Remote Access (MRA).
If you would like to make it easier for users to log in, you
enable this field so that the Expressway login credentials are
persistent. The user then only has to enter their login credentials
the first time. Any time after that (when the phone is powered
on off-premise), the login information is prepopulated on the
Sign-in screen.
For more information, see the Mobile and Remote Access
Through Expressway, on page 167.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
User Credentials
Persistent for
Expressway Sign in
Provides the URL for the Problem Report Tool (PRT).
If you deploy devices with Mobile and Remote Access through
Expressway, you must also add the PRT server address to the
HTTP Server Allow list on the Expressway server.
For more information, see the Mobile and Remote Access
Through Expressway, on page 167.
String, up to 256
characters
Customer support
upload URL
Enables or disables administrator access to the phone web
pages through a web browser
For more information, see the Configure the Administration
Page for Phone, on page 102.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
DisabledDisabled
Enabled
Web Admin
Defines the administrator password when you access the phone
web pages as an administrator.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
String of 8–127
characters
Admin Password
Specifies the SCEP Server that the phone uses to obtain
certificates for WLAN authentication. Enter the hostname or
the IP address (using standard IP addressing format) of the
server.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
String of up to 256
characters
WLAN SCEP Server
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
151
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Specifies the SHA256 or SHA1 fingerprint of the Root CA to
use for validation during the SCEP process when issuing
certificates for WLAN authentication. We recommend that you
use the SHA256 fingerprint, which can be obtained via
OpenSSL (e.g. openssl x509 -in rootca.cer -noout -sha256
-fingerprint) or using a Web Browser to inspect the certificate
details.
Enter the 64 hexadecimal character value for the SHA256
fingerprint or the 40 hexadecimal character value for the SHA1
fingerprint with a common separator (colon, dash, period,
space) or without a separator. If using a separator, then the
separator should be consistently placed after every 2, 4, 8, 16,
or 32 hexadecimal characters for a SHA256 fingerprint or every
2, 4, or 8 hexadecimal characters for a SHA1 fingerprint.
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.
String of up to 95
characters
WLAN Root CA
Fingerprint (SHA256
or SHA1)
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.WLAN
Authentication
Attempts
Phones that do not support this feature do not display the field.DisabledDisabled
Enabled
WLAN Profile 1
Prompt Mode
Controls the line display on the phone.
• Session Line Mode—The buttons on one side of the screen
are line keys.
• Enhanced Line Mode—The buttons on both sides of the
phone screen are line keys. Predictive dialing and
Actionable incoming call alerts are enabled by default in
Enhanced line mode.
Session Line ModeSession Line Mode
Enhanced Line Mode
Line Mode
Controls the ringtone and the ability for users to set the
ringtone.
• When set to Disabled, users can configure the default
ringtone on their phones.
• For all other values, users cannot change the ringtone.
The Ringtone menu item in the Settings menu is grayed
out.
DisabledDisabled
Sunrise
Chirp1
Chirp2
Admin Configurable
Ringer
For Cisco TAC use only.EmptyString of up to 64
characters
Customer Support Use
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
152
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Disables the selected TLS cipher.
Disable more than one cipher suite by selecting and holding
the Ctrl key on your computer keyboard.
If you select all of the phone ciphers, then phone TLS service
is impacted.
NoneSee Disable Transport
Layer Security Ciphers,
on page 156.
Disable TLS Ciphers
Controls the Lower your voice feature.
• Disabled:
• The phone doesn't display the Lower your voice
menu item in the Settings menu.
• Users won't see the message on their screen when
they speak loudly.
• Enabled:
• Users control the feature from the Lower your voice
menu item in the Settings menu. By default, the field
is set to On.
EnabledEnabled
Disabled
Lower Your Voice
Alert
Controls the Mark call as spam feature.
• Disabled:
• The phone doesn't display the Mark spam softkey.
• The Spam list item in the Settings menu doesn't
display.
• If there was a spam list, the list is cleared and can't
be recovered.
• Enabled:
• The phone displays the Mark spam softkey.
• The Spam list item in the Settings menu displays.
EnabledEnabled
Disabled
Mark Call As Spam
Controls whether a parked call occupies one line or not.
For more information, see the Cisco Unified Communications
Manager documentation.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Dedicate one line for
Call Park
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
153
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Product Specific Configuration

Description and Usage GuidelinesDefaultField Type
or Choices
Field Name
Controls the line label display during a call when Enhanced
Line Mode is configured
• Enabled
• If the caller's name is configured, it displays the name
in the first line of the call session and the local line
label in the second line.
• If the caller's name is not configured, it displays the
remote number in the first line and the local line label
in the second line.
• Disabled
• If the caller’s name is configured, it displays the
name in the first line of the call session and number
in the second line.
• If the caller's name is not configured, it displays only
the remote number.
This field is required.
EnabledDisabled
Enabled
Line Text Label
Display in ELM
Codec negotiation involves two steps:
1. The phone advertises the supported codec to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager. Not all endpoints
support the same set of codecs.
2. When the Cisco Unified Communications Manager gets the list of supported codecs from all phones
involved in the call attempt, it chooses a commonly supported codec based on various factors, including
the region pair setting.
Note
Feature Configuration Best Practices
You can set up the phone features to suit your users' needs. But we have some recommendations for certain
situations and deployments that might help you.
High Call Volume Environments
In a high call volume environment, we recommend that you set up some features in a specific way.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
154
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Feature Configuration Best Practices

Recommended SettingAdministration AreaField
Off or On
For more information, see Field:
Always Use Prime Line, on page
156.
Device InformationAlways Use Prime Line
Show for all Incoming CallProduct Specific Configuration
Layout
Actionable Incoming Call Alert
EnabledProduct Specific Configuration
Layout
Show All Calls on Primary Line
EnabledProduct Specific Configuration
Layout
Revert to All Calls
Multiline Environments
In a multiline environment, we recommend that you set up some features in a specific way.
Recommended SettingAdministration AreaField
Off
For more information, see Field:
Always Use Prime Line, on page
156.
Device InformationAlways Use Prime Line
Show for all Incoming CallProduct Specific Configuration
Layout
Actionable Incoming Call Alert
EnabledProduct Specific Configuration
Layout
Show All Calls on Primary Line
EnabledProduct Specific Configuration
Layout
Revert to All Calls
Session Line Mode Environment
Enhanced Line Mode is the preferred tool for handling most call environments. However, if Enhanced Line
Mode does not suit your needs, then you can use Session line mode.
Recommended Setting for Session
Line Mode
Administration AreaField
DisabledProduct Specific Configuration
Layout
Show All Calls on Primary Line
DisabledProduct Specific Configuration
Layout
Revert to All Calls
Enabled by default (Firmware
Release 11.5(1) and later).
Product Specific Configuration
Layout
Actionable Incoming Call Alert
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
155
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Multiline Environments

Related Topics
Set Up Additional Line Keys, on page 189
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode, on page 190
Field: Always Use Prime Line
This field specifies whether the primary line on an IP phone is chosen when a user goes off-hook. If this
parameter is set to True, when a phone goes off-hook, the primary line is chosen and becomes the active line.
Even if a call rings on the second line of the user, when the phone goes off-hook, it makes only the first line
active. It does not answer the inbound call on the second line. In this case, the user must choose the second
line to answer the call. The default value is set to False.
The purpose of the Always Use Prime Line field is very similar to the combination of Show All Calls on the
Primary Line and Revert to All Calls when both of those two features are enabled. However, the main difference
is that when Always Use Prime Line is enabled, inbound calls are not answered on the second line. Only dial
tone is heard on the prime line. There are certain high call volume environments where this is the desired user
experience. In general, it is best to leave this field disabled except for high call volume environments that
require this feature.
Disable Transport Layer Security Ciphers
You can disable Transport Layer Security (TLS) ciphers with the Disable TLS Ciphers parameter. This
allows you to tailor your security for known vulnerabilities, and to align your network with your company's
policies for ciphers.
None is the default setting.
Disable more than one cipher suite by selecting and holding the Ctrl key on your computer keyboard. If you
select all of the phone ciphers, then phone TLS service is impacted. Your choices are:
• None
• TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
• TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
• TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
• TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
• TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
• TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
• TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
For more information about phone security, see Cisco IP Phone 7800 and 8800 Series Security Overview
White Paper (https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collaboration-endpoints/unified-ip-phone-8800-series/
white-paper-listing.html).
Enable Call History for Shared Line
Allows you to view your shared line activity in the Call History. This feature:
• Logs missed calls for a shared line.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
156
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Field: Always Use Prime Line

• Logs all answered and placed calls for a shared line.
Before you begin
Disable Privacy before you enable Call History for Shared Line. Otherwise Call History doesn't display the
calls other users answer.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate the phone to be configured.
Step 3 Navigate to the Record Call Log from Shared Line drop-down in the Product Specific Configuration area.
Step 4 Select Enabled from the drop-down list.
Step 5 Select Save.
Schedule Power Save for Cisco IP Phone
To conserve power and ensure the longevity of the phone screen display, you can set the display to turn off
when it is not needed.
You can configure settings in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration to turn off the display
at a designated time on some days and all day on other days. For example, you may choose to turn off the
display after business hours on weekdays and all day on Saturdays and Sundays.
You can take any of these actions to turn on the display any time it is off:
• Press any button on the phone.
The phone takes the action designated by that button in addition to turning on the display.
• Lift the handset.
When you turn the display on, it remains on until the phone has remained idle for a designated length of time,
then it turns off automatically.
For more information, see Product Specific Configuration, on page 136
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate the phone that you need to set up.
Step 3 Navigate to the Product Specific Configuration area and set the following fields:
• Days Display Not Active
• Display On Time
• Display On Duration
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
157
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Schedule Power Save for Cisco IP Phone

• Display Idle Timeout
Table 32: PowerSave Configuration Fields
DescriptionField
Days that the display does not turn on automatically at the time specified in the Display On Time
field.
Choose the day or days from the drop-down list. To choose more than one day, Ctrl-click each day
that you want.
Days Display Not Active
Time each day that the display turns on automatically (except on the days specified in the Days
Display Not Active field).
Enter the time in this field in 24-hour format, where 0:00 is midnight.
For example, to automatically turn the display on at 07:00a.m., (0700), enter 07:00. To turn the
display on at 02:00p.m. (1400), enter 14:00.
If this field is blank, the display will automatically turn on at 0:00.
Display On Time
Length of time that the display remains on after turning on at the time specified in the Display On
Time field.
Enter the value in this field in the format hours:minutes.
For example, to keep the display on for 4 hours and 30 minutes after it turns on automatically,
enter 04:30.
If this field is blank, the phone will turn off at the end of the day (0:00).
If Display On Time is 0:00 and the display on duration is blank (or 24:00), the display
will remain on continuously.
Note
Display On Duration
Length of time that the phone is idle before the display turns off. Applies only when the display
was off as scheduled and was turned on by a user (by pressing a button on the phone or lifting the
handset).
Enter the value in this field in the format hours:minutes.
For example, to turn the display off when the phone is idle for 1 hour and 30 minutes after a user
turns the display on, enter 01:30.
The default value is 01:00.
Display Idle Timeout
Step 4 Select Save.
Step 5 Select Apply Config.
Step 6 Restart the phone.
Schedule EnergyWise on Cisco IP Phone
To reduce power consumption, configure the phone to sleep (power down) and wake (power up) if your system
includes an EnergyWise controller.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
158
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Schedule EnergyWise on Cisco IP Phone

You configure settings in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration to enable EnergyWise and
configure sleep and wake times. These parameters are closely tied to the phone display configuration parameters.
When EnergyWise is enabled and a sleep time is set, the phone sends a request to the switch to wake it up at
the configured time. The switch returns either an acceptance or a rejection of the request. If the switch rejects
the request or if the switch does not reply, the phone does not power down. If the switch accepts the request,
the idle phone goes to sleep, thus reducing the power consumption to a predetermined level. A phone that is
not idle sets an idle timer and goes to sleep after the idle timer expires.
To wake up the phone, press Select. At the scheduled wake time, the system restores power to the phone,
waking it up.
For more information, see Product Specific Configuration, on page 136
Procedure
Step 1 From the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate the phone that you need to set up.
Step 3 Navigate to the Product Specific Configuration area and set the following fields.
• Enable Power Save Plus
• Phone On Time
• Phone Off Time
• Phone Off Idle Timeout
• Enable Audible Alert
• EnergyWise Domain
• EnergyWise Secret
• Allow EnergyWise Overrides
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
159
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Schedule EnergyWise on Cisco IP Phone

Table 33: EnergyWise Configuration Fields
DescriptionField
Selects the schedule of days for which the phone powers off. Select multiple days by pressing
and holding the Control key while clicking on the days for the schedule.
By default, no days are selected.
When Enable Power Save Plus is checked, you receive a message that warns about emergency
(e911) concerns.
While Power Save Plus Mode (the “Mode”) is in effect, endpoints that are configured
for the mode are disabled for emergency calling and from receiving inbound calls.
By selecting this mode, you agree to the following: (i) You take full responsibility
for providing alternate methods for emergency calling and receiving calls while the
mode is in effect; (ii) Cisco has no liability in connection with your selection of the
mode and all liability in connection with enabling the mode is your responsibility;
and (iii) You fully inform users of the effects of the mode on calls, calling and
otherwise.
Caution
To disable Power Save Plus, you must uncheck the Allow EnergyWise Overrides
check box. If the Allow EnergyWise Overrides remains checked but no days are
selected in the Enable Power Save Plus field, Power Save Plus is not disabled.
Note
Enable Power Save Plus
Determines when the phone automatically turns on for the days that are in the Enable Power Save
Plus field.
Enter the time in this field in 24-hour format, where 00:00 is midnight.
For example, to automatically power up the phone at 07:00 a.m. (0700), enter 07:00. To power
up the phone at 02:00 p.m. (1400), enter 14:00.
The default value is blank, which means 00:00.
The Phone On Time must be at least 20 minutes later than the Phone Off Time. For
example, if the Phone Off Time is 07:00, the Phone On Time must be no earlier than
07:20.
Note
Phone On Time
The time of day that the phone powers down for the days that are selected in the Enable Power
Save Plus field. If the Phone On Time and the Phone Off Time fields contain the same value, the
phone does not power down.
Enter the time in this field in 24-hour format, where 00:00 is midnight.
For example, to automatically power down the phone at 7:00 a.m. (0700), enter 7:00. To power
down the phone at 2:00 p.m. (1400), enter 14:00.
The default value is blank, which means 00:00.
The Phone On Time must be at least 20 minutes later than the Phone Off Time. For
example, if the Phone Off Time is 7:00, the Phone On Time must be no earlier than
7:20.
Note
Phone Off Time
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
160
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Schedule EnergyWise on Cisco IP Phone

DescriptionField
The length of time that the phone must be idle before the phone powers down.
The timeout occurs under the following conditions:
• When the phone was in Power Save Plus mode, as scheduled, and was taken out of Power
Save Plus mode because the phone user pressed the Select key.
• When the phone is repowered by the attached switch.
• When the Phone Off Time is reached but the phone is in use.
The range of the field is 20 to 1440 minutes.
The default value is 60 minutes.
Phone Off Idle Timeout
When enabled, instructs the phone to play an audible alert starting 10 minutes before the time
that the Phone Off Time field specifies.
The audible alert uses the phone ringtone, which briefly plays at specific times during the 10-minute
alerting period. The alerting ringtone plays at the user-designated volume level. The audible alert
schedule is:
• At 10 minutes before power down, play the ringtone four times.
• At 7 minutes before power down, play the ringtone four times.
• At 4 minutes before power down, play the ringtone four times.
• At 30 seconds before power down, play the ringtone 15 times or until the phone powers off.
This check box applies only if the Enable Power Save Plus list box has one or more days selected.
Enable Audible Alert
The EnergyWise domain that the phone is in.
The maximum length of this field is 127 characters.
EnergyWise Domain
The security secret password that is used to communicate with the endpoints in the EnergyWise
domain.
The maximum length of this field is 127 characters.
EnergyWise Secret
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
161
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Schedule EnergyWise on Cisco IP Phone

DescriptionField
This check box determines whether you allow the EnergyWise domain controller policy to send
power level updates to the phones. The following conditions apply:
• One or more days must be selected in the Enable Power Save Plus field.
• The settings in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration take effect on
schedule even if EnergyWise sends an override.
For example, assuming the Phone Off Time is set to 22:00 (10:00 p.m.), the value in the Phone
On Time field is 06:00 (6:00 a.m.), and the Enable Power Save Plus has one or more days selected.
• If EnergyWise directs the phone to turn off at 20:00 (8:00 p.m.), that directive remains in
effect (assuming no phone user intervention occurs) until the configured Phone On Time at
6:00 a.m.
• At 6:00 a.m., the phone turns on and resumes receiving the power level changes from the
settings in Unified Communications Manager Administration.
• To change the power level on the phone again, EnergyWise must reissue a new power level
change command.
To disable Power Save Plus, you must uncheck the Allow EnergyWise Overrides
check box. If the Allow EnergyWise Overrides remains checked but no days are
selected in the Enable Power Save Plus field, Power Save Plus is not disabled.
Note
Allow EnergyWise Overrides
Step 4 Select Save.
Step 5 Select Apply Config.
Step 6 Restart the phone.
Set Up Do Not Disturb
When Do Not Disturb (DND) is turned on, either no audible rings occur during the ringing-in state of a call,
or no audible or visual notifications of any type occur.
When Do Not Disturb (DND) is enabled, the header section of the phone screen changes color, and Do not
disturb is displayed on the phone.
You can configure the phone with a phone-button template with DND as one of the selected features.
For more information, see the Do Not Disturb information in the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate the phone to be configured.
Step 3 Set the following parameters.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
162
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Do Not Disturb

• Do Not Disturb: This check box allows you to enable DND on the phone.
• DND Option: Ring Off, Call Reject, or Use Common Phone Profile Setting.
Do not choose Call Reject if you want priority (MLPP) calls to ring this phone when DND is turned on.
• DND Incoming Call Alert: Choose the type of alert, if any, to play on a phone for incoming calls when
DND is active.
This parameter is located on in the Common Phone Profile window and the Phone
Configuration window. The Phone Configuration window value takes precedence.
Note
Step 4 Select Save.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Enable Agent Greeting
The Agent Greeting feature allows an agent to create and update a prerecorded greeting that plays at the
beginning of a call, such as a customer call, before the agent begins the conversation with the caller. The agent
can prerecord a single greeting or multiple greetings, as needed, and create and update the greetings.
When a customer calls, the agent and the caller hear the prerecorded greeting. The agent can remain on mute
until the greeting ends or the agent can answer the call over the greeting.
All codecs supported for the phone are supported for Agent Greeting calls.
For more information, see the barge and privacy information in the documentation for your particular Cisco
Unified Communications Manager release.
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate the IP phone that you want to configure.
Step 3 Scroll to the Device Information Layout pane and set Built In Bridge to On or Default.
Step 4 Select Save.
Step 5 Check the setting of the bridge:
a) Choose System > Service Parameters.
b) Select the appropriate Server and Service.
c) Scroll to the Clusterwide Parameters (Device - Phone) pane and set Builtin Bridge Enable to On.
d) Select Save.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
163
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Enable Agent Greeting

Set Up Monitoring and Recording
The Monitoring and Recording feature allows a supervisor to monitor an active call silently. Neither party on
the call can hear the supervisor. The user may receive an audible alert during a call when it is being monitored.
When a call is secure, a lock icon displays. Callers may also receive an audible alert to indicate that the call
is being monitored. The connected parties may also receive an audible alert that indicates that the call is secure
and is being monitored.
When an active call is being monitored or recorded, the user can receive or place intercom calls; however, if
the user places an intercom call, the active call is put on hold. This action causes the recording session to
terminate and the monitoring session to suspend. To resume the monitoring session, the person being monitored
must resume the call.
For more information, see the monitoring and recording information in the documentation for your particular
Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
The following procedure adds a user to the standard monitoring user groups.
Before you begin
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager must be configured to support Monitoring and Recording.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select User Management > Application User.
Step 2 Check the Standard CTI Allow Call Monitoring user group and the Standard CTI Allow Call Recording user
groups.
Step 3 Click Add Selected.
Step 4 Click Add to User Group.
Step 5 Add the user phones to the list of Application Users controlled devices.
Step 6 Select Save.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Set Up Call Forward Notification
You can control the call forward settings.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate the phone to be set up.
Step 3 Configure the Call Forward Notification fields.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
164
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Monitoring and Recording

DescriptionField
When this check box is checked, the caller name displays in the notification
window.
By default, this check box is checked.
Caller Name
When this check box is checked, the caller number displays in the notification
window.
By default, this check box is not checked.
Caller Number
When this check box is checked, the information about the caller who last
forwarded the call displays in the notification window.
Example: If Caller A calls B, but B has forwarded all calls to C and C has
forwarded all calls to D, the notification box that D sees contains the phone
information for caller C.
By default, this check box is not checked.
Redirected Number
When this check box is checked, the information about the original recipient
of the call displays in the notification window.
Example: If Caller A calls B, but B has forwarded all calls to C and C has
forwarded all calls to D, then the notification box that D sees contains the
phone information for caller B.
By default, this check box is checked.
Dialed Number
Step 4 Select Save.
Enable BLF for Call Lists
The BLF for Call Lists field also controls the Line Status for Corporate Directory feature.
Procedure
Step 1 In the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select System > Enterprise Parameters.
Step 2 For the BLF for Call Lists field, enable or disable the feature.
By default, the feature is disabled.
Parameters that you set in the Product Specific Configuration area may also appear in the Device Configuration
window for various devices and in the Enterprise Phone Configuration window. If you set these same parameters
in these other windows as well, the setting that takes precedence is determined in the following order:
a. Device Configuration window settings
b. Common Phone Profile window settings
c. Enterprise Phone Configuration window settings
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
165
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Enable BLF for Call Lists

Step 3 Select Save.
Set Up Energy Efficient Ethernet for Switch and PC Port
IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) is an extension of the IEEE 802.3 standard that provides a
method for reducing energy usage without reducing the vital function of network interfaces. Configurable
EEE enables the administrator to control EEE functions on personal computer port and switch port.
Administrators must confirm that the Override Check box is checked on all applicable UCM pages or EEE
will not function.
Note
The administrator controls the EEE functions with the following two parameters:
• Energy Efficient Ethernet: PC Port: Provides seamless connection with personal computers.
Administrator can select Enabled or Disabled options to control the function.
• Energy Efficient Ethernet: Switch Port: Provides seamless connection
For more information, seeProduct Specific Configuration, on page 136
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select one of the following windows:
• Device > Phone
• Device > Device Settings > Common Phone Profile
• System > Enterprise Phone Configurations
If you configure the parameter in multiple windows, the precedence order is:
a. Device > Phone
b. Device > Device Settings > Common Phone Profile
c. System > Enterprise Phone Configurations
Step 2 If required, locate the phone.
Step 3 Set the Energy Efficient Ethernet: PC Port and Energy Efficient Ethernet: Switch Port fields.
• Energy Efficient Ethernet: PC Port
• Energy Efficient Ethernet: Switch Port
Step 4 Select Save.
Step 5 Select Apply Config.
Step 6 Restart the phone.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
166
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Energy Efficient Ethernet for Switch and PC Port

Set Up RTP/sRTP Port Range
You configure the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) and secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (sRTP)
port values in the SIP profile. RTP and sRTP port values range from 2048 to 65535, with a default range of
16384 to 32764. Some port values within the RTP and sRTP port range are designated for other phone services.
You cannot configure these ports for RTP and sRTP.
For more information, see SIP Profile information in the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Procedure
Step 1 Select Device > Device Settings > SIP Profile
Step 2 Choose the search criteria to use and click Find.
Step 3 Select the profile to modify.
Step 4 Set the Start Media Port and Stop Media Port to contain the start and end of the port range.
The following list identifies the UDP ports that are used for other phone services and thus not available for
RTP and sRTP use:
port 4051
used for the Peer Firmware Sharing (PFS) feature
port 5060
used for SIP over UDP transport
port range 49152 to 53247
used for local ephemeral ports
port range 53248 to 65535
used for the VxC single tunnel VPN feature
Step 5 Click Save.
Step 6 Click Apply Config.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway
Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway(MRA) lets remote workers easily and securely connect into
the corporate network without using a virtual private network (VPN) client tunnel. Expressway uses Transport
Layer Security (TLS) to secure network traffic. For a phone to authenticate an Expressway certificate and
establish a TLS session, a public Certificate Authority that the phone firmware trusts must sign the Expressway
certificate. It is not possible to install or trust other CA certificates on phones for authenticating an Expressway
certificate.
The list of CA certificates embedded in the phone firmware is available at
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/collaboration-endpoints/unified-ip-phone-8800-series/products-technical-reference-list.html.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
167
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up RTP/sRTP Port Range

Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway (MRA)works with Cisco Expressway. You must be familiar
with the Cisco Expressway documentation, including the Cisco Expressway Administrator Guide and the
Cisco Expressway Basic Configuration Deployment Guide. Cisco Expressway documentation is available at
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/unified-communications/expressway-series/tsd-products-support-series-home.html.
Only the IPv4 protocol is supported for Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway users.
For additional information about working with Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway, see:
• Cisco Preferred Architecture for Enterprise Collaboration, Design Overview
• Cisco Preferred Architecture for Enterprise Collaboration, CVD
• Unified Communications Mobile and Remote Access via Cisco VCS Deployment Guide
• Cisco TelePresence Video Communication Server (VCS), Configuration Guides
• Mobile and Remote Access Through Cisco Expressway Deployment Guide
During the phone registration process, the phone synchronizes the displayed date and time with the Network
Time Protocol (NTP) server. With MRA, the DHCP option 42 tag is used to locate the IP addresses of the
NTP servers designated for time and date synchronization. If the DHCP option 42 tag is not found in the
configuration information, the phone looks for the 0.tandberg.pool.ntp.org tag to identify the NTP servers.
After registration, the phone uses information from the SIP message to synchronize the displayed date and
time unless an NTP server is configured in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager phone configuration.
If the phone security profile for any of your phones has TFTP Encrypted Config checked, you cannot use the
phone with Mobile and Remote Access. The MRA solution does not support device interaction with Certificate
Authority Proxy Function (CAPF).
Note
Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway supports Enhanced line mode.
SIP OAuth mode is supported for MRA. This mode allows you to use OAuth access tokens for authentication
in secure environments.
For SIP OAuth in Mobile and Remote Access (MRA) mode, use only Activation Code Onboarding with
Mobile and Remote Access when you deploy the phone. Activation with a username and password is not
supported.
Note
SIP OAuth mode requires Expressway x14.0(1) and later, or Cisco Unified Communications Manager 14.0(1)
and later.
For additional information on SIP OAuth mode see Feature Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, Release 14.0(1) or later.
Deployment Scenarios
The following sections show various deployment scenarios for Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
168
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Deployment Scenarios

On-Premises User Logs In to the Enterprise Network
After Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway is deployed, log in to the enterprise network when
on-premises. The phone detects the network, and registers with Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Off-Premises User Logs In to the Enterprise Network
When you are away from the office, the phone detects that it is in off-premises mode. The Mobile and Remote
Access Through Expressway Sign-In window appears, and you connect to the corporate network.
Note the following:
• You must have a valid service domain, username, and password to connect to the network.
• Reset the service mode to clear the Alternate TFTP setting before you try to access the company network.
This clears the Alternate TFTP Server setting so the phone detects the off-premises network, and it stops
the phone from making a VPN connection. Skip this step if a phone is being deployed for the first time.
• If you have DHCP option 150 or option 66 enabled on your network router, you may not be able to sign
into the corporate network. Reset your service mode to enter MRA mode.
Off-Premises User Logs In to the Enterprise Network with VPN
When you are off-premises, log in to the enterprise network with VPN, after deploying Mobile and Remote
Access Through Expressway.
Perform a Basic Reset to reset your phone configurations if your phone experiences an error.
You must configure the Alternate TFTP setting (Admin settings > Network settings > IPv4, field Alternate
TFTP server 1).
Related Topics
Basic Reset, on page 259
Media Paths and Interactive Connectivity Establishment
You can deploy Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE) to improve the reliability of Mobile and Remote
Access (MRA) calls that cross a firewall or Network Address Translation (NAT). ICE is an optional deployment
that uses Serial Tunneling and Traversal Using Relays around NAT services to select the best media path for
a call.
Secondary Turn Server and Turn Server Failover is not supported.
For more information about MRA and ICE, see System Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications
Manager, Release 12.0(1) or later. You can also find additional information in the Internet Engineering Task
Force (IETF) Request for Comment documents:
• Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN): Relay Extensions to Session Traversal Utilities for NAT
(STUN)(RFC 5766)
• Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE): A Protocol for Network Addr ess Translator (NAT) Traversal
for Offer/Answer Protocols (RFC 5245)
Phone Features Available for Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway
Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway provides secure VPN-less access to collaboration services
for Cisco mobile and remote users. But to preserve network security, it limits access to some phone features.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
169
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Media Paths and Interactive Connectivity Establishment

The following list shows the phone features available with Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway.
Table 34: Feature Support and Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway
Phone Firmware ReleasePhone Feature
10.3(1) and laterAbbreviated Dialing
11.5(1)SR1 and laterAnswer Oldest
10.3(1) and laterAssisted Directed Call Park
11.5(1)SR1 and laterAuto Answer
11.5(1)SR1 and laterBarge and cBarge
10.3(1) and laterBusy Lamp Field (BLF)
10.3(1) and laterBusy Lamp Field (BLF) Pickup
10.3(1) and laterBusy Lamp Field (BLF) Speed Dial
10.3(1) and laterCall Back
10.3(1) and laterCall Forward
10.3(1) and laterCall Forward Notification
10.3(1) and laterCall Park
10.3(1) and laterCall Pickup
11.5(1)SR1 and laterCisco Unified Serviceability
11.5(1)SR1 and laterClient Access License (CAL)
10.3(1) and laterConference
11.5(1)SR1 and laterConference List / Remove Participant
11.5(1)SR1 and laterCorporate Directory
11.5(1)SR1 and laterCTI Applications (CTI Controlled)
10.3(1) and laterDirect Transfer
10.3(1) and laterDirected Call Park
11.5(1)SR1 and laterDistinctive Ring
10.3(1) and laterDivert
12.1(1) and laterEnhanced line mode
10.3(1) and laterDivert
11.5(1)SR1 and laterForced Access Codes and Client Matter Codes
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
170
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Phone Features Available for Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway

Phone Firmware ReleasePhone Feature
10.3(1) and laterGroup Call Pickup
10.3(1) and laterHold/Resume
10.3(1) and laterHold Reversion
10.3(1) and laterImmediate Divert
10.3(1) and laterJoin
11.5(1)SR1 and laterMalicious Caller Identification (MCID)
10.3(1) and laterMeet Me Conference
10.3(1) and laterMessage Waiting Indicator
10.3(1) and laterMobile Connect
10.3(1) and laterMobile Voice Access
11.5(1)SR1 and laterMultilevel Precedence and Preemption (MLPP)
11.5(1)SR1 and laterMultiline
10.3(1) and laterMusic On Hold
10.3(1) and laterMute
11.5(1)SR1 and laterNetwork profiles (Automatic)
10.3(1) and laterOff-hook Dialing
10.3(1) and laterOn-hook Dialing
10.3(1) and laterPlus Dialing
11.5(1)SR1 and laterPrivacy
11.5(1)SR1 and laterPrivate Line Automated Ringdown (PLAR)
10.3(1) and laterRedial
10.3(1) and laterSpeed Dial (does not support a pause)
11.5(1)SR1 and laterServices URL button
10.3(1) and laterTransfer
10.3(1) and laterUniform Resource Identifier (URI) Dialing
Configure User Credentials Persistent for Expressway Sign-In
When a user signs in to the network with Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway, the user is prompted
for a service domain, username, and password. If you enable the User Credentials Persistent for Expressway
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
171
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Configure User Credentials Persistent for Expressway Sign-In

Sign-In parameter, user login credentials are stored so that they do not need to reenter this information. This
parameter is disabled by default.
You can set up credentials to persist for a single phone, a group of phones, or all phones.
Related Topics
Phone Feature Configuration, on page 135
Product Specific Configuration, on page 136
Generate a QR Code for MRA Sign-In
Users who have a phone with a camera can scan a QR code to sign into MRA, instead of entering the service
domain and their username manually.
Procedure
Step 1 Use a QR code generator to generate a QR code with either the service domain, or the service domain and
username separated by a comma. For example: mra.example.com or mra.example.com,username.
Step 2 Print the QR code and provide it to the user.
Problem Report Tool
Users submit problem reports to you with the Problem Report Tool.
The Problem Report Tool logs are required by Cisco TAC when troubleshooting problems. The logs are
cleared if you restart the phone. Collect the logs before you restart the phones.
Note
To issue a problem report, users access the Problem Report Tool and provide the date and time that the problem
occurred, and a description of the problem.
If the PRT upload fails, you can access the PRT file for the phone from the URL
http://<phone-ip-address>/FS/<prt-file-name>. This URL is displayed on the phone in
the following cases:
• If the phone is in the factory default state. The URL is active for 1 hour. After 1 hour, the user should
try to submit the phone logs again.
• If the phone has downloaded a configuration file and the call control system allows web access to the
phone.
You must add a server address to the Customer Support UploadURL field on Cisco Unified Communications
Manager.
If you are deploying devices with Mobile and Remote Access through Expressway, you must also add the
PRT server address to the HTTP Server Allow list on the Expressway server.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
172
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Generate a QR Code for MRA Sign-In

Configure a Customer Support Upload URL
You must use a server with an upload script to receive PRT files. The PRT uses an HTTP POST mechanism,
with the following parameters included in the upload (utilizing multipart MIME encoding):
• devicename (example: “SEP001122334455”)
• serialno (example: “FCH12345ABC”)
• username (the username configured in Cisco Unified Communications Manager, the device owner)
• prt_file (example: “probrep-20141021-162840.tar.gz”)
A sample script is shown below. This script is provided for reference only. Cisco does not provide support
for the upload script installed on a customer's server.
<?php
// NOTE: you may need to edit your php.ini file to allow larger
// size file uploads to work.
// Modify the setting for upload_max_filesize
// I used: upload_max_filesize = 20M
// Retrieve the name of the uploaded file
$filename = basename($_FILES['prt_file']['name']);
// Get rid of quotes around the device name, serial number and username if they exist
$devicename = $_POST['devicename'];
$devicename = trim($devicename, "'\"");
$serialno = $_POST['serialno'];
$serialno = trim($serialno, "'\"");
$username = $_POST['username'];
$username = trim($username, "'\"");
// where to put the file
$fullfilename = "/var/prtuploads/".$filename;
// If the file upload is unsuccessful, return a 500 error and
if(!move_uploaded_file($_FILES['prt_file']['tmp_name'], $fullfilename)) {
header("HTTP/1.0 500 Internal Server Error");
die("Error: You must select a file to upload.");
}
?>
The phones only support HTTP URLs.
Note
Procedure
Step 1 Set up a server that can run your PRT upload script.
Step 2 Write a script that can handle the parameters listed above, or edit the provided sample script to suit your needs.
Step 3 Upload your script to your server.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
173
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Configure a Customer Support Upload URL

Step 4 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager, go to the Product Specific Configuration Layout area of the
individual device configuration window, Common Phone Profile window, or Enterprise Phone Configuration
window.
Step 5 Check Customer support upload URL and enter your upload server URL.
Example:
http://example.com/prtscript.php
Step 6 Save your changes.
Set the Label for a Line
You can set up a phone to display a text label instead of the directory number. Use this label to identify the
line by name or function. For example, if your user shares lines on the phone, you could identify the line with
the name of the person that shares the line.
When adding a label to a key expansion module, only the first 25 characters are displayed on a line.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate the phone to be configured.
Step 3 Locate the line instance and set the Line Text Label field.
Step 4 (Optional) If the label needs to be applied to other devices that share the line, check the Update Shared Device
Settings check box and click Propagate Selected.
Step 5 Select Save.
Set Up Dual Bank Information
To set up Dual Bank Information, follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Device Defaults.
Step 2 Check the load information in the Inactive Load Information field.
Step 3 Choose Bulk Administration > Import/Export > Export > Device Defaults, and schedule an export job.
Step 4 Download the exported tar file and untar it.
Step 5 Check the file format in the exported CSV file and verify that the CSV file has an Inactive Load Information
column with the correct value.
The CSV file value must match the Device Default value in the Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Administration window.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
174
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set the Label for a Line

Park Monitoring
Park monitoring is supported only when a Cisco IP phone parks a call. Park monitoring then monitors the
status of a parked call. The park monitoring call bubble does not clear until the parked call gets retrieved or
is abandoned by the parked call. This parked call can be retrieved by using the same call bubble on the phone
that parked the call.
Set Up Park Monitoring Timers
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration provides three cluster-wide service timer parameters
for park monitoring: Park Monitoring Reversion Timer, Park Monitoring Periodic Reversion Timer, and Park
Monitoring Forward No Retrieve Timer. Each service parameter includes a default and requires no special
configuration. These timer parameters are for park monitoring only; the Call Park Display Timer and Call
Park Reversion Timer are not used for park monitoring. See the following table for descriptions of these
parameters.
Configure the timers in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Service Parameters page.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose System > Service Parameters.
Step 2 Update the Park Monitoring Reversion Timer, Park Monitoring Periodic Reversion Timer, and Park Monitoring
Forward No Retrieve Timer fields in the Clusterwide Parameters (Feature-General) pane.
Table 35: Service Parameters for Park Monitoring
DescriptionField
Default is 60 seconds. This parameter determines the number of seconds that Cisco Unified Communications
Manager waits before prompting the user to retrieve a call that the user parked. This timer starts when the
user presses Park on the phone, and a reminder is issued when the timer expires.
You can override the value that this service parameter specifies on a per-line basis in the Park Monitoring
section of the Directory Number Configuration window (in Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration, choose Call Routing > Directory Number). Specify a value of 0 to immediately utilize
the periodic reversion interval that the Park Monitoring Periodic Reversion Timer service parameter
specifies. (See the description that follows.) For example, if this parameter is set to zero and the Park
Monitoring Periodic Reversion Timer is set to 15, the user is immediately prompted about the parked call
and every 15 seconds thereafter until the Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve Timer (see the description
that follows) expires.
Park Monitoring
Reversion Timer
Default is 30 seconds. This parameter determines the interval (in seconds) that Cisco Unified
Communications Manager waits before prompting the user again that a call is parked. To connect to the
parked call, the user can simply go off-hook during one of these prompts. Cisco Unified Communications
Manager continues to prompt the user about the parked call as long as the call remains parked and until
the time that the Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve Timer (see the description that follows) specifies
expires. Specify a value of 0 to disable periodic prompts about the parked call.
Park Monitoring
Periodic Reversion
Timer
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
175
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Park Monitoring

DescriptionField
Default is 300 seconds. This parameter determines the number of seconds that park reminder notifications
occur before the parked call forwards to the Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve destination that is
specified in the parker Directory Number Configuration window. (If no forward destination is provided in
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, the call returns to the line that parked the call.)
This parameter starts when the time that the Park Monitoring Reversion Timer service parameter specifies
expires. When the Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve Timer expires, the call is removed from park and
forwards to the specified destination or returns to the parker line.
Park Monitoring
Forward No Retrieve
Timer
Set Park Monitoring Parameters for Directory Numbers
The Directory Number Configuration window contains a Park Monitoring area where you can configure the
three parameters.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Call Routing > Directory Number.
Step 2 Set the park monitoring fields as described in the following table.
Table 36: Park Monitoring Parameters
DescriptionField
When the parkee is an external party, the call forwards to the specified
destination in the parker Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve Destination
External parameter. If the Forward No Retrieve Destination External field value
is empty, the parkee is redirected to the parker line.
Park Monitoring Forward
No Retrieve Destination
External
When the parkee is an internal party, the call forwards to the specified
destination in the parker’s Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve Destination
Internal parameter. If the Forward No Retrieve Destination Internal is empty,
the parkee is redirected to the parker line.
Park Monitoring Forward
No Retrieve Destination
Internal
This parameter determines the number of seconds that Cisco Unified
Communications Manager waits before prompting the user to retrieve a call
that the user parked. This timer starts when the user presses Park on the phone,
and a reminder is issued when the timer expires.
Default: 60 seconds
If you configure a nonzero value, this value overrides the value of this parameter
set in the Service Parameters window. However, if you configure a value of 0
here, then the value in the Service Parameters window is used.
Park Monitoring Reversion
Timer
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
176
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Park Monitoring Parameters for Directory Numbers

Set Up Park Monitoring for Hunt Lists
When a call that was routed via the hunt list is parked, the Hunt Pilot Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve
Destination parameter value is used (unless it is blank) when the Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve Timer
expires.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Call Routing > Route/Hunt > Hunt
Pilot.
Step 2 Set the Hunt Pilot Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve Destination parameter.
If the Hunt Pilot Park Monitoring Forward No Retrieve Destination parameter value is blank, the call forwards
to the destination that is configured in the Directory Number Configuration window when the Park Monitoring
Forward No Retrieve Timer expires.
Set Up the Audio and Video Port Range
Audio and video traffic can be sent to different RTP port ranges in order to improve Quality of Service (QoS).
The following fields control the port ranges in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration:
• Audio ports
• Start Media Port (default: 16384)
• Stop Media Port (default: 32766)
• Video ports
• Start Video (This is to set the video start port).
• Minimum: 2048
• Maximum: 65535
• Stop Video (This is to set the video stop port)
• Minimum: 2048
• Maximum: 65535
The following rules apply when configuring the video port fields:
After the Start Video RTP Port and Stop Video RTP Port are configured, the phone uses ports within the video
port range for video traffic. The audio traffic uses the media ports.
If the audio and video port ranges overlap, the overlapped ports carry both audio and video traffic. If the video
port range is not configured correctly, the phone uses the configured audio ports for both audio and video
traffic.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
177
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Park Monitoring for Hunt Lists

For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Device Settings > SIP Profile
Step 2 Set the Start Media Port and Stop Media Port fields for the audio port range.
Step 3 Select Save.
Step 4 Select one of the following windows:
• System > Enterprise Phone Configuration
• Device > Device Settings > Common Phone Profile
• Device > Phone > Phone Configuration
Step 5 Set the Start Video RTP Port and Stop Video RTP Port fields for the range of ports required.
The following rules apply when configuring the video port fields:
• The value in the Stop Video RTP Port field must be larger than the value in the Start Video RTP Port
field.
• The difference between the Start Video RTP Port field and the Stop Video RTP Port field must be at
least 16.
Step 6 Select Save.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Set up Cisco IP Manager Assistant
Cisco IP Manager Assistant (IPMA) provides call routing and other call management features to help managers
and assistants handle phone calls more effectively.
IPMA services must be configured in Cisco Unified Communications Manager before you can access them.
For detailed information on configuring IPMA, see the Feature Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
IPMA has three key components:
Manager
A manager has calls intercepted by the call routing service.
Assistant
An assistant handles calls on behalf of a manager.
Assistant Console
The assistant console is a desktop application assistants can use to perform tasks and manage most
features.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
178
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set up Cisco IP Manager Assistant

IPMA supports two modes of operation: proxy line support and shared line support. Both modes support
multiple calls per line for the manager. The IPMA service supports both proxy line and shared line support
in a cluster.
In shared-line mode, the manager and assistant share a directory number and calls are handled on the shared
line. Both the manager phone and the assistant phone ring when a call is received on the shared line. Shared-line
mode does not support default assistant selection, assistant watch, call filtering or divert all calls.
If you configure Cisco IPMA in shared-line mode, the manager and assistant share a directory number; for
example, 1701. The assistant handles calls for a manager on the shared directory number. When a manager
receives a call on directory number 1701, both the manager phone and the assistant phone rings.
Not all IPMA features are available in shared-line mode including default assistant selection, assistant watch,
call filtering, and divert all calls. An assistant cannot see or access these features on the Assistant Console
application. The assistant phone does not have the softkey for the Divert All feature. The manager phone does
not have the softkeys for Assistant Watch, Call Intercept, or Divert All feature.
In order to access shared-line support on user devices, you must first use Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Administration to configure and start the Cisco IP Manager Assistant service.
In proxy-line mode, the assistant handles calls on behalf of a manager using a proxy number. Proxy-line mode
supports all IPMA features.
When you configure Cisco IPMA in proxy-line mode, the manager and assistant do not share a directory
number. The assistant handles calls for a manager using a proxy number. The proxy number is not the directory
number for the manager. It is an alternate number chosen by the system and is used by an assistant to handle
manager calls. In proxy-line mode, a manager and an assistant have access to all features that are available
in IPMA, which include default assistant selection, assistant watch, call filtering, and divert all.
In order to access proxy-line support on user devices, you must first use Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Administration to configure and start the Cisco IP Manager Assistant service.
You access IPMA features using softkeys and through Phone Services. The softkey template is configured in
Cisco Unified Communications Manager. IPMA supports the following standard softkey templates:
Standard Manager
Supports manager for proxy mode.
Standard Shared Mode Manager
Supports manager for shared mode.
Standard Assistant
Supports assistant in proxy or in shared mode.
The following table describes the softkeys available in the softkey templates.
Table 37: IPMA Softkeys
DescriptionCall StateSoftkey
Divert the selected call to a
pre-configured target.
Ringing, Connected, On HoldRedirect
Divert a call from the assistant's
phone to the manager's phone and
auto answer it.
All statesIntercept
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
179
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set up Cisco IP Manager Assistant

DescriptionCall StateSoftkey
View the status of call handled by
an assistant.
All statesSet Watch
Redirect the selected call to the
manager's voice mail.
Ringing, Connected, On HoldTransVM
Divert all calls that are routed to the
manager to a preconfigured target.
All statesDivert All
Intercept, Set Watch, and Divert All should only be configured for a manager phone in proxy line mode.
Note
The following procedure is an overview of the steps required.
Procedure
Step 1 Configure the phones and users.
Step 2 Associate the phones to the users.
Step 3 Activate the Cisco IP Manager Assistant service in the Service Activation window.
Step 4 Configure system administration parameters.
Step 5 If required, configure IPMA clusterwide services parameters.
Step 6 (Optional) Configure the user CAPF profile
Step 7 (Optional) Configure the IPMA service parameters for security
Step 8 Stop and restart the IPMA service.
Step 9 Configure phone parameter, manager, and assistant settings, including the softkey templates.
Step 10 Configure Cisco Unified Communications Manager Assistant application.
Step 11 Configure dial rules.
Step 12 Install the Assistant Console application.
Step 13 Configure the manager and assistant console applications.
Set up Visual Voicemail
Visual Voicemail is configured for all Cisco IP Phones or to an individual user or group of users, from the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration.
For configuration information, see the Cisco Visual Voicemail documentation at http://www.cisco.com/c/en/
us/support/unified-communications/visual-voicemail/model.html.
Note
The Visual Voicemail client is not supported as a midlet on any of the Cisco IP Phone 8800 phones.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
180
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set up Visual Voicemail

Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Device Settings > Phone
Services.
Step 2 Select Add New to create a new service for Visual Voicemail.
Step 3 In the IP Phone Service Configuration window, enter the following information in their respective fields:
• Service Name—Enter VisualVoiceMail.
• ASCII Service Name—Enter VisualVoiceMail.
• Service URL—Enter as Application:Cisco/VisualVoiceMail.
• Service Category—Select XML Service from the pulldown menu.
• Service Type—Select Messages from the pulldown menu.
Step 4 Check Enable and click Save.
Ensure that you do not check Enterprise Subscription.
Note
Step 5 In the Service Parameter Information window, click New Parameter and enter the following information in
their respective fields:
• Parameter Name. Enter voicemail_server.
• Parameter Display Name. Enter voicemail_server.
• Default Value. Enter the hostname of the primary Unity Server.
• Parameter Description
Step 6 Check Parameter is Required and click Save.
Ensure that you do not check Parameter is a Password (mask contents).
Note
Step 7 Close the window and select Save again in the Phone Service Configuration window.
Set Up Visual Voicemail for a Specific User
Use the following procedure to configure Visual Voicemail for a specific user.
For configuration information, see the Cisco Visual Voice Mail documentation at http://www.cisco.com/c/
en/us/support/unified-communications/visual-voicemail/model.html.
Note
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Phone.
Step 2 Select the device associated to the user you are searching for.
Step 3 In the Related Links drop-down, choose Subscribe/Unsubscribe Services and click Go.
Step 4 Select the VisualVoiceMail Service you created, then choose Next > Subscribe.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
181
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Visual Voicemail for a Specific User

Visual Voicemail Setup for a User Group
To add a batch of Cisco IP phones to Cisco Unified Communications Manager with Visual Voicemail
subscribed, create a phone template in BAT tool for each phone type and in each phone template. You can
then subscribe to the Visual Voicemail service, and use the template to insert the phones.
If you already have your Cisco IP phones registered and want to get phones subscribed to the Visual Voicemail
service, create a phone template in BAT, subscribe to the Visual Voicemail service in the template, and then
use BAT tool to update phones.
For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/unified-communications/visual-voicemail/
model.html.
Assured Services SIP
Assured Services SIP(AS-SIP) is a collection of features and protocols that offer a highly secure call flow for
Cisco IP Phones and third-party phones. The following features are collectively known as AS-SIP:
• Multilevel Precedence and Preemption (MLPP)
• Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP)
• Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP)
• Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)
AS-SIP is often used with Multilevel Precedence and Preemption (MLPP) to prioritize calls during an
emergency. With MLPP, you assign a priority level to your outgoing calls, from level 1 (low) to level 5 (high).
When you receive a call, a precedence level icon displays on the phone that shows the call priority.
To configure AS-SIP, complete the following tasks on Cisco Unified Communications Manager:
• Configure a Digest User—Configure the end user to use digest authentication for SIP requests.
• Configure SIP Phone Secure Port—Cisco Unified Communications Manager uses this port to listen to
SIP phones for SIP line registrations over TLS.
• Restart Services—After configuring the secure port, restart the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
and Cisco CTL Provider services. Configure SIP Profile for AS-SIP-Configure a SIP profile with SIP
settings for your AS-SIP endpoints and for your SIP trunks. The phone-specific parameters are not
downloaded to a third-party AS-SIP phone. They are used only by Cisco Unified Manager. Third-party
phones must locally configure the same settings.
• Configure Phone Security Profile for AS-SIP—You can use the phone security profile to assign security
settings such as TLS, SRTP, and digest authentication.
• Configure AS-SIP Endpoint—Configure a Cisco IP Phone or a third-party endpoint with AS-SIP support.
• Associate Device with End Use—Associate the endpoint with a user.
• Configure SIP Trunk Security Profile for AS-SIP—You can use the sip trunk security profile to assign
security features such as TLS or digest authentication to a SIP trunk.
• Configure SIP Trunk for AS-SIP—Configure a SIP trunk with AS-SIP support.
• Configure AS-SIP Features—Configure additional AS-SIP features such as MLPP, TLS, V.150, and
IPv6.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
182
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Visual Voicemail Setup for a User Group

For detailed information about configuring AS-SIP, see the "Configure AS-SIP Endpoints" chapter, System
Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Migration of your Phone to a Multiplatform Phone Directly
You can migrate your enterprise phone to a multiplatform phone easily in one step without using transition
firmware load. All you need is to obtain and authorize the migration license from the server.
For more information, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/voice_ip_comm/cuipph/MPP/
MPP-conversion/enterprise-to-mpp/cuip_b_conversion-guide-ipphone.html
Multilevel Precedence and Preemption
Multilevel Precedence and Preemption (MLPP) allows you to prioritize calls during emergencies or other
crisis situations. You assign a priority to your outgoing calls that range from 1 to 5. Incoming calls display
an icon that shows the call priority. Authenticated users can preempt calls either to targeted stations or through
fully subscribed TDM trunks.
This capability assures high-ranking personnel of communication to critical organizations and personnel.
MLPP is often used with Assured Services SIP(AS-SIP). For detailed information about configuring MLPP,
see the "Configure Multilevel Precedence and Preemption" chapter, System Configuration Guide for Cisco
Unified Communications Manager.
Set Up Softkey Template
Using Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, you can associate a maximum of 18 softkeys
with applications that are supported by the phone. Cisco Unified Communications Manager supports the
Standard User and Standard Feature softkey template.
An application that supports softkeys has one or more standard softkey templates associated with it. You
modify a standard softkey template by copying it, renaming it, and then updating the new template. You can
also modify a nonstandard softkey template.
The Softkey Control parameter shows if softkeys of a phone are controlled by the Softkey Template feature.
The Softkey Control parameter is a required field.
For more information about configuring this feature, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
The Cisco IP Phones do not support all the softkeys that are configurable in Softkey Template Configuration
on Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration. Cisco Unified Communications Manager allows
you to enable or disable some softkeys in the control policy configuration settings. The following table lists
the features and the softkeys that can be configured on a softkey template, and identifies whether it is supported
on the Cisco IP Phones.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager allows you to configure any softkey in a softkey template, but
unsupported softkeys do not display on the phone.
Note
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
183
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Migration of your Phone to a Multiplatform Phone Directly

Table 38: Configurable Softkeys
NotesSupported as a SoftkeyConfigurable Softkeys in the Softkey Template
configuration
Feature
—SupportedAnswer (Answer)Answer
—SupportedCall Back (CallBack)Call Back
Phone displays Forward all or Forward off.SupportedForward All (cfwdAll)Call Forward All
—SupportedCall Park (Park)Call Park
—SupportedPick Up (Pickup)Call Pickup
Barge uses the built-in conference bridgeSupportedBargeBarge
cBarge uses the Cisco Unified Communications Manager conference
bridge. The softkey label is Barge.
SupportedConference BargecBarge
Conference is a dedicated button.SupportedConference (Confrn)Conference
Phone displays Show detail.SupportedConference List (ConfList)Conference List
Phone displays Decline.SupportedImmediate Divert (iDivert)Divert
Configure Do Not Disturb as a programmable line button or as a softkey.SupportedToggle Do Not Disturb (DND)Do Not Disturb
—SupportedEnd Call (EndCall)End Call
—SupportedGroup Pick UP (GPickUp)Group Pickup
Hold is a dedicated button.SupportedHold (Hold)Hold
Configure Hunt Group as a programmable feature button.SupportedHLog (HLog)Hunt Group
—Not supportedJoin (Join)Join
Configure Malicious Call Identification as a programmable feature button
or as a softkey.
SupportedToggle Malicious Call Identification (MCID)Malicious Call Identification
—SupportedMeet Me (MeetMe)Meet Me
Configure Mobile Connect as a softkey.SupportedMobility (Mobility)Mobile Connect
—SupportedNew Call (NewCall)New Call
—SupportedOther Pickup (oPickup)Other Pickup
—Not supportedQueue StatusPLK Support for Queue Statistics
Configure Quality Reporting Tool as a programmable feature button or
as a softkey.
SupportedQuality Reporting Tool (QRT)Quality Reporting Tool
—SupportedRedial (Redial)Redial
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
184
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Softkey Template

NotesSupported as a SoftkeyConfigurable Softkeys in the Softkey Template
configuration
Feature
—Not supportedRemove Last Conference Participant (Remove)Remove Last Conference
Participant
—SupportedResume (Resume)Resume
—Not supportedSelect (Select)Select
Phone displays SpeedDial.SupportedAbbreviated Dial (AbbrDial)Speed Dial
Transfer is a dedicated button.SupportedTransfer (Trfr)Transfer
—Not supportedVideo Mode Command (VidMode)Video Mode Command
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select one of the following windows:
• To configure softkey templates, select Device > Device Settings > SoftkeyTemplate.
• To assign a softkey template to a phone, select Device > Phone and configure the Softkey Template
field.
Step 2 Save the changes.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Phone Button Templates
Phone button templates let you assign speed dials and call-handling features to programmable buttons.
Call-handling features that can be assigned to buttons include Answer, Mobility, and All Calls.
Ideally, you modify templates before you register phones on the network. In this way, you can access customized
phone button template options from Cisco Unified Communications Manager during registration.
Modify Phone Button Template
For more information about IP Phone services and configuring line buttons, see the documentation for your
particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Device Settings > Phone
Button Template.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
185
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Phone Button Templates

Step 2 Click Find.
Step 3 Select the phone model.
Step 4 Select Copy, enter a name for the new template, and then select Save.
The Phone Button Template Configuration window opens.
Step 5 Identify the button that you would like to assign, and select Service URL from the Features drop-down list
that associates with the line.
Step 6 Select Save to create a new phone button template that uses the service URL.
Step 7 Choose Device > Phone and open the Phone Configuration window for the phone.
Step 8 Select the new phone button template from the Phone Button Template drop-down list.
Step 9 Select Save to store the change and then select Apply Config to implement the change.
The phone user can now access the Self Care Portal and associate the service with a button on the phone.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Assign Phone Button Template for All Calls
Assign an All Calls button in the phone template for users with multiple shared lines.
When you configure an All Calls button on the phone, users use the All Calls button to:
• See a consolidated list of current calls from all lines on the phone.
• See (under Call History) a list of all missed calls from all lines on the phone.
• Place a call on the user's primary line when the user goes off-hook. All Calls automatically defaults to
the user primary line for any outgoing call.
Procedure
Step 1 Modify the phone button template to include the All Calls button.
Step 2 Assign the template to the phone.
Set Up PAB or Speed Dial as IP Phone Service
You can modify a phone button template to associate a service URL with a programmable button. Doing so
provides users with single-button access to the PAB and Speed Dials. Before you modify the phone button
template, you must configure PAB or Speed Dials as an IP Phone service. For more information, see the
documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
To configure PAB or Speed Dial as an IP Phone service (if it is not already a service), follow these steps:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
186
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Assign Phone Button Template for All Calls

Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Device Settings > Phone
Services.
The Find and List IP Phone Services window displays.
Step 2 Click Add New.
The IP Phone Services Configuration window displays.
Step 3 Enter the following settings:
• Service Name: Enter Personal Address Book.
• Service Description: Enter an optional description of the service.
• Service URL
For PAB, enter the following URL:
http://<Unified CM-server-name>:8080/ccmpd/login.do?name=#DEVICENAME#&service=pab
For Fast Dial, enter the following URL:
http://<Unified-CM-server-name>:8080/ccmpd/login.do?name=#DEVICENAME#&service=fd
• Secure Service URL
For PAB, enter the following URL:
https://<Unified CM-server-name>:8443/ccmpd/login.do?name=#DEVICENAME#&service=pab
For Fast Dial, enter the following URL:
https://<Unified-CM-server-name>:8443/ccmpd/login.do?name=#DEVICENAME#&service=fd
• Service Category: Select XML Service.
• Service Type: Select Directories.
• Enable: Select the check box.
http://<IP_address> or https://<IP_address> (Depends on the protocol that the Cisco IP Phone supports.)
Step 4 Select Save.
If you change the service URL, remove an IP Phone service parameter, or change the name of a
phone service parameter for a phone service to which users are subscribed, you must click Update
Subscriptions to update all currently subscribed users with the changes; otherwise, users must
resubscribe to the service to rebuild the correct URL.
Note
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
187
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up PAB or Speed Dial as IP Phone Service

Modify Phone Button Template for PAB or Fast Dial
You can modify a phone button template to associate a service URL with a programmable button. Doing so
provides users with single-button access to the PAB and Speed Dials. Before you modify the phone button
template, you must configure PAB or Speed Dials as an IP Phone service.
For more information about IP Phone services and configuring line buttons, see the documentation for your
particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Device > Device Settings > Phone
Button Template.
Step 2 Click Find.
Step 3 Select the phone model.
Step 4 Select Copy, enter a name for the new template, and then select Save.
The Phone Button Template Configuration window opens.
Step 5 Identify the button that you would like to assign, and select Service URL from the Features drop-down list
that associates with the line.
Step 6 Select Save to create a new phone button template that uses the service URL.
Step 7 Choose Device > Phone and open the Phone Configuration window for the phone.
Step 8 Select the new phone button template from the Phone Button Template drop-down list.
Step 9 Select Save to store the change and then select Apply Config to implement the change.
The phone user can now access the Self Care Portal and associate the service with a button on the phone.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
VPN Configuration
The Cisco VPN feature helps you to preserve network security while giving users a safe, reliable method to
connect to your corporate network. Use this feature when:
• A phone is located outside a trusted network
• Network traffic between the phone and Cisco Unified Communications Manager crosses an untrusted
network
With a VPN, there are three common approaches to client authentication:
• Digital certificates
• Passwords
• Username and password
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
188
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Modify Phone Button Template for PAB or Fast Dial

Each method has its advantages. But if your corporate security policy permits it, we recommend a
certificate-based approach because certificates allow for a seamless sign-in without any user intervention.
Both LSC and MIC certificates are supported.
To configure any of the VPN features, provision the device on-premises first and then you can deploy the
device off-premise.
For more information about certification authentication and working with VPN network, see the Technical
Note AnyConnect VPN Phone with Certificate Authentication on an ASA Configuration Example. The URL
for this document is
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/unified-communications/unified-communications-manager-callmanager/115785-anyconnect-vpn-00.html.
With a password, or username and password approach a user is prompted for sign-in credentials. Set the user
sign-in credentials in accordance with your company security policy. You can also configure the Enable
Password Persistence setting so that the user password is saved on the phone. The user password is saved
until either a failed log-in attempt occurs, a user manually clears the password, or the phone resets or loses
power.
Another useful tool is the Enable Auto Network Detection setting. When you enable this check box, the VPN
client can only run when it detects that it is outside the corporate network. This setting is disabled by default.
Your Cisco phone supports Cisco SVC IPPhone Client v1.0 as the client type.
For additional information about maintaining, configuring, and operating a virtual private network with a
VPN, see Security Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager, "Virtual Private Network Setup"
chapter. The URL for this document is
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/unified-communications/unified-communications-manager-callmanager/products-maintenance-guides-list.html.
The Cisco VPN feature uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to preserve network security.
Enter the Alternate TFTP server setting when you're configuring an off-premises phone for SSL VPN to ASA
using a built-in client.
Note
Set Up Additional Line Keys
Enable Enhanced line mode to use the buttons on both sides of the phone screen as line keys. Predictive dialing
and Actionable incoming call alerts are enabled by default in Enhanced line mode.
Before you begin
You must create a new, customized phone button template.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Locate the phone that you need to set up.
Step 3 Navigate to the Product Specific Configuration area and set the Line Mode field to Enhanced Line Mode.
Step 4 Navigate to the Device Information area and set the Phone Button Template field to a customized template.
Step 5 Select Apply Config.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
189
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Additional Line Keys

Step 6 Select Save.
Step 7 Restart the phone.
Related Topics
Session Line Mode Environment, on page 155
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode
Enhanced line mode (ELM) can be used with Mobile and Remote Access Through Expressway.
ELM can also be used with a rollover line, a call routing configuration in which calls are forwarded to another
shared line if the initial shared line is busy. When ELM is used with a rollover line, recent calls to shared lines
are consolidated under a single directory number. For more information about rollover lines, see Feature
Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
12.0(1) or later.
ELM supports most but not all features. Enabling a feature does not imply support. Read the following table
to confirm that a feature is supported.
Table 39: Feature Support and Enhanced Line Mode
Firmware ReleaseSupportedFeature
11.5(1) and laterYesAnswer
11.5(1) and laterYesAutomatically Answer Calls
11.5(1) and laterYesBarge/cBarge
12.0(1) and laterYesDirected Call Park with BLF
-NoBluetooth Smartphone integration
11.5(1) and laterYesBluetooth USB Headsets
11.5(1) and laterYesCall Back
-NoCall Chaperone
11.5(1) and laterYesCall Forward All
12.0(1) and laterYesCall Park
12.0(1) and laterYesCall Park Line Status
11.5(1) and laterYesCall Pickup
11.5(1) and laterYesCall Pickup Line Status
11.5(1) and laterYesCall Forward All on Multiple Lines
12.0(1) and later supports this
feature.
YesCisco Extension Mobility Cross
Cluster
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
190
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode

Firmware ReleaseSupportedFeature
-NoCisco IP Manager Assistant
(IPMA)
-NoCisco Unified Communications
Manager Express
11.5(1) and laterYesConference
11.5(1) and laterYesComputer Telephony Integration
(CTI) applications
11.5(1) and laterYesDecline
11.5(1)SR1 and laterYesDevice Invoked Recording
11.5(1) and laterYesDo Not Disturb
-NoEnhanced SRST
11.5(1) and laterYesExtension Mobility
12.0(1) and later supports this
feature.
YesGroup Pickup
11.5(1) and laterYesHold
12.0(1) and laterYes.Hunt Groups
-NoIncoming Call Alert with
configurable timer
11.5(1) and laterYesIntercom
12.0(1) and laterCisco IP Phone 8851/8861 Key
Expansion Module and Cisco IP
Phone 8865 Key Expansion
Module support Enhanced Line
Mode
Key Expansion Module
11.5(1) and laterYesMalicious Call Identification
(MCID)
11.5(1) and laterYesMeet Me
11.5(1) and laterYesMobile Connect
-NoMultilevel Precedence and
Preemption
11.5(1) and laterYesMute
12.0(1) and laterYesOther PickUp
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
191
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Features Available in Enhanced Line Mode

Firmware ReleaseSupportedFeature
11.5(1) and laterYesProgrammable Line Key (PLK)
Support for Queue Status
11.5(1) and laterYesPrivacy
11.5(1) and laterYesQueue Status
11.5(1) and laterYesQuality Reporting Tool (QRT)
-NoRight to Left locale support
11.5(1) and laterYesRedial
11.5(1)SR1 and laterYesSilent Monitoring and Recording
11.5(1) and laterYesSpeed Dial
11.5(1) and laterYesSurvivable Remote Site Telephony
(SRST)
11.5(1) and laterYesTransfer
11.5(1) and laterYesUniform Resource Identifier (URI)
Dialing
11.5(1) and laterYesVideo Calls
11.5(1) and laterYesVisual Voicemail
11.5(1) and laterYesVoicemail
Related Topics
Session Line Mode Environment, on page 155
Set Up TLS Resumption Timer
TLS Session resumption enables a TLS session to resume without repeating the entire TLS authentication
process. It can significantly reduce the time taken for TLS connection to exchange data.
Although the phones support TLS sessions, all TLS sessions do not support TLS resumption. The following
list describes the different sessions and TLS resumption support:
• TLS session for SIP signaling: supports resumption
• HTTPs client: supports resumption
• CAPF: supports resumption
• TVS: supports resumption
• EAP-TLS: does not support resumption
• EAP-FAST: does not support resumption
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
192
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up TLS Resumption Timer

• VPN client: does not support resumption
For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Set the TLS Resumption Timer parameter.
The range for the timer is 0 to 3600 sec. The default value is 3600. If the field is set to 0, then TLS session
resumption is disabled.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Enable Intelligent Proximity
This procedure only applies to Bluetooth enabled phones. Cisco IP Phone 8811, 8841, 8851NR, and 8865NR
do not support Bluetooth.
Note
Intelligent Proximity enables users to take advantage of the acoustic properties of the phone with their mobile
device or tablet. The user pairs the mobile device or tablet to the phone using Bluetooth.
With a mobile device paired, the user can place and receive mobile calls on the phone. With a tablet, the user
can route the audio from the tablet to the phone.
Users can pair multiple mobile devices, tablets, and a Bluetooth headset to the phone. However, only one
device and one headset can be connected at the same time.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select Phone > Device.
Step 2 Locate the phone you want to modify.
Step 3 Locate the Bluetooth field and set the field to Enabled.
Step 4 Locate the Allow Bluetooth Mobile Handsfree Mode field, and set the field to Enabled.
Step 5 Save the changes and apply them to the phone.
Video Transmit Resolution Setup
Cisco IP Phone 8845, 8865, and 8865NR supports the following video formats:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
193
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Enable Intelligent Proximity

• 720p (1280x720)
• WVGA(800x480)
• 360p (640x360)
• 240p (432x240)
• VGA (640x480)
• CIF (352x288)
• SIF (352x240)
• QCIF (176x144)
Cisco IP Phones with video capacity negotiate best resolution for bandwidth based on phone configures or
resolution limitations. Example: On a direct 88x5 to 88x5 call, the phones do not send true 720p, they send
800x480. This limitation is purely due to the 5-inch WVGA screen resolution on the 88x5 being 800 x 480.
Video bit rate rangeFrames per second (fps)Video resolutionVideo type
1360–2500 kbps301280 x 720720p
790–1359 kbps151280 x 720720p
660–789 kbps30800 x 480WVGA
350–399 kbps15800 x 480WVGA
400–659 kbps30640 x 360360p
210–349kbps15640 x 360360p
180–209kbps30432 x 240240p
64–179kbps15432 x 240240p
520–1500kbps30640 x 480VGA
280–519kbps15640 x 480VGA
200–279 kbps30352 x 288CIF
120–199 kbps15352 x 288CIF
200–279 kbps30352 x 240SIF
120–199 kbps15352 x 240SIF
94–119 kbps30176 x 144QCIF
64–93 kbps15176 x 144QCIF
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
194
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Video Transmit Resolution Setup

Headset Management on Older Versions of Cisco Unified
Communications Manager
If you have a version of Cisco Unified Communications Manager older than 12.5(1)SU1, you can remotely
configure your Cisco headset settings for use with on-premises phones.
Remote headset configuration on Cisco Unified Communication Manager version 10.5(2), 11.0(1), 11.5(1),
12.0(1), and 12.5(1) requires you to download a file from the Cisco Software Download website, edit the file,
and then upload the file on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager TFTP server. The file is a JavaScript
Object Notification (JSON) file. The updated headset configuration is applied to the enterprise headsets over
a 10 to 30-minute time frame to prevent a traffic backlog on the TFTP server.
You can manage and configure headsets through Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration
version 11.5(1)SU7.
Note
Note the following as you work with the JSON file:
• The settings aren't applied if you are missing a bracket or brackets in the code. Use an online tool such
as JSON Formatter and check the format.
• Set the updatedTime setting to the current epoch time or the configuration is not applied. Alternatively,
you can increase the updatedTime value by +1 to make it larger than the previous version.
• Do not change the parameter name or the setting will not be applied.
For more information on the TFTP service, see the "Manage Device Firmware" chapter of the Administration
Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager and IM and Presence Service.
Upgrade your phones to the latest firmware release before you apply the defaultheadsetconfig.json
file. The following table describes the default settings you can adjust with the JSON file.
Download the Default Headset Configuration File
Before configuring the headset parameters remotely, you must download the latest JavaScript Object Notation
(JSON) sample file.
Procedure
Step 1 Go to the following URL: https://software.cisco.com/download/home/286320550.
Step 2 Choose Headsets 500 Series.
Step 3 Select your headset series.
Step 4 Choose a release folder and select the zip file.
Step 5 Click the Download or Add to cart button, and follow the prompts.
Step 6 Unzip the file to a directory on your PC.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
195
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Headset Management on Older Versions of Cisco Unified Communications Manager

What to do next
Modify the Default Headset Configuration File, on page 196
Modify the Default Headset Configuration File
Note the following as you work with the JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) file:
• The settings aren't applied if you are missing a bracket or brackets in the code. Use an online tool such
as JSON Formatter and check the format.
• Set the "updatedTime" setting to the current epoch time or the configuration is not applied.
• Confirm that firmwareName is LATEST or the configurations will not be applied.
• Do not change a parameter name or the setting will not be applied.
Procedure
Step 1 Open the defaultheadsetconfig.json file with a text editor.
Step 2 Edit the updatedTime and the headset parameter values you wish to modify.
A sample script is shown below. This script is provided for reference only. Use it as a guide as you configure
your headset parameters. Use the JSON file that was included with your firmware load.
{
"headsetConfig": {
"templateConfiguration": {
"configTemplateVersion": "1",
"updatedTime": 1537299896,
"reportId": 3,
"modelSpecificSettings": [
{
"modelSeries": "530",
"models": [
"520",
"521",
"522",
"530",
"531",
"532"
],
"modelFirmware": [
{
"firmwareName": "LATEST",
"latest": true,
"firmwareParams": [
{
"name": "Speaker Volume",
"access": "Both",
"usageId": 32,
"value": 7
},
{
"name": "Microphone Gain",
"access": "Both",
"usageId": 33,
"value": 2
},
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
196
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Modify the Default Headset Configuration File

{
"name": "Sidetone",
"access": "Both",
"usageId": 34,
"value": 1
},
{
"name": "Equalizer",
"access": "Both",
"usageId": 35,
"value": 3
}
]
}
]
},
{
"modelSeries": "560",
"models": [
"560",
"561",
"562"
],
"modelFirmware": [
{
"firmwareName": "LATEST",
"latest": true,
"firmwareParams": [
{
"name": "Speaker Volume",
"access": "Both",
"usageId": 32,
"value": 7
},
{
"name": "Microphone Gain",
"access": "Both",
"usageId": 33,
"value": 2
},
{
"name": "Sidetone",
"access": "Both",
"usageId": 34,
"value": 1
},
{
"name": "Equalizer",
"access": "Both",
"usageId": 35,
"value": 3
},
{
"name": "Audio Bandwidth",
"access": "Admin",
"usageId": 36,
"value": 0
},
{
"name": "Bluetooth",
"access": "Admin",
"usageId": 39,
"value": 0
},
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
197
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Modify the Default Headset Configuration File

{
"name": "DECT Radio Range",
"access": "Admin",
"usageId": 37,
"value": 0
}
{
"name": "Conference",
"access": "Admin",
"usageId": 41,
"value": 0
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
Step 3 Save the defaultheadsetconfig.json.
What to do next
Install the default configuration file.
Install the Default Configuration File on Cisco Unified Communications
Manager
After you edit the defaultheadsetconfig.json file, install it on Cisco Unified Communications
Manager using the TFTP File Management tool.
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified OS Administration, choose Software Upgrades > TFTP File Management.
Step 2 Select Upload File.
Step 3 Select Choose File and navigate to the defaultheadsetconfig.json file.
Step 4 Select Upload File.
Step 5 Click Close.
Restart the Cisco TFTP Server
After you upload the defaultheadsetconfig.json file to the TFTP directory, restart the Cisco TFTP
server and reset the phones. After about 10–15 minutes, the download process begins and the new configurations
are applied to the headsets. It takes an additional 10 to 30 minutes for the settings to be applied.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
198
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Install the Default Configuration File on Cisco Unified Communications Manager

Procedure
Step 1 Log in to Cisco Unified Serviceability and choose Tools > Control Center - Feature Services.
Step 2 From the Server drop-down list box, choose the server on which the Cisco TFTP service is running.
Step 3 Click the radio button that corresponds to the Cisco TFTP service.
Step 4 Click Restart.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
199
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Restart the Cisco TFTP Server

Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
200
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Restart the Cisco TFTP Server

CHAPTER 10
Corporate and Personal Directory
• Corporate Directory Setup, on page 201
• Personal Directory Setup, on page 201
• User Personal Directory Entries Setup, on page 202
Corporate Directory Setup
The Corporate Directory allows a user to look up phone numbers for coworkers. To support this feature, you
must configure corporate directories.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager uses a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory to
store authentication and authorization information about users of Cisco Unified Communications Manager
applications that interface with Cisco Unified Communications Manager. Authentication establishes user
rights to access the system. Authorization identifies the telephony resources that a user is permitted to use,
such as a specific phone extension.
Cisco IP Phones use dynamic allocation for SecureApp on both client and servers. This ensures your phone
can read certificates larger than 4KB, and reduces the frequency of Host Not Found error messages when a
user accesses their directory.
For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
After you complete the LDAP directory configuration, users can use the Corporate Directory service on their
phone to look up users in the corporate directory.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Personal Directory Setup
The Personal Directory allows a user to store a set of personal numbers.
Personal Directory consists of the following features:
• Personal Address Book (PAB)
• Speed Dials
• Address Book Synchronization Tool (TABSynch)
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
201

Users can use these methods to access Personal Directory features:
• From a web browser—Users can access the PAB and Speed Dials features from the Cisco Unified
Communications Self Care Portal.
• From the CiscoIP Phone—Choose Contacts to search the corporate directory or the user personal
directory.
• From a Microsoft Windows application—Users can use the TABSynch tool to synchronize their PABs
with Microsoft Windows Address Book (WAB). Customers who want to use the Microsoft Outlook
Address Book (OAB) should begin by importing the data from the OAB into the WAB. TabSync can
then be used to synchronize the WAB with Personal Directory. For instructions about TABSync, see
Download Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer, on page 202 and Set Up Synchronizer, on page
203.
Cisco IP Phones use dynamic allocation for SecureApp on both client and servers. This ensures your phone
can read certificates larger than 4KB, and reduces the frequency of Host Not Found error messages when a
user accesses their directory.
To ensure that Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer users access only their end-user data, activate the
Cisco UXL Web Service in Cisco Unified Serviceability.
To configure Personal Directory from a web browser, users must access their Self Care Portal. You must
provide users with a URL and sign-in information.
User Personal Directory Entries Setup
Users can configure personal directory entries on the Cisco IP Phone. To configure a personal directory, users
must have access to the following:
• Self Care Portal: Make sure that users know how to access their Self Care Portal. See Set Up User Access
to the Self Care Portal, on page 77 for details.
• Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer: Make sure to provide users with the installer. See Download
Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer, on page 202.
The Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer is only supported on unsupported
versions of Windows (for example, Windows XP and earlier). The tool is not
supported on newer versions of Windows. In future, it will be removed from the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager plug-ins list.
Note
Download Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer
To download a copy of the synchronizer to send to your users, follow these steps:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
202
Cisco IP Phone Administration
User Personal Directory Entries Setup

Procedure
Step 1 To obtain the installer, choose Application > Plugins from Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration.
Step 2 Select Download, which is located next to the Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer plugin name.
Step 3 When the file download dialog box displays, select Save.
Step 4 Send the TabSyncInstall.exe file and the instructions in Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer
Deployment, on page 203 to all users who require this application.
Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer Deployment
The Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer synchronizes data that is stored in your Microsoft Windows
address book with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager directory and the Self Care Portal Personal
Address Book.
To successfully synchronize the Windows address book with the Personal Address Book, all Windows address
book users should be entered in the Windows address book before you perform the following procedures.
Tip
Install Synchronizer
To install the Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer, follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 Get the Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer installer file from your system administrator.
Step 2 Double-click the TabSyncInstall.exe file that your administrator provided.
Step 3 Select Run.
Step 4 Select Next.
Step 5 Read the license agreement information, and select the I Accept. Select Next.
Step 6 Choose the directory in which you want to install the application and select Next.
Step 7 Select Install.
Step 8 Select Finish.
Step 9 To complete the process, follow the steps in Set Up Synchronizer, on page 203.
Set Up Synchronizer
To configure the Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer, perform these steps:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
203
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer Deployment

Procedure
Step 1 Open the Cisco IP Phone Address Book Synchronizer.
If you accepted the default installation directory, you can open the application by choosing Start > All
Programs > Cisco Systems > TabSync.
Step 2 To configure user information, select User.
Step 3 Enter the Cisco IP Phone user name and password and select OK.
Step 4 To configure Cisco Unified Communications Manager server information, select Server.
Step 5 Enter the IP address or host name and the port number of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server
and select OK.
If you do not have this information, contact your system administrator.
Step 6 To start the directory synchronization process, select Synchronize.
The Synchronization Status window provides the status of the address book synchronization. If you chose the
user intervention for duplicate entries rule and you have duplicate address book entries, the Duplicate Selection
window displays.
Step 7 Choose the entry that you want to include in your Personal Address Book and select OK.
Step 8 When synchronization is complete, select Exit to close the Cisco Unified CallManager Address Book
Synchronizer.
Step 9 To verify whether the synchronization worked, sign in to your Self Care Portal and choose Personal Address
Book. The users from your Windows address book should be listed.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
204
Cisco IP Phone Administration
Set Up Synchronizer

CHAPTER 11
Monitoring Phone Systems
• Cisco IP Phone Status, on page 207
• Cisco IP Phone Web Page, on page 222
• Request Information from the Phone in XML, on page 237
Cisco IP Phone Status
This section describes how to view model information, status messages, and network statistics on the Cisco
IP Phone 8800 series.
• Model Information: Displays hardware and software information about the phone.
• Status menu: Provides access to screens that display the status messages, network statistics, and statistics
for the current call.
You can use the information that displays on these screens to monitor the operation of a phone and to assist
with troubleshooting.
You can also obtain much of this information, and obtain other related information, remotely through the
phone web page.
For more information about troubleshooting, see Troubleshooting, on page 241.
Display Phone Information Window
To display the Model Information screen, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Select Phone Information.
If the user is connected to a secure or authenticated server, a corresponding icon (lock or certificate) displays
in the Phone Information Screen to the right of the server option. If the user is not connected to a secure or
authenticated server, no icon appears.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
207

Step 3 To exit the Model Information screen, press Exit.
Phone Information Fields
The following table describes the phone information settings.
Table 40: Phone Information Settings
DescriptionOption
Model number of the phone.Model number
IP address of the phone.IPv4 Address
Host name of the phone.Host name
Version of firmware currently installed on the phone. The user can
press Details for more information.
Active load
Inactive load appears only when a download is in progress. A
download icon and a status of “Upgrade in Progress” or “Upgrade
Failed” also display. If a user presses Details during an upgrade, the
download filename and components are listed.
A new firmware image can be set to download in advance of a
maintenance window. Thus instead of waiting for all of the phones
to download the firmware, the system switches more rapidly between
resetting an existing load to Inactive status and installing the new
load.
When the download is complete, the icon changes to indicate the
completed status; and a check mark displays for a successful
download, or an “X” displays for a failed download. If possible, the
rest of the loads continue to download.
Inactive load
Date of the most recent firmware upgrade.Last upgrade
Domain name of the server to which the phone is registered.Active server
Domain name of the standby server.Stand-by server
Display Status Menu
The Status menu includes the following options, which provide information about the phone and phone
operations:
• Status Messages: Displays the Status Messages screen, which shows a log of important system messages.
• Ethernet Statistic: Displays the Ethernet Statistics screen, which shows Ethernet traffic statistics.
• Wireless Statistics: Displays the Wireless Statistics screen, if applicable.
• Call Statistics: Displays counters and statistics for the current call.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
208
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Phone Information Fields

• Current Access Point: Displays the Current Access Point screen, if applicable.
To display the Status menu, perform these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 To display the Status menu, press Applications .
Step 2 Select Admin settings > Status.
Step 3 To exit the Status menu, press Exit.
Display Status Messages Window
The Status Messages window displays the 30 most recent status messages that the phone has generated. You
can access this screen at any time, even if the phone has not finished starting up.
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Select Admin settings > Status > Status messages.
Step 3 To remove the current status messages, press Clear.
Step 4 To exit the Status Messages screen, press Exit.
Status Messages Fields
The following table describes the status messages that display on the Status Messages screen of the phone.
Table 41: Status Messages on the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Possible explanation and actionDescriptionMessage
Power cycle the phone.The configuration file is too large for file system on the
phone.
CFG TFTP Size Error
Obtain a new copy of the phone firmware and place it in
the TFTPPath directory. You should only copy files into
this directory when the TFTP server software is shut down;
otherwise, the files may be corrupted.
Downloaded software file is corrupted.Checksum Error
Confirm that the DHCP server is available and that an IP
address is available for the phone.
The phone has not previously obtained an IP address from
a DHCP Server. This can occur when you perform an out
of box or factory reset.
Could not acquire an IP address from DHCP
None. This message is informational only. Neither the CTL
file nor the ITL file was installed previously.
The CTL and ITL files are installed on the phone.CTL and ITL installed
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
209
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Display Status Messages Window

Possible explanation and actionDescriptionMessage
None. This message is informational only. The CTL file
was not installed previously.
A certificate trust list (CTL) file is installed in the phone.CTL Installed
Problem with the CTL file on the TFTP server.The phone could not update the certificate trust list (CTL)
file.
CTL update failed
Network is busy: The errors should resolve themselves when
the network load reduces.
No network connectivity between the DHCP server and the
phone: Verify the network connections.
DHCP server is down: Check configuration of DHCP server.
Errors persist: Consider assigning a static IP address.
DHCP server did not respond.DHCP timeout
Network is busy: The errors should resolve themselves when
the network load reduces.
No network connectivity between the DNS server and the
phone: Verify the network connections.
DNS server is down: Check configuration of the DNS server.
DNS server did not respond.DNS timeout
Verify that the host names of the TFTP server or Cisco
Unified Communications Manager are configured properly
in DNS.
Consider using IP addresses rather than host names
DNS could not resolve the name of the TFTP server or
Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
DNS unknown host
If the phone has a static IP address, verify that you did not
assigned a duplicate IP address.
If you are using DHCP, check the DHCP server
configuration.
Another device is using the IP address that is assigned to
the phone.
Duplicate IP
None. This message is informational only.Erasing CTL or ITL file.Erasing CTL and ITL files
From Cisco Unified Operating System Administration, check
that the following files are located within subdirectories in
the TFTP File Management:
• Located in subdirectory with same name as network
locale:
• tones.xml
• Located in subdirectory with same name as user locale:
• glyphs.xml
• dictionary.xml
• kate.xml
One or more localization files could not be found in the
TFTPPath directory or were not valid. The locale was not
changed.
Error update locale
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
210
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Status Messages Fields

Possible explanation and actionDescriptionMessage
The configuration file for a phone is created when the phone
is added to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
database. If the phone does not exist in the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager database, the TFTP server
generates a CFG File Not Found response.
• Phone is not registered with Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
You must manually add the phone to Cisco Unified
Communications Manager if you are not allowing
phones to autoregister. See Phone Addition Methods,
on page 68 for details.
• If you are using DHCP, verify that the DHCP server
is pointing to the correct TFTP server.
• If you are using static IP addresses, check configuration
of the TFTP server.
The name-based and default configuration file was not
found on the TFTP Server.
File not found <Cfg File>
No impact; the phone can still register to Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
This message displays on the phone when the Cisco
Unified Communications Manager cluster is not in secure
mode.
File Not Found <CTLFile.tlv>
The phone remains idle until it is power cycled or until you
reset the DHCP address.
The phone is configured to release the IP address.IP address released
None. This message is informational only. The ITL file was
not installed previously.
The ITL file is installed in the phone.ITL installed
Occurs if you attempted to install a version of software on
this phone that did not support hardware changes on this
phone.
Check the load ID that is assigned to the phone (from Cisco
Unified Communications Manager, choose Device >
Phone). Reenter the load that displays on the phone.
The application that was downloaded is not compatible
with the phone hardware.
Load rejected HC
If the phone has a static IP address, verify that the default
router is configured.
If you are using DHCP, the DHCP server has not provided
a default router. Check the DHCP server configuration.
DHCP or static configuration did not specify a default
router.
No default router
If the phone has a static IP address, verify that the DNS
server is configured.
If you are using DHCP, the DHCP server has not provided
a DNS server. Check the DHCP server configuration.
A name was specified but DHCP or static IP configuration
did not specify a DNS server address.
No DNS server IP
The trust list is not configured on the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager, which does not support security
by default.
The CTL file or the ITL file is not installed on the phone.No Trust List installed
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
211
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Status Messages Fields

Possible explanation and actionDescriptionMessage
Update the certificate.FIPS requires that the RSA server certificate is 2048 bits
or greater.
Phone failed to register. Cert key size is not FIPS
compliant.
Configuration changes were likely made to the phone in
Cisco Unified Communications Manager, and Apply was
pressed so that the changes take effect.
The phone is restarting due to on a request from Cisco
Unified Communications Manager.
Restart requested by Cisco Unified
Communications Manager
If you are using DHCP, verify that the DHCP server is
pointing to the correct TFTP server.
If you are using static IP addresses, check configuration of
TFTP server.
TFTP server is pointing to a directory that does not exist.TFTP access error
Contact Cisco TAC.The phone does not recognize an error code that the TFTP
server provided.
TFTP error
Network is bus: The errors should resolve themselves when
the network load reduces.
No network connectivity between the TFTP server and the
phone: Verify the network connections.
TFTP server is down: Check configuration of TFTP server.
TFTP server did not respond.TFTP timeout
Authentication typically times out if 802.1X is not
configured on the switch.
Supplicant attempted 802.1X transaction but timed out to
due the absence of an authenticator.
Timed Out
Phone has CTL and ITL files installed and it failed to update
the new CTL and ITL files.
Possible reasons for failure:
• Network failure occurred.
• TFTP server was down.
• The new security token that was used to sign CTL file
and the TFTP certificate that was used to sign ITL file
are introduced, but are not available in the current CTL
and ITL files in the phone.
• Internal phone failure occurred.
Possible solutions:
• Check network connectivity.
• Check whether the TFTP server is active and
functioning normally.
• If the Transactional Vsam Services (TVS) server is
supported on Cisco Unified Communications Manager,
check whether the TVS server is active and functioning
normally.
• Verify whether the security token and the TFTP server
are valid.
Manually delete the CTL and ITL files if all the preceding
solutions fail; reset the phone.
Update of the CTL and ITL files failed.Trust List update failed
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
212
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Status Messages Fields

Possible explanation and actionDescriptionMessage
None. This message is informational only.The CTL file, the ITL file, or both files are updated.Trust List updated
Make sure that the phone load file has the correct name.The name of the phone load file is incorrect.Version error
None. This message indicates the name of the configuration
file for the phone.
Name of the configuration file.XmlDefault.cnf.xml, or .cnf.xml corresponding to
the phone device name
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Display Network Information Screen
Use the information displayed on the Network Info screen to resolve connection issues on a phone.
A message is displayed on the phone if a user has trouble connecting to a phone network.
Procedure
Step 1 To display the Status menu, press Applications .
Step 2 Select Admin settings > Status > Status messages.
Step 3 Select Network Info.
Step 4 To exit Network Info, press Exit.
Display Network Statistics Screen
The Networks Statistics screen displays information about the phone and network performance.
To display the Network Statistics screen, follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Select Admin settings>Status>Network statistics.
Step 3 To reset the Rx Frames, Tx Frames, and Rx Broadcasts statistics to 0, press Clear.
Step 4 To exit the Ethernet Statistics screen, press Exit.
Ethernet Statistics Information
The following tables describe the information in the Ethernet Statistics screen.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
213
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Display Network Information Screen

Table 42: Ethernet Statistics Information
DescriptionItem
Number of packets that the phone received.Rx Frames
Number of packets that the phone sent.Tx Frames
Number of broadcast packets that the phone received.Rx Broadcasts
Cause of the last reset of the phone. Specifies one of the following values:
• Initialized
• TCP-timeout
• CM-closed-TCP
• TCP-Bad-ACK
• CM-reset-TCP
• CM-aborted-TCP
• CM-NAKed
• KeepaliveTO
• Failback
• Phone-Keypad
• Phone-Re-IP
• Reset-Reset
• Reset-Restart
• Phone-Reg-Rej
• Load Rejected HC
• CM-ICMP-Unreach
• Phone-Abort
Restart Cause
Amount of time that has elapsed since the phone last rebooted.Elapsed Time
Link state and connection of the Network port. For example, Auto 100
Mb Full-Duplex means that the Network port is in a link-up state
and has autonegotiated a full-duplex, 100-Mbps connection.
Port 1
Link state and connection of the PC port.Port 2
• In IPv4-only mode, displays only the DHCPv4 state, such as DHCP
BOUND.
• In IPv6-mode, displays only the DHCPv6 state, such as ROUTER
ADVERTISE.
• DHCPv6 state information is displayed.
DHCP state (IPv4 / IPv6)
The following tables describe the messages that appear for DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 states.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
214
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Ethernet Statistics Information

Table 43: DHCPv4 ethernet statistics messages
DescriptionDHCPv4 state
CDP is not bound or WLAN is not in serviceCDP INIT
DHCPv4 is BOUNDDHCP BOUND
DHCPv4 is disabledDHCP DISABLED
DHCPv4 is INITDHCP INIT
DHCPv4 is INVALID; this is initial stateDHCP INVALID
DHCPv4 is RENEWINGDHCP RENEWING
DHCPv4 is REBINDINGDHCP REBINDING
DHCPv4 is init-rebootDHCP REBOOT
DHCPv4 is requestingDHCP REQUESTING
DHCPv4 is RESYNCHDHCP RESYNC
DHCPv4 is bootingDHCP WAITING COLDBOOT TIMEOUT
Unrecognized DHCPv4 stateDHCP UNRECOGNIZED
Duplicated IPv4 AddressDISABLED DUPLICATE IP
DHCPv4 TimeoutDHCP TIMEOUT
Phone is in IPv6-only mode with IPv4 Stack turned
off
IPV4 STACK TURNED OFF
Illegal IPv4 state and should not happenILLEGAL IPV4 STATE
Table 44: DHCPv6 ethernet statistics messages
DescriptionDHCPv6 State
CDP is initializingCDP INIT
DHCPv6 is BOUNDDHCP6 BOUND
DHCPv6 is DISABLEDDHCP6 DISABLED
DHCPv6 is renewingDHCP6 RENEW
DHCPv6 is rebindingDHCP6 REBIND
DHCPv6 is initializingDHCP6 INIT
DHCPv6 is solicitingDHCP6 SOLICIT
DHCPv6 is requestingDHCP6 REQUEST
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
215
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Ethernet Statistics Information

DescriptionDHCPv6 State
DHCPv6 is releasingDHCP6 RELEASING
DHCPv6 is releasedDHCP6 RELEASED
DHCPv6 is disablingDHCP6 DISABLING
DHCPv6 is decliningDHCP6 DECLINING
DHCPv6 is declinedDHCP6 DECLINED
DHCPv6 is INFOREQDHCP6 INFOREQ
DHCPv6 is INFOREQ DONEDHCP6 INFOREQ DONE
DHCPv6 is INVALID; this is initial stateDHCP6 INVALID
DHCP6 is DISABLED, but DUPLICATE IPV6
DETECTED
DISABLED DUPLICATE IPV6
DHCP6 is DECLINED -- DUPLICATE IPV6
DETECTED
DHCP6 DECLINED DUPLICATE IP
Duplicated autoconfigured IPv6 addressROUTER ADVERTISE., (DUPLICATE IP)
DHCPv6 is bootingDHCP6 WAITING COLDBOOT TIMEOUT
DHCPv6 timeout, using the value saved in flash
memory
DHCP6 TIMEOUT USING RESTORED VAL
DHCP6 timeout and there is no backup from flash
memory
DHCP6 TIMEOUT CANNOT RESTORE
Phone is in IPv4-only mode with IPv6 Stack turned
off
IPV6 STACK TURNED OFF
ROUTER ADVERTISE., (GOOD IP)
ROUTER ADVERTISE., (BAD IP)
IPv6 Address is not from router or DHCPv6 serverUNRECOGNIZED MANAGED BY
Illegal IPv6 state and should not happenILLEGAL IPV6 STATE
Display Wireless Statistics Screen
This procedure only applies to the wireless Cisco IP Phone 8861.
To display the Wireless Statistics screen, follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
216
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Display Wireless Statistics Screen

Step 2 Select Admin settings>Status > Wireless Statistics.
Step 3 To reset the Wireless statistics to 0, press Clear.
Step 4 To exit the Wireless Statistics screen, press Exit.
WLAN Statistics
The following table describes the WLAN statistics on the phone.
Table 45: WLAN Statistics on the Cisco Unified IP Phone
DescriptionItem
Number of bytes that the phone transmitted.tx bytes
Number of bytes that the phone received.rx bytes
Number of packets that the phone transmitted.tx packets
Number of packets that the phone received.rx packets
The number of packets dropped during transmission.tx packets dropped
The number of packets dropped during reception.rx packets dropped
The number of erroneous packets that phone transmitted.tx packets errors
The number of erroneous packets that phone received.rx packets errors
The number of successfully transmitted MSDU.Tx frames
The nunber of successfully transmitted multicast MSDU.tx multicast frames
The number of MSDU that is successfully transmitted after one or more
retransmissions.
tx retry
The number of multicast MSDU that is successfully transmitted after one
or more retransmissions.
tx multi retry
This number of MSDU that is not transmitted successfully due to the number
of transmit attempts exceeding the retry limit.
tx failure
This counter shall increment when a CTS is received in response to an RTS.rts succeess
This counter shall increment when a CTS is not received in response to an
RTS.
rts failure
This counter shall increment when an ACK is not received when expected.ack failure
The number of received frame that the Sequence Control field indicates is
a duplicate.
rx duplicate frames
The number of successfully received MPDU of type Data or Management.rx fraagmented packets
The number of succesful roaming.Roaming count
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
217
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
WLAN Statistics

Display Call Statistics Window
You can access the Call Statistics screen on the phone to display counters, statistics, and voice-quality metrics
of the most recent call.
You can also remotely view the call statistics information by using a web browser to access the Streaming
Statistics web page. This web page contains additional RTCP statistics that are not available on the phone.
Note
A single call can use multiple voice streams, but data is captured for only the last voice stream. A voice stream
is a packet stream between two endpoints. If one endpoint is put on hold, the voice stream stops even though
the call is still connected. When the call resumes, a new voice packet stream begins, and the new call data
overwrites the former call data.
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Select Admin settings > Status > Call statistics.
Step 3 To exit the Call Statistics screen, press Exit.
Call Statistics Fields
The following table describes the items on the Call Statistics screen.
Table 46: Call Statistics items for the Cisco Unified Phone
DescriptionItem
Type of received voice stream (RTP streaming audio from codec):
• G.729
• G.722
• G722.2 AMR-WB
• G.711 mu-law
• G.711 A-law
• iLBC
• Opus
• iSAC
Receiver codec
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
218
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Display Call Statistics Window

DescriptionItem
Type of transmitted voice stream (RTP streaming audio from codec):
• G.729
• G.722
• G722.2 AMR-WB
• G.711 mu-law
• G.711 A-law
• iLBC.
• Opus
• iSAC
Sender codec
Size of voice packets, in milliseconds, in the receiving voice stream (RTP
streaming audio).
Receiver size
Size of voice packets, in milliseconds, in the transmitting voice stream.Sender size
Number of RTP voice packets that were received since voice stream opened.
This number is not necessarily identical to the number of RTP
voice packets that were received since the call began because
the call might have been placed on hold.
Note
Receiver packets
Number of RTP voice packets that were transmitted since voice stream
opened.
This number is not necessarily identical to the number of RTP
voice packets that were transmitted since the call began because
the call might have been placed on hold.
Note
Sender packets
Estimated average RTP packet jitter (dynamic delay that a packet encounters
when going through the network), in milliseconds, that was observed since
the receiving voice stream opened.
Avg jitter
Maximum jitter, in milliseconds, that was observed since the receiving voice
stream opened.
Max jitter
Number of RTP packets in the receiving voice stream that were discarded
(bad packets, too late, and so on).
The phone discards payload type 19 comfort noise packets that
Cisco Gateways generate, because they increment this counter.
Note
Receiver discarded
Missing RTP packets (lost in transit).Receiver lost packets
Voice-Quality Metrics
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
219
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Call Statistics Fields

DescriptionItem
Total number of concealment frames divided by total number of speech
frames that were received from start of the voice stream.
Cumulative conceal ratio
Ratio of concealment frames to speech frames in preceding 3-second interval
of active speech. If using voice activity detection (VAD), a longer interval
might be required to accumulate 3 seconds of active speech.
Interval conceal ratio
Highest interval concealment ratio from start of the voice stream.Max conceal ratio
Number of seconds that have concealment events (lost frames) from the start
of the voice stream (includes severely concealed seconds).
Conceal seconds
Number of seconds that have more than 5 percent concealment events (lost
frames) from the start of the voice stream.
Severely conceal seconds
Estimate of the network latency, expressed in milliseconds. Represents a
running average of the round-trip delay, measured when RTCP receiver
report blocks are received.
Latency
Display Current Access Point Window
The Current Access Point screen displays statistics about the access point that the Cisco IP Phone 8861 uses
for wireless communications.
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Select Admin settings > Status > Current Access Point.
Step 3 To exit the Current Access Point screen, press Exit.
Current Access Points Fields
The following table describes the fields in the Current Access Point screen.
Table 47: Current Access Point Items
DescriptionItem
Name of the AP, if it is CCX-compliant; otherwise, the MAC address displays here.AP name
MAC address of the AP.MAC address
The latest frequency where this AP was observed.Frequency
The latest channel where this AP was observed.Current channel
The latest RSSI in which this AP was observed.Last RSSI
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
220
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Display Current Access Point Window

DescriptionItem
Number of time units between beacons. A time unit is 1.024 ms.Beacon interval
This field contains a number of subfields that are used to indicate requested or
advertised optional capabilities.
Capability
Data rates that the AP requires and the AP at which the station must be capable of
operating.
Basic rates
Data rates that the AP supports and the AP that are optional for the station to operate
at.
Optional rates
VHT Supported RX MCS Set received from AP.Supported VHT(rx)
rates
VHT Supported TX MCS Set received from AP.Supported VHT(tx)
rates
HT Supported MCS Set received from AP.Supported HT MCS
Every nth beacon is a dtime period. After each DTIM beacon, the AP sends any
broadcast or multicast packets that are queued for power-save devices.
DTIM period
A two-digit country code. Country information might not be display if the country
information element (IE) is not present in the beacon.
Country code
A list of supported channels (from the country IE).Channels
The amount of power by which the maximum transmit power should be reduced
from the regulatory domain limit.
Power constraint
Maximum transmit power in dBm that is permitted for that channel.Power limit
The percentage of time, normalized to 255, in which the AP sensed the medium
was busy, as indicated by the physical or virtual carrier sense (CS) mechanism.
Channel utilization
The total number of STAs currently associated with this AP.Station count
An unsigned integer that specifies the remaining amount of medium time that is
available through explicit admission control, in units of 32 microseconds per second.
If the value is 0, the AP does not support this information element and the capacity
is unknown.
Admission capacity
Support for Wi-Fi multimedia extensions.WMM supported
The AP supports Unscheduled Automatic Power Save Delivery. May only be
available if WMM is supported. This feature is critical for talk time and for achieving
maximum call density on the wireless IP Phone.
UAPSD Supported
CCX-compliant AP supports responding to IP ARP requests on behalf of the
associated station. This feature is critical to standby time on the wireless IP Phone.
Proxy ARP
If the AP is CCX compliant, this field shows the CCX version.CCX version
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
221
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Current Access Points Fields

DescriptionItem
Contains information related to the Best Effort queue.Best Effort
Contains information related to the Background queue.Background
Contains information related to the Video queue.Video
Contains information related to the Voice queue.Voice
Cisco IP Phone Web Page
Each Cisco IP Phone has a web page from which you can view a variety of information about the phone,
including:
• Device information: Displays device settings and related information for the phone.
• Network setup: Displays network setup information and information about other phone settings.
• Network statistics: Displays hyperlinks that provide information about network traffic.
• Device logs: Displays hyperlinks that provide information that you can use for troubleshooting.
• Streaming statistic: Displays hyperlinks that display a variety of streaming statistics.
• System: Displays a hyperlink to restart the phone.
This section describes the information that you can obtain from the phone web page. You can use this
information to remotely monitor the operation of a phone and to assist with troubleshooting.
You can also obtain much of this information directly from a phone.
Access Web Page for Phone
To access the web page for a phone, follow these steps:
If you cannot access the web page, it may be disabled by default.
Note
Procedure
Step 1 Obtain the IP address of the Cisco IP Phone by using one of these methods:
a) Search for the phone in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration by choosing Device >
Phone. Phones that register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager display the IP address on the
Find and List Phones window and at the top of the Phone Configuration window.
b) On the Cisco IP Phone, press Applications , choose Admin settings > Network setup > Ethernet
setup > IPv4 setup, and then scroll to the IP Address field.
Step 2 Open a web browser and enter the following URL, where IP_address is the IP address of the Cisco IP Phone:
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
222
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Cisco IP Phone Web Page

http://IP_address
Device Information
The Device information area on a phone web page displays device settings and related information for the
phone. The following table describes these items.
Some of the items in the following table do not apply to all phone models.
Note
To display the Device information area, access the web page for the phone as described in Access Web Page
for Phone, on page 222, and then click the Device information hyperlink.
Table 48: Device Information Area Items
DescriptionItem
The service mode for the phone.Service mode
The domain for the service.Service name
The current state of the service.Service state
Media Access Control (MAC) address of the phone.MAC Address
Unique, fixed name that is automatically assigned to the phone based on the MAC
address.
Host name
Directory number that is assigned to the phone.Phone DN
Application firmware version that is running on the phone.App load ID
Boot firmware version.Boot load ID
Identifier of the firmware that is running on the phone.Version
Identifier for the first key expansion module, if applicable.
Applicable to Cisco IP Phone 8851, 8851NR, 8861, 8865, and 8865NR.
Key expansion
module 1
Identifier for the second key expansion module, if applicable.
Applicable to Cisco IP Phone 8851, 8851NR, 8861, 8865, and 8865NR.
Key expansion
module 2
Identifier for the third key expansion module, if applicable.
Applicable to Cisco IP Phone 8851, 8851NR, 8861, 8865, and 8865NR.
Key expansion
module 3
Minor revision value of the phone hardware.Hardware revision
Unique serial number of the phone.Serial number
Model number of the phone.Model number
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
223
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Device Information

DescriptionItem
Indicates whether is a voice message is waiting on the primary line for this phone.Message waiting
Displays the following Cisco Unique Device Identifier (UDI) information about the
phone:
• Device type—Indicates hardware type. For example, phone displays for all phone
models.
• Device description—Displays the name of the phone associated with the indicated
model type.
• Product identifier—Specifies the phone model.
• Version ID (VID)—Specifies the major hardware version number.
• Serial number—Displays the unique serial number of the phone.
UDI
Cisco Unique Device Identifier (UDI) of the key expansion module.
Applicable to Cisco IP Phone 8851, 8851NR, 8861, 8865, and 8865NR.
Key expansion
module UDI
Displays the name of the attached Cisco headset in the left column. The right column
contains this information:
• Port—Displays how the headset connects to the phone.
• USB
• AUX
• Version—Displays the headset firmware version.
• Radio range—Displays the strength configured for the DECT radio. Applicable
to the Cisco Headset 560 Series only.
• Bandwidth—Displays if the headset uses Wide band or Narrow band. Applicable
to the Cisco Headset 560 Series only.
• Bluetooth—Displays if Bluetooth is enabled or disabled. Applicable to the Cisco
Headset 560 Series only.
• Conference—Displays if the conference feature is enabled or disabled. Applicable
to the Cisco Headset 560 Series only.
• Firmware source—Displays the permitted firmware upgrade method:
• Restrict to UCM only
• Allow from UCM or Cisco Cloud
Applicable to the Cisco Headset 560 Series only.
Name of the Headset
Time for the Date/Time Group to which the phone belongs. This information comes
from Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Time
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
224
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Device Information

DescriptionItem
Time zone for the Date/Time Group to which the phone belongs. This information
comes from Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Time zone
Date for the Date/Time Group to which the phone belongs. This information comes
from Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Date
Amount of unused memory on the phoneSystem free memory
Amount of free internal Java heap memoryJava heap free
memory
Amount of free internal Java pool memoryJava pool free
memory
Indicates if the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) Mode is enabled.FIPS mode enabled
Network Setup
The Network setup area on a phone web page displays network setup information and information about other
phone settings. The following table describes these items.
You can view and set many of these items from the Network Setup menu on the Cisco IP Phone.
Some of the items in the following table do not apply to all phone models.
Note
To display the Network Setup area, access the web page for the phone as described in Access Web Page for
Phone, on page 222, and then click the Network setup hyperlink.
Table 49: Network Setup Area Items
DescriptionItem
Media Access Control (MAC) address of the phone.MAC address
Host name that the DHCP server assigned to the phone.Host name
Name of the Domain Name System (DNS) domain in which the phone resides.Domain name
IP address of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server from which the phone obtains
the IP address.
DHCP server
Indicates whether the phone obtains the configuration from a Bootstrap Protocol (BootP) server.BOOTP server
Indicates whether the phone uses DHCP.DHCP
Internet Protocol (IPv4) address of the phone.IP address
Subnet mask that the phone uses.Subnet mask
Default router used that the phone uses.Default router
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
225
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Network Setup

DescriptionItem
Primary Domain Name System (DNS) server (DNS Server 1) and optional backup DNS servers (DNS
Server 2 and 3) that the phone uses.
DNS server 1–3
Indicates whether the phone is using an alternative TFTP server.Alternate TFTP
Primary Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server used that the phone uses.TFTP server 1
Backup Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server used that the phone uses.TFTP server 2
Indicates the setting of the DHCP address rReleased option on the phone Network Configuration menu.DHCP address released
Operational Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) that is configured on a Cisco Catalyst switch in
which the phone is a member.
Operational VLAN ID
Auxiliary VLAN in which the phone is a member.Admin VLAN ID
Host names or IP addresses, in prioritized order, of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers
with which the phone can register. An item can also show the IP address of an SRST router that is
capable of providing limited Cisco Unified Communications Manager functionality, if such a router is
available.
For an available server, an item shows the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server IP address
and one of the following states:
• Active—Cisco Unified Communications Manager server from which the phone is currently
receiving call-processing services
• Standby—Cisco Unified Communications Manager server to which the phone switches if the
current server becomes unavailable
• Blank—No current connection to this Cisco Unified Communications Manager server
An item may also include the Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) designation, which identifies
an SRST router capable of providing Cisco Unified Communications Manager functionality with a
limited feature set. This router assumes control of call processing if all other Cisco Unified
Communications Manager servers become unreachable. The SRST Cisco Unified Communications
Manager always appears last in the list of servers, even if it is active. You configure the SRST router
address in the Device Pool section in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Configuration window.
CUCM server1–5
URL of the help text that appears on the phone.Information URL
URL of the server from which the phone obtains directory information.Directories URL
URL of the server from which the phone obtains message services.Messages URL
URL of the server from which the phone obtains Cisco Unified IP Phone services.Services URL
URL that the phone displays when the phone is idle for the time that the Idle URL Time field specifies
and no menu is open.
Idle URL
Number of seconds that the phone is idle and no menu is open before the XML service that the Idle
URL specifies activates.
Idle URL time
URL of proxy server, which makes HTTP requests to nonlocal host addresses on behalf of the phone
HTTP client and provides responses from the nonlocal host to the phone HTTP client.
Proxy server URL
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
226
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Network Setup

DescriptionItem
URL that the phone uses to validate requests that are made to the phone web server.Authentication URL
Speed and duplex of the switch port, where:
• A = Auto Negotiate
• 10H = 10-BaseT/half duplex
• 10F = 10-BaseT/full duplex
• 100H = 100-BaseT/half duplex
• 100F = 100-BaseT/full duplex
• 1000F = 1000-BaseT/full duplex
• No Link= No connection to the switch port
SW port setup
Speed and duplex of the PC port, where:
• A = Auto Negotiate
• 10H = 10-BaseT/half duplex
• 10F = 10-BaseT/full duplex
• 100H = 100-BaseT/half duplex
• 100F = 100-BaseT/full duplex
• 1000F = 1000-BaseT/full duplex
• No Link = No connection to the PC port
PC port setup
Indicates whether the PC port on the phone is enabled or disabled.PC port disabled
User locale that associates with the phone user. Identifies a set of detailed information to support users,
including language, font, date and time formatting, and alphanumeric keyboard text information.
User locale
Network locale that associates with the phone user. Identifies a set of detailed information to support
the phone in a specific location, including definitions of the tones and cadences that the phone uses.
Network locale
Version of the user locale that is loaded on the phone.User locale version
Version of the network locale that is loaded on the phone.Network locale version
Indicates whether the speakerphone is enabled on the phone.Speaker enabled
Indicates whether the phone learns MAC addresses from Gratuitous ARP responses.GARP enabled
Indicates whether the phone forwards packets that are transmitted and received on the network port to
the access port.
Span to PC port
Indicates whether the phone can participate in video calls when it connects to an appropriately equipped
camera.
Video capability enabled
Indicates whether the phone allows a device that is attached to the PC port to access the Voice VLAN.Voice VLAN enabled
VLAN that identifies and removes 802.1P/Q tags from packets that are sent to the PC.PC VLAN enabled
Identifies if the phone automatically selects a line when the phone goes off hook.Auto line select enabled
DSCP IP classification for call control signaling.DSCP protocol control
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
227
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Network Setup

DescriptionItem
DSCP IP classification for any phone configuration transfer.DSCP for configuration
DSCP IP classification for phone-based services.DSCP for services
Security mode that is set for the phone.Security mode (nonsecure)
Indicates whether web access is enabled (Yes) or disabled (No) for the phone.Web access enabled
Indicates if the SSH port has been enabled or disabled.SSH access enabled
Indicates whether CDP support exists on the switch port (default is enabled).
Enable CDP on the switch port for VLAN assignment for the phone, power negotiation, QoS
management, and 802.1x security.
Enable CDP on the switch port when the phone connects to a Cisco switch.
When CDP is disabled in Cisco Unified Communications Manager, a warning is presented, indicating
that CDP should be disabled on the switch port only if the phone connects to a non-Cisco switch.
The current PC and switch port CDP values are shown on the Settings menu.
CDP: SW Port
Indicates whether CDP is supported on the PC port (default is enabled).
When CDP is disabled in Cisco Unified Communications Manager, a warning is displays to indicate
that disabling CDP on the PC port prevents CVTA from working.
The current PC and switch port CDP values are shown in the Settings menu.
CDP: PC Port
Indicates whether Link Layer Discovery Protocol Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) is enabled
on the switch port.
LLDP-MED:SW Port
Indicates whether LLDP-MED is enabled on the PC port.LLDP-MED:PC Port
Phone power priority to the switch, thus enabling the switch to appropriately provide power to the
phones. Settings include:
• Unknown: This is the default value.
• Low
• High
• Critical
LLDP Power Priority
Asset ID that is assigned to the phone for inventory management.LLDP Asset ID
MD5 hash of the CTL file.CTL file
The ITL file contains the initial trust list.ITL file
MD5 hash of the ITL fileITL signature
CPF server in useCAPF server
The main component of Security by Default. Trust Verification Services (TVS) enables Cisco Unified
IP Phones to authenticate application servers, such as EM services, directory, and MIDlet, during
HTTPS establishment.
TVS
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
228
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Network Setup

DescriptionItem
The name of the TFTP Server used by the phone.TFTP server
The name of the TFTP Server used by the phone.TFTP server
Indicates if the phone automatically synchronizes port speed to eliminate packet loss.Automatic port
synchronization
Indicates if the SW port is remotely controlled.Switch port remote
configuration
Indicates if the PC port is remotely controlled.PC port remote
configuration
Identifies the addressing mode:
• IPv4 Only
• IPv4 and IPv6
• IPv6 Only
IP addressing mode
Indicates the IP address version that the phone uses during signaling with Cisco Unified Communications
Manager when both IPv4 and IPv6 are both available on the phone.
IP preference mode
control
IP preference mode for
media
Indicates that for media the device uses an IPv4 address to connect to the Cisco Unified Communications
Manager.
IPv6 auto configuration
IPv6 duplicate address
protection
Indicates if phone accepts the redirect messages from the same router that is used for the destination
number.
IPv6 accept redirect
message
Indicates that the phone sends an Echo Reply message in response to an Echo Request message sent
to an IPv6-only address.
IPv6 reply multicast echo
request
Used to optimize installation time for phone firmware upgrades and off load the WAN by storing
images locally, negating the need to traverse the WAN link for each phone's upgrade.
IPv6 load server
IPv6 log server
Indicates the IP address and port of the remote logging machine to which the phone sends log messages.IPv6 CAPF server
Indicates the method that the phone uses to get the IPv6-only address.
When DHCPv6 is enabled, the phone gets the IPv6 address either from DHCPv6 server or from SLAAC
by RA sent by the IPv6-enabled router. And if DHCPv6 is disabled, the phone will not have any stateful
(from DHCPv6 server) or stateless (from SLAAC) IPv6 address.
Unlike DHCPv4, even DHCPv6 is disabled the phone can still generate a SLAAC address
if autoconfigure is enabled.
Note
DHCPv6
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
229
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Network Setup
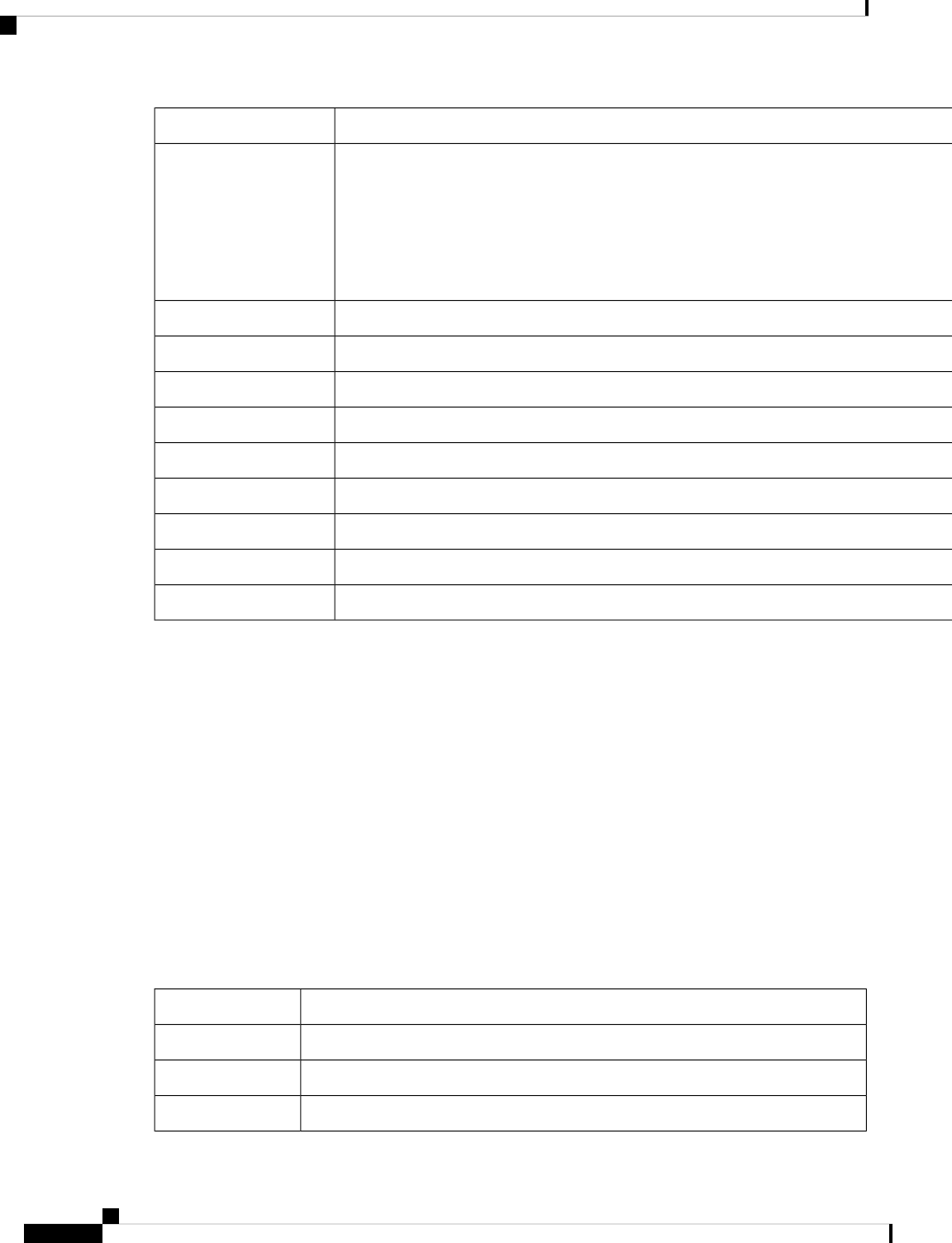
DescriptionItem
Displays the current IPv6-only address of the phone.
Two address formats are supported:
• Eight sets of hexadecimal digits separated by colons X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X
• Compressed format to collapse a single run of consecutive zero groups into a single group
represented by a double colon.
IPv6 address
Displays the current IPv6-only prefix length for the subnet.IPv6 prefix length
Displays the default IPv6 router used by the phone.IPv6 default router
Displays the primary and secondary DNSv6 server used by the phoneIPv6 DNS server 1–2
Displays if an alternate IPv6 TFTP server is used.IPv6 Alternate TFTP
Displays the primary and secondary IPv6 TFTP server used by the phone.IPv6 TFTP server 1–2
Displays if the user has released the IPv6-related information.IPv6 address released
The power level that is used when the phone is sleeping.EnergyWise power level
The EnergyWise domain that the phone is in.EnergyWise domain
Indicates the DF bit setting for packets.DF_BIT
Network Statistics
The following Network statistics hyperlinks on a phone web page provide information about network traffic
on the phone:
• Ethernet information: Displays information about Ethernet traffic.
• Access: Displays information about network traffic to and from the PC port on the phone.
• Network: Displays information about network traffic to and from the network port on the phone.
To display a Network statistics area, access the web page for the phone, and then click the Ethernet
Information, the Access, or the Network hyperlink.
Ethernet Information Web Page
The following table describes the contents of the Ethernet information web page.
Table 50: Ethernet Information Items
DescriptionItem
Total number of packets that the phone transmits.Tx Frames
Total number of broadcast packets that the phone transmits.Tx broadcast
Total number of multicast packets that the phone transmits.Tx multicast
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
230
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Network Statistics

DescriptionItem
Total number of unicast packets that the phone transmits.Tx unicast
Total number of packets received by the phone.Rx Frames
Total number of broadcast packets that the phone receives..Rx broadcast
Total number of multicast packets that the phone receives.Rx multicast
Total number of unicast packets that the phone receives.Rx unicast
Total number of shed packets that the no Direct Memory Access (DMA) descriptor
causes.
Rx PacketNoDes
Access and Network Web Pages
The following table describes the information in the Access and Network web pages.
Table 51: Access and Network Fields
DescriptionItem
Total number of packets that the phone received.Rx totalPkt
Total number of packets that were received with CRC failed.Rx crcErr
Total number of packets between 64 and 1522 bytes in length that were
received and that have a bad Frame Check Sequence (FCS).
Rx alignErr
Total number of multicast packets that the phone received.Rx multicast
Total number of broadcast packets that the phone received.Rx broadcast
Total number of unicast packets that the phone received.Rx unicast
Total number of received FCS error packets or Align error packets that are
less than 64 bytes in size.
Rx shortErr
Total number of received good packets that are less than 64 bytes size.Rx shortGood
Total number of received good packets that are greater than 1522 bytes in
size.
Rx longGood
Total number of received FCS error packets or Align error packets that are
greater than 1522 bytes in size.
Rx longErr
Total number of received packets, including bad packets, that are between
0 and 64 bytes in size.
Rx size64
Total number of received packets, including bad packets, that are between
65 and 127 bytes in size.
Rx size65to127
Total number of received packets, including bad packets, that are between
128 and 255 bytes in size.
Rx size128to255
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
231
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Access and Network Web Pages

DescriptionItem
Total number of received packets, including bad packets, that are between
256 and 511 bytes in size.
Rx size256to511
Total number of received packets, including bad packets, that are between
512 and 1023 bytes in size.
Rx size512to1023
Total number of received packets, including bad packets, that are between
1024 and 1518 bytes in size.
Rx size1024to1518
Total number of packets that were dropped due to lack of resources (for
example, FIFO overflow).
Rx tokenDrop
Total number of packets that were delayed from transmitting due to busy
medium.
Tx excessDefer
Number of times that collisions occurred later than 512 bit times after the
start of packet transmission.
Tx lateCollision
Total number of good packets (multicast, broadcast, and unicast) that the
phone received.
Tx totalGoodPkt
Total number of collisions that occurred while a packet was transmitted.Tx Collisions
Total number of packets that were not transmitted because the packet
experienced 16 transmission attempts.
Tx excessLength
Total number of broadcast packets that the phone transmitted.Tx broadcast
Total number of multicast packets that the phone transmitted.Tx multicast
Total number of LLDP frames that the phone sent out.LLDP FramesOutTotal
Total number of LLDP frames that timed out in the cache.LLDP AgeoutsTotal
Total number of LLDP frames that were discarded when any of the
mandatory TLVs is missing, out of order, or contains out of range string
length.
LLDP FramesDiscardedTotal
Total number of LLDP frames that were received with one or more
detectable errors.
LLDP FramesInErrorsTotal
Total number of LLDP frames that the phone receives.LLDP FramesInTotal
Total number of LLDP TLVs that are discarded.LLDP TLVDiscardedTotal
Total number of LLDP TLVs that are not recognized on the phone.LLDP TLVUnrecognizedTotal
Identifier of a device connected to this port that CDP discovered.CDP Neighbor Device ID
IP address of the neighbor device discovered that CDP protocol discovered.CDP Neighbor IPv6 address
Neighbor device port to which the phone is connected discovered by CDP
protocol.
CDP Neighbor Port
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
232
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Access and Network Web Pages

DescriptionItem
Identifier of a device connected to this port discovered by LLDP discovered.LLDP Neighbor Device ID
IP address of the neighbor device that LLDP protocol discovered.LLDP Neighbor IPv6 address
Neighbor device port to which the phone connects that LLDP protocol
discovered.
LLDP Neighbor Port
Speed and duplex information.Port Information
Device Logs
The following Device log hyperlinks on a phone web page provide information that helps to monitor and
troubleshoot the phone.
• Console logs: Includes hyperlinks to individual log files. The console log files include debug and error
messages that the phone received.
• Core dumps: Includes hyperlinks to individual dump files. The core dump files include data from a phone
crash.
• Status messages: Displays the 10 most recent status messages that the phone has generated since it last
powered up. The Status Messages screen on the phone also displays this information.
• Debug display: Displays debug messages that might be useful to Cisco TAC if you require assistance
with troubleshooting.
Streaming Statistics
A Cisco Unified IP Phone can stream information to and from up to three devices simultaneously. A phone
streams information when it is on a call or is running a service that sends or receives audio or data.
The Streaming statistics areas on a phone web page provide information about the streams.
The following table describes the items in the Streaming Statistics areas.
Table 52: Streaming Statistics area items
DescriptionItem
IP address and UDP port of the destination of the stream.Remote address
IP address and UPD port of the phone.Local address
Internal time stamp indicates when Cisco Unified Communications Manager requested that the
phone start transmitting packets.
Start time
Indication of whether streaming is active or not.Stream status
Unique, fixed name that is automatically assigned to the phone based on the MAC address.Host name
Total number of RTP data packets that the phone transmitted since it started this connection.
The value is 0 if the connection is set to receive-only mode.
Sender packets
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
233
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Device Logs

DescriptionItem
Total number of payload octets that the phone transmitted in RTP data packets since it started
this connection. The value is 0 if the connection is set to receive-only mode.
Sender octets
Type of audio encoding that is for the transmitted stream.Sender codec
Number of times the RTCP Sender Report has been sent.Sender reports sent
(see note)
Internal time-stamp indication as to when the last RTCP Sender Report was sent.Sender report time sent
(see note)
Total number of RTP data packets that have been lost since data reception started on this
connection. Defined as the number of expected packets less the number of packets actually
received, where the number of received packets includes any that are late or are duplicates. The
value displays as 0 if the connection was set to send-only mode.
Rcvr lost packets
Estimate of mean deviation of the RTP data packet interarrival time, measured in milliseconds.
The value displays as 0 if the connection was set to send-only mode.
Avg jitter
Type of audio encoding that is used for the received stream.Receiver codec
Number of times the RTCP Receiver Reports have been sent.Receiver reports sent
(see note)
Internal time-stamp indication as to when a RTCP Receiver Report was sent.Receiver report time sent
(see note)
Total number of RTP data packets that the phone has received since data reception started on
this connection. Includes packets that were received from different sources if this call is a
multicast call. The value displays as 0 if the connection was set to send-only mode.
Rcvr packets
Total number of payload octets that the device received in RTP data packets since reception
started on the connection. Includes packets that were received from different sources if this call
is a multicast call. The value displays as 0 if the connection was set to send-only mode.
Rcvr octets
Score that is an objective estimate of the mean opinion score (MOS) for listening quality (LQK)
that rates from 5 (excellent) to 1(bad). This score is based on audible concealment events that
are to frame loss in the preceding eight-second interval of the voice stream. For more information,
see Voice Quality Monitoring, on page 262.
The MOS LQK score can vary due to the codec type that the Cisco Unified IP
Phone uses.
Note
MOS LQK
Average MOS LQK score that was observed for the entire voice stream.Avg MOS LQK
Lowest MOS LQK score that was observed from the start of the voice stream.Min MOS LQK
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
234
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Streaming Statistics

DescriptionItem
Baseline or highest MOS LQK score that was observed from start of the voice stream.
These codecs provide the following maximum MOS LQK score under normal conditions with
no frame loss:
• G.711 yields 4.5.
• G.729 A /AB yields 3.7.
Max MOS LQK
Version of the Cisco proprietary algorithm that is used to calculate MOS LQK scores.MOS LQK version
Total number of concealment frames divided by total number of speech frames that were received
from the start of the voice stream.
Cumulative conceal ratio
Ratio of concealment frames to speech frames in the preceding 3-second interval of active
speech. If voice activity detection (VAD) is in use, a longer interval might be required to
accumulate three seconds of active speech.
Interval conceal ratio
Highest interval concealment ratio from the start of the voice stream.Max conceal ratio
Number of seconds that have concealment events (lost frames) from the start of the voice stream
(includes severely concealed seconds).
Conceal secs
Number of seconds that have more than five percent concealment events (lost frames) from the
start of the voice stream.
Severely conceal secs
Estimate of the network latency, expressed in milliseconds. Represents a running average of
the round-trip delay, measured when RTCP receiver report blocks are received.
Latency
(see note)
Maximum value of instantaneous jitter, in milliseconds.Max jitter
RTP packet size, in milliseconds, for the transmitted stream.Sender size
Number of times RTCP Sender Reports have been received.Sender reports received
(see note)
Most recent time when an RTCP Sender Report was received.Sender report time received
(see note)
RTP packet size, in milliseconds, for the received stream.Receiver size
RTP packets that were received from the network but were discarded from the jitter buffers.Receiver discarded
Number of times RTCP Receiver Reports have been received.Receiver reports received
(see note)
Most recent time when an RTCP Receiver Report was received.Receiver report time received
(see note)
Indicates if the receiver is using encryption.Rcvr encrypted
Indicates if the sender is using encryption.Sender encrypted
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
235
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Streaming Statistics

DescriptionItem
Number of frames sent.Sender frames
Number of partial frames sent.Sender partial frames
Number of I frames sent. I frames are used in video transmission.Sender i frames
Number of instantaneous decoder refresh (IDR) frames sent. IDR frames are used in video
transmission.
Sender IDR frames
Rate at which the sender is sending frames.Sender frame rate
Bandwidth for the sender.Sender bandwidth
Video resolution of the sender.Sender resolution
Number of frames receivedRcvr frames
Number of partial frames receivedRcvr partial frames
Number of I frames received.Rcvr i frames
Number of IDR frames received.Rcvr IDR frames
Number of requested IDR frames receivedRcvr IFrames req
Rate at which the receiver is receiving frames.Rcvr frame rate
Number of frames that were not received.Rcvr frames lost
Number of frames that were not received.Rcvr frame errors
Bandwidth of the receiver.Rcvr bandwidth
Video resolution of the receiver.Rcvr resolution
Domain that the phone resides in.Domain
Number of times the sender joined.Sender joins
Number of times the receiver joinedRcvr joins
Number of “Bye” framesByes
Time that the sender started.Sender start time
Time that the receiver started.Rcvr start time
Whether the phone is streamingRow status
Type of audio encoding used for the streamSender tool
RTCP Sender ReportsSender reports
Last time at which an RTCP Sender Report was sent.Sender report time
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
236
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Streaming Statistics

DescriptionItem
Maximum jitter of streamRcvr Jitter
Type of audio encoding used for the streamReceiver tool
Number of times this streaming statistics report has been accessed from the web page.Rcvr reports
Internal time stamp indicating when this streaming statistics report was generatedRcvr report time
Indicates if the call was a video call or audio only.Is video
Identification of the callCall ID
Identification of the group that the phone is in.Group ID
When the RTP Control Protocol is disabled, no data generates for this field and thus displays as 0.
Note
Request Information from the Phone in XML
For troubleshooting purposes, you can request information from the phone. The resulting information is in
XML format. The following information is available:
• CallInfo is call session information for a specific line.
• LineInfo is line configuration information for the phone.
• ModeInfo is phone mode information.
Before you begin
Web access needs to be enabled to get the information.
The phone must be associated with a user.
Procedure
Step 1 For Call Info, enter the following URL in a browser: http://<phone ip
address>/CGI/Java/CallInfo<x>
where
• <phone ip address> is the IP address of the phone
• <x> is the line number to obtain information about.
The command returns an XML document.
Step 2 For Line Info, enter the following URL in a browser: http://<phone ip
address>/CGI/Java/LineInfo
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
237
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Request Information from the Phone in XML

where
• <phone ip address> is the IP address of the phone
The command returns an XML document.
Step 3 For Model Info, enter the following URL in a browser: http://<phone ip
address>/CGI/Java/ModeInfo
where
• <phone ip address> is the IP address of the phone
The command returns an XML document.
Sample CallInfo Output
The following XML code is an example of the output from the CallInfo command.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<CiscoIPPhoneCallLineInfo>
<Prompt/>
<Notify/>
<Status/>
<LineDirNum>1030</LineDirNum>
<LineState>CONNECTED</LineState>
<CiscoIPPhoneCallInfo>
<CallState>CONNECTED</CallState>
<CallType>INBOUND</CallType>
<CallingPartyName/>
<CallingPartyDirNum>9700</CallingPartyDirNum>
<CalledPartyName/>
<CalledPartyDirNum>1030</CalledPartyDirNum>
<HuntPilotName/>
<CallReference>30303060</CallReference>
<CallDuration>12835</CallDuration>
<CallStatus>null</CallStatus>
<CallSecurity>UNAUTHENTICATED</CallSecurity>
<CallPrecedence>ROUTINE</CallPrecedence>
<FeatureList/>
</CiscoIPPhoneCallInfo>
<VisibleFeatureList>
<Feature Position="1" Enabled="true" Label="End Call"/>
<Feature Position="2" Enabled="true" Label="Show Detail"/>
</VisibleFeatureList>
</CiscoIPPhoneCallLineInfo>
Sample LineInfo Output
The following XML code is an example of the output from the LineInfo command.
<CiscoIPPhoneLineInfo>
<Prompt/>
<Notify/>
<Status>null</Status>
<CiscoIPPhoneLines>
<LineType>9</LineType>
<lineDirNum>1028</lineDirNum>
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
238
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Sample CallInfo Output

<MessageWaiting>NO</MessageWaiting>
<RingerName>Chirp1</RingerName>
<LineLabel/>
<LineIconState>ONHOOK</LineIconState>
</CiscoIPPhoneLines>
<CiscoIPPhoneLines>
<LineType>9</LineType>
<lineDirNum>1029</lineDirNum>
<MessageWaiting>NO</MessageWaiting> <RingerName>Chirp1</RingerName>
<LineLabel/>
<LineIconState>ONHOOK</LineIconState>
</CiscoIPPhoneLines>
<CiscoIPPhoneLines>
<LineType>9</LineType>
<lineDirNum>1030</lineDirNum>
<MessageWaiting>NO</MessageWaiting>
<RingerName>Chirp1</RingerName>
<LineLabel/>
<LineIconState>CONNECTED</LineIconState>
</CiscoIPPhoneLines>
<CiscoIPPhoneLines>
<LineType>2</LineType>
<lineDirNum>9700</lineDirNum>
<MessageWaiting>NO</MessageWaiting>
<LineLabel>SD9700</LineLabel>
<LineIconState>ON</LineIconState>
</CiscoIPPhoneLines>
</CiscoIPPhoneLineInfo>
Sample ModeInfo Output
The following XML code is an example of the output from the ModeInfo command.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<CiscoIPPhoneModeInfo>
<PlaneTitle>Applications</PlaneTitle>
<PlaneFieldCount>12</PlaneFieldCount>
<PlaneSoftKeyIndex>0</PlaneSoftKeyIndex>
<PlaneSoftKeyMask>0</PlaneSoftKeyMask>
<Prompt></Prompt>
<Notify></Notify>
<Status></Status>
<CiscoIPPhoneFields>
<FieldType>0</FieldType>
<FieldAttr></FieldAttr>
<fieldHelpIndex>0</fieldHelpIndex>
<FieldName>Call History</FieldName>
<FieldValue></FieldValue>
</CiscoIPPhoneFields>
<CiscoIPPhoneFields>
<FieldType>0</FieldType>
<FieldAttr></FieldAttr>
<fieldHelpIndex>0</fieldHelpIndex>
<FieldName>Preferences</FieldName>
<FieldValue></FieldValue>
</CiscoIPPhoneFields>
...
</CiscoIPPhoneModeInfo>
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
239
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Sample ModeInfo Output

Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
240
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Sample ModeInfo Output

CHAPTER 12
Troubleshooting
• General Troubleshooting Information, on page 241
• Startup Problems, on page 242
• Phone Reset Problems, on page 246
• Phone Cannot Connect to LAN, on page 248
• Cisco IP Phone Security Problems, on page 249
• Video Call Problems, on page 251
• General Telephone Call Problems, on page 252
• Troubleshooting Procedures, on page 253
• Control Debug Information from Cisco Unified Communications Manager, on page 257
• Additional Troubleshooting Information, on page 258
General Troubleshooting Information
The following table provides general troubleshooting information for the Cisco IP Phone.
Table 53: Cisco IP Phone troubleshooting
ExplanationSummary
Cisco does not support connecting an IP phone to another IP Phone through the PC
port. Each IP Phone should connect directly to a switch port. If phones are connected
together in a line by using the PC port, the phones do not work.
Connecting a Cisco IP Phone to another
Cisco IP Phone
A prolonged Layer 2 broadcast storm (lasting several minutes) on the voice VLAN
may cause IP phones to reset, lose an active call, or be unable to initiate or answer a
call. Phones may not come up until a broadcast storm ends.
Prolonged broadcast storms cause IP phones
to reset, or be unable to make or answer a
call
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
241

ExplanationSummary
If you power your phone through the network connection, you must be careful if you
decide to unplug the network connection of the phone and plug the cable into a desktop
computer.
The network card in the computer cannot receive power through the
network connection; if power comes through the connection, the network
card can be destroyed. To protect a network card, wait 10 seconds or
longer after unplugging the cable from the phone before plugging it into
a computer. This delay gives the switch enough time to recognize that
there is no longer a phone on the line and to stop providing power to
the cable.
Caution
Moving a network connection from the phone
to a workstation
By default, the network configuration options are locked to prevent users from making
changes that could impact their network connectivity. You must unlock the network
configuration options before you can configure them. See Apply a Phone Password,
on page 48 for details.
If the administrator password is not set in common phone profile, then
user can modify the network settings.
Note
Changing the telephone configuration
The RxType and the TxType statistics show the codec that is used for a conversation
between this Cisco IP Phone and the other device. The values of these statistics should
match. If they do not, verify that the other device can handle the codec conversation,
or that a transcoder is in place to handle the service.
Codec mismatch between the phone and
another device
The RxSize and the TxSize statistics show the size of the voice packets that are used
in a conversation between this Cisco IP Phone and the other device. The values of
these statistics should match.
Sound sample mismatch between the phone
and another device
A loopback condition can occur when the following conditions are met:
• The SW Port Configuration option in the Network Configuration menu on the
phone is set to 10 Half (10-BaseT/half duplex).
• The phone receives power from an external power supply.
• The phone is powered down (the power supply is disconnected).
In this case, the switch port on the phone can become disabled and the following
message appears in the switch console log:
HALF_DUX_COLLISION_EXCEED_THRESHOLD
To resolve this problem, reenable the port from the switch.
Loopback condition
Startup Problems
After you install a phone into your network and add it to Cisco Unified Communications Manager, the phone
should start up as described in the related topic below.
If the phone does not start up properly, see the following sections for troubleshooting information.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
242
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Startup Problems

Related Topics
Phone Startup Verification, on page 62
Cisco IP Phone Does Not Go Through the Normal Startup Process
Problem
When you connect a Cisco IP Phone to the network port, the phone does not go through the normal startup
process as described in the related topic and the phone screen does not display information.
Cause
If the phone does not go through the startup process, the cause may be faulty cables, bad connections, network
outages, lack of power, or the phone may not be functional.
Solution
To determine whether the phone is functional, use the following suggestions to eliminate other potential
problems.
• Verify that the network port is functional:
• Exchange the Ethernet cables with cables that you know are functional.
• Disconnect a functioning Cisco IP Phone from another port and connect it to this network port to
verify that the port is active.
• Connect the Cisco IP Phone that does not start up to a different network port that is known to be
good.
• Connect the Cisco IP Phone that does not start up directly to the port on the switch, eliminating the
patch panel connection in the office.
• Verify that the phone is receiving power:
• If you are using external power, verify that the electrical outlet is functional.
• If you are using in-line power, use the external power supply instead.
• If you are using the external power supply, switch with a unit that you know to be functional.
• If the phone still does not start up properly, power up the phone from the backup software image.
• If the phone still does not start up properly, perform a factory reset of the phone.
• After you attempt these solutions, if the phone screen on the Cisco IP Phone does not display any characters
after at least five minutes, contact a Cisco technical support representative for additional assistance.
Related Topics
Phone Startup Verification, on page 62
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
243
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Cisco IP Phone Does Not Go Through the Normal Startup Process

CiscoIPPhoneDoesNotRegisterwithCiscoUnifiedCommunicationsManager
If the phone proceeds past the first stage of the startup process (LED buttons flashing on and off) but continues
to cycle through the messages that displays on the phone screen, the phone is not starting up properly. The
phone cannot successfully start up unless it connects to the Ethernet network and it registers with a Cisco
Unified Communications Manager server.
In addition, problems with security may prevent the phone from starting up properly. See Troubleshooting
Procedures, on page 253 for more information.
Phone Displays Error Messages
Problem
Status messages display errors during startup.
Solution
While the phone cycles through the startup process, you can access status messages that might provide you
with information about the cause of a problem.
Related Topics
Display Status Messages Window, on page 209
Phone Cannot Connect to TFTP Server or to Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Problem
If the network is down between the phone and either the TFTP server or Cisco Unified Communications
Manager, the phone cannot start up properly.
Solution
Ensure that the network is currently running.
Phone Cannot Connect to TFTP Server
Problem
The TFTP server settings may not be correct.
Solution
Check the TFTP settings.
Related Topics
Check TFTP Settings, on page 254
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
244
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Cisco IP Phone Does Not Register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager

Phone Cannot Connect to Server
Problem
The IP addressing and routing fields may not be configured correctly.
Solution
You should verify the IP addressing and routing settings on the phone. If you are using DHCP, the DHCP
server should provide these values. If you have assigned a static IP address to the phone, you must enter these
values manually.
Phone Cannot Connect Using DNS
Problem
The DNS settings may be incorrect.
Solution
If you use DNS to access the TFTP server or Cisco Unified Communications Manager, you must ensure that
you specify a DNS server.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager and TFTP Services Are Not Running
Problem
If the Cisco Unified Communications Manager or TFTP services are not running, phones may not be able to
start up properly. In such a situation, it is likely that you are experiencing a systemwide failure, and other
phones and devices are unable to start up properly.
Solution
If the Cisco Unified Communications Manager service is not running, all devices on the network that rely on
it to make phone calls are affected. If the TFTP service is not running, many devices cannot start up successfully.
For more information, see Start Service, on page 257.
Configuration File Corruption
Problem
If you continue to have problems with a particular phone that other suggestions in this chapter do not resolve,
the configuration file may be corrupted.
Solution
Create a new phone configuration file.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
245
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Phone Cannot Connect to Server

Cisco Unified Communications Manager Phone Registration
Problem
The phone is not registered with the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Solution
A Cisco IP Phone can register with a Cisco Unified Communications Manager server only if the phone is
added to the server or if autoregistration is enabled. Review the information and procedures in Phone Addition
Methods, on page 68 to ensure that the phone is added to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
database.
To verify that the phone is in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database, choose Device > Phone
from Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration. Click Find to search for the phone based on
the MAC Address. For information about determining a MAC address, see Determine the Phone MAC Address,
on page 68.
If the phone is already in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database, the configuration file may
be damaged. See Configuration File Corruption, on page 245 for assistance.
Cisco IP Phone Cannot Obtain IP Address
Problem
If a phone cannot obtain an IP address when it starts up, the phone may not be on the same network or VLAN
as the DHCP server, or the switch port to which the phone connects may be disabled.
Solution
Ensure that the network or VLAN to which the phone connects has access to the DHCP server, and ensure
that the switch port is enabled.
Phone Not Registering
Problem
The phone screen displays the prompt "Enter activation code or service domain.”
Solution
The phone is missing a TFTP address. Check that option 150 is provided by the DHCP server or an alternate
TFTP is manually configured.
Phone Reset Problems
If users report that their phones are resetting during calls or while the phones are idle, you should investigate
the cause. If the network connection and Cisco Unified Communications Manager connection are stable, a
phone should not reset.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
246
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Phone Registration

Typically, a phone resets if it has problems in connecting to the network or to Cisco Unified Communications
Manager.
Phone Resets Due to Intermittent Network Outages
Problem
Your network may be experiencing intermittent outages.
Solution
Intermittent network outages affect data and voice traffic differently. Your network might be experiencing
intermittent outages without detection. If so, data traffic can resend lost packets and verify that packets are
received and transmitted. However, voice traffic cannot recapture lost packets. Rather than retransmitting a
lost network connection, the phone resets and attempts to reconnect to the network. Contact the system
administrator for information on known problems in the voice network.
Phone Resets Due to DHCP Setting Errors
Problem
The DHCP settings may be incorrect.
Solution
Verify that you have properly configured the phone to use DHCP. Verify that the DHCP server is set up
properly. Verify the DHCP lease duration. We recommend that you set the lease duration to 8 days.
Phone Resets Due to Incorrect Static IP Address
Problem
The static IP address assigned to the phone may be incorrect.
Solution
If the phone is assigned a static IP address, verify that you have entered the correct settings.
Phone Resets During Heavy Network Usage
Problem
If the phone appears to reset during heavy network usage, it is likely that you do not have a voice VLAN
configured.
Solution
Isolating the phones on a separate auxiliary VLAN increases the quality of the voice traffic.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
247
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Phone Resets Due to Intermittent Network Outages

Phone Resets Due to Intentional Reset
Problem
If you are not the only administrator with access to Cisco Unified Communications Manager, you should
verify that no one else has intentionally reset the phones.
Solution
You can check if a Cisco IP Phone received a command from Cisco Unified Communications Manager to
reset by pressing Applications on the phone and choosing Admin settings > Status > Network statistics.
• If the Restart Cause field displays Reset-Reset, the phone receives a Reset/Reset from Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Administration.
• If the Restart Cause field displays Reset-Restart, the phone closed because it received a Reset/Restart
from Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration.
Phone Resets Due to DNS or Other Connectivity Issues
Problem
The phone reset continues and you suspect DNS or other connectivity issues.
Solution
If the phone continues to reset, eliminate DNS or other connectivity errors by following the procedure in
Determine DNS or Connectivity Issues, on page 254.
Phone Does Not Power Up
Problem
The phone does not appear to be powered up.
Solution
In most cases, a phone restarts if it powers up by using external power but loses that connection and switches
to PoE. Similarly, a phone may restart if it powers up by using PoE and then connects to an external power
supply.
Phone Cannot Connect to LAN
Problem
The physical connection to the LAN may be broken.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
248
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Phone Resets Due to Intentional Reset

Solution
Verify that the Ethernet connection to which the Cisco IP Phone connects is up. For example, check whether
the particular port or switch to which the phone connects is down and that the switch is not rebooting. Also
ensure that no cable breaks exist.
Cisco IP Phone Security Problems
The following sections provide troubleshooting information for the security features on the Cisco IP Phone.
For information about the solutions for any of these issues, and for additional troubleshooting information
about security, see Cisco Unified Communications Manager Security Guide.
CTL File Problems
The following sections describe troubleshooting problems with the CTL file.
Authentication Error, Phone Cannot Authenticate CTL File
Problem
A device authentication error occurs.
Cause
CTL file does not have a Cisco Unified Communications Manager certificate or has an incorrect certificate.
Solution
Install a correct certificate.
Phone Cannot Authenticate CTL File
Problem
Phone cannot authenticate the CTL file.
Cause
The security token that signed the updated CTL file does not exist in the CTL file on the phone.
Solution
Change the security token in the CTL file and install the new file on the phone.
CTL File Authenticates but Other Configuration Files Do Not Authenticate
Problem
Phone cannot authenticate any configuration files other than the CTL file.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
249
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Cisco IP Phone Security Problems

Cause
A bad TFTP record exists, or the configuration file may not be signed by the corresponding certificate in the
phone Trust List.
Solution
Check the TFTP record and the certificate in the Trust List.
ITL File Authenticates but Other Configuration Files Do Not Authenticate
Problem
Phone cannot authenticate any configuration files other than the ITL file.
Cause
The configuration file may not be signed by the corresponding certificate in the phone Trust List.
Solution
Re-sign the configuration file by using the correct certificate.
TFTP Authorization Fails
Problem
Phone reports TFTP authorization failure.
Cause
The TFTP address for the phone does not exist in the CTL file.
If you created a new CTL file with a new TFTP record, the existing CTL file on the phone may not contain
a record for the new TFTP server.
Solution
Check the configuration of the TFTP address in the phone CTL file.
Phone Does Not Register
Problem
Phone does not register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Cause
The CTL file does not contain the correct information for the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server.
Solution
Change the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server information in the CTL file.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
250
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
ITL File Authenticates but Other Configuration Files Do Not Authenticate

Signed Configuration Files Are Not Requested
Problem
Phone does not request signed configuration files.
Cause
The CTL file does not contain any TFTP entries with certificates.
Solution
Configure TFTP entries with certificates in the CTL file.
Video Call Problems
No Video Between Two Cisco IP Video Phones
Problem
Video isn't streaming between between two Cisco IP video phones.
Solution
Check to make sure no Media Termination Point (MTP) is being used in the call flow.
Video Stutters or Drops Frames
Problem
When I'm on a video call, the video buffers or drops frames.
Solution
The quality of the image depends upon the bandwidth of the call. Raising the bit rate increases the quality of
your video, but requires extra network resources. Always use the bit rate best suited for your type of video.
A video call that is 720p and 15 frames per second requires a bit rate of 790 kbps or higher. A video call that
is 720p and 30 frames per second requires a bit rate of 1360 kbps or higher.
For additional information about bandwidth, see the Video Transmit Resolution Setup section of the "Phone
Features and Setup" chapter.
Solution
Confirm that the Maximum Session Bit Rate for Video Calls parameter is configured to be at least the minimum
video bit rate range. On the Cisco Unified Communications Manager, navigate to System > Region
Information > Region.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
251
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Signed Configuration Files Are Not Requested

Cannot Transfer a Video Call
Problem
I can't transfer a video call from my desk phone to my mobile device.
Solution
Cisco Unified Mobility does not extend to video calls. A video call that is received at the desk phone cannot
be picked up on the mobile phone.
No Video During a Conference call
Problem
A video call goes to an audio call when I add two or more people to the call.
You must use a video conference bridge for ad hoc and meet-me video conferencing.
General Telephone Call Problems
The following sections help troubleshoot general telephone call problems.
Phone Call Cannot Be Established
Problem
A user complains about not being able to make a call.
Cause
The phone does not have a DHCP IP address, is unable to register to Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Phones with an LCD display show the message Configuring IP or Registering. Phones without an
LCD display play the reorder tone (instead of dial tone) in the handset when the user attempts to make a call.
Solution
1. Verify the following:
a. The Ethernet cable is attached.
b. The Cisco CallManager service is running on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server.
c. Both phones are registered to the same Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
2. Audio server debug and capture logs are enabled for both phones. If needed, enable Java debug.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
252
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Cannot Transfer a Video Call

Phone Does Not Recognize DTMF Digits or Digits Are Delayed
Problem
The user complains that numbers are missed or delayed when the keypad is used.
Cause
Pressing the keys too quickly can result in missed or delayed digits.
Solution
Keys should not be pressed rapidly.
Troubleshooting Procedures
These procedures can be used to identify and correct problems.
Create a Phone Problem Report from Cisco Unified Communications Manager
You can generate a problem report for the phones from Cisco Unified Communications Manager. This action
results in the same information that the Problem Report Tool (PRT) softkey generates on the phone.
The problem report contains information about the phone and the headsets.
Procedure
Step 1 In Cisco Unified CM Administration, select Device > Phone.
Step 2 Click Find and select one or more Cisco IP Phones.
Step 3 Click Generate PRT for Selected to collect PRT logs for the headsets used on the selected Cisco IP Phones.
Create a Console Log from Your Phone
You generate a console log when your phone will not connect to the network and you cannot access the
Problem Report Tool (PRT).
Before you begin
Connect a console cable to the Auxiliary port on the back of your phone.
Procedure
Step 1 On your phone, press Applications .
Step 2 Navigate Admin settings > Aux port.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
253
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Phone Does Not Recognize DTMF Digits or Digits Are Delayed

Step 3 Select Collect console log to collect device logs.
Check TFTP Settings
Procedure
Step 1 On the Cisco IP Phone, press A pplications , choose Admin settings > Network setup > Ethernet setup >
IPv4 setup > TFTP Server 1.
Step 2 If you have assigned a static IP address to the phone, you must manually enter a setting for the TFTP Server
1 option.
Step 3 If you are using DHCP, the phone obtains the address for the TFTP server from the DHCP server. Check that
the IP address is configured in Option 150.
Step 4 You can also enable the phone to use an alternate TFTP server. Such a setting is particularly useful if the
phone recently moved from one location to another.
Step 5 If the local DHCP does not offer the correct TFTP address, enable the phone to use an alternate TFTP server.
This is often necessary in VPN scenario.
Determine DNS or Connectivity Issues
Procedure
Step 1 Use the Reset Settings menu to reset phone settings to their default values.
Step 2 Modify DHCP and IP settings:
a) Disable DHCP.
b) Assign static IP values to the phone. Use the same default router setting that other functioning phones
use.
c) Assign a TFTP server. Use the same TFTP server that other functioning phones use.
Step 3 On the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server, verify that the local host files have the correct Cisco
Unified Communications Manager server name mapped to the correct IP address.
Step 4 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager, choose System > Server and verify that reference to the
server is made by the IP address and not by the DNS name.
Step 5 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager, choose Device > Phone. Click Find to search for this phone.
Verify that you have assigned the correct MAC address to this Cisco IP Phone.
Step 6 Power cycle the phone.
Related Topics
Basic Reset, on page 259
Determine the Phone MAC Address, on page 68
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
254
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Check TFTP Settings

Check DHCP Settings
Procedure
Step 1 On the phone, press Applications .
Step 2 Select Wi-Fi > Network Setup > IPv4 Setup, and look at the following options:
• DHCP Server: If you have assigned a static IP address to the phone, you do not need to enter a value for
the DHCP Server option. However, if you are using a DHCP server, this option must have a value. If no
value is found, check your IP routing and VLAN configuration. See the Troubleshooting Switch Port
and Interface Problems document, available at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/customer/products/hw/switches/ps708/prod_tech_notes_list.html
• IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Router: If you have assigned a static IP address to the phone, you
must manually enter settings for these options.
Step 3 If you are using DHCP, check the IP addresses that your DHCP server distributes.
See the Understanding and Troubleshooting DHCP in Catalyst Switch or Enterprise Networks document,
available at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk648/tk361/technologies_tech_note09186a00800f0804.shtml
Create a New Phone Configuration File
When you remove a phone from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database, the configuration file
is deleted from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager TFTP server. The phone directory number or
numbers remain in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database. They are called unassigned DNs
and can be used for other devices. If unassigned DNs are not used by other devices, delete these DNs from
the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database. You can use the Route Plan Report to view and delete
unassigned reference numbers. For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Changing the buttons on a phone button template, or assigning a different phone button template to a phone,
may result in directory numbers that are no longer accessible from the phone. The directory numbers are still
assigned to the phone in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database, but the phone has no button
on the phone with which calls can be answered. These directory numbers should be removed from the phone
and deleted if necessary.
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager, choose Device > Phone and click Find to locate the phone
that is experiencing problems.
Step 2 Choose Delete to remove the phone from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
255
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Check DHCP Settings

When you remove a phone from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database, the
configuration file is deleted from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager TFTP server. The
phone directory number or numbers remain in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
database. They are called unassigned DNs and can be used for other devices. If unassigned DNs
are not used by other devices, delete these DNs from the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
database. You can use the Route Plan Report to view and delete unassigned reference numbers.
Note
Step 3 Add the phone back to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database.
Step 4 Power cycle the phone.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Phone Addition Methods, on page 68
Identify 802.1X Authentication Problems
Procedure
Step 1 Verify that you have properly configured the required components.
Step 2 Confirm that the shared secret is configured on the phone.
• If the shared secret is configured, verify that you have the same shared secret on the authentication server.
• If the shared secret is not configured on the phone, enter it, and ensure that it matches the shared secret
on the authentication server.
Verify DNS Settings
To verify DNS settings, follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Select Administrator Settings > Network Setup > IPv4 Setup > DNS Server 1.
Step 3 You should also verify that a CNAME entry was made in the DNS server for the TFTP server and for the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager system.
You must also ensure that DNS is configured to do reverse lookups.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
256
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Identify 802.1X Authentication Problems

Start Service
A service must be activated before it can be started or stopped.
Procedure
Step 1 From Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, choose Cisco Unified Serviceability from
the Navigation drop-down list and click Go.
Step 2 Choose Tools > Control Center - Feature Services.
Step 3 Choose the primary Cisco Unified Communications Manager server from the Server drop-down list.
The window displays the service names for the server that you chose, the status of the services, and a service
control panel to start or stop a service.
Step 4 If a service has stopped, click the corresponding radio button and then click Start.
The Service Status symbol changes from a square to an arrow.
Control Debug Information from Cisco Unified Communications
Manager
If you are experiencing phone problems that you cannot resolve, Cisco TAC can assist you. You will need to
turn debugging on for the phone, reproduce the problem, turn debugging off, and send the logs to TAC for
analysis.
Because debugging captures detailed information, the communication traffic can slow down the phone, making
it less responsive. After you capture the logs, you should turn debugging off to ensure phone operation.
The debug information may include a single digit code that reflects the severity of the situation. Situations
are graded as follows:
• 0 - Emergency
• 1 - Alert
• 2 - Critical
• 3 - Error
• 4 - Warn
• 5 - Notification
• 6 - Information
• 7 - Debugging
Contact Cisco TAC for more information and assistance.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
257
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Start Service

Procedure
Step 1 In the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, select one of the following windows:
• Device > Device settings > Common Phone Profile
• System > Enterprise Phone Configuration
• Device > Phone
Step 2 Set the following parameters:
• Log Profile - values: Preset (default), Default, Telephony, SIP, UI, Network, Media, Upgrade, Accessory,
Security, Wi-Fi, VPN, Energywise, MobileRemoteAccess
To implement multilevel and multi-section support of the parameters, check the Log Profile
check box.
Note
• Remote Log - values: Disable (default), Enable
• IPv6 Log Server or Log Server - IP address (IPv4 or IPv6 address)
When the Log Server cannot be reached, the phone stops sending debug messages.
Note
• The format for the IPv4 Log Server address is address:<port>@@base=<0-7>;pfs=<0-1>
• The format for the IPv6 Log Server address is [address]:<port>@@base=<0-7>;pfs=<0-1>
• Where:
• the IPv4 address is separated with dot (.)
• the IPv6 address is separated with colon (:)
Additional Troubleshooting Information
If you have additional questions about troubleshooting your phone, go to the following Cisco website and
navigate to the desired phone model:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/collaboration-endpoints/unified-ip-phone-8800-series/
series.html#Troubleshooting
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
258
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Additional Troubleshooting Information

CHAPTER 13
Maintenance
• Basic Reset, on page 259
• Perform Network Configuration Reset, on page 261
• Perform User Network Configuration Reset, on page 261
• Remove CTL File, on page 261
• Quality Report Tool, on page 262
• Voice Quality Monitoring, on page 262
• Cisco IP Phone Cleaning, on page 263
Basic Reset
Performing a basic reset of a CiscoIP Phone provides a way to recover if the phone experiences an error and
provides a way to reset or restore various configuration and security settings.
The following table describes the ways to perform a basic reset. You can reset a phone with any of these
operations after the phone has started up. Choose the operation that is appropriate for your situation.
Table 54: Basic Reset Methods
ExplanationActionOperation
Resets any user and network setup changes that you have made, but that the phone has not
written to its Flash memory, to previously saved settings, then restarts the phone.
Press Applications . Go to Admin settings > Reset settings >
Reset device.
Restart phone
Resets user and network setup settings to their default values, and restarts the phone.
To reset settings, press Applications and choose Administrator
Settings > Reset Settings > Network.
Reset settings
Resets the CTL file.
To reset the CTL file, press Applications and choose
Administrator Settings > Reset Settings > Security.
Reset the Phone to the Factory Settings from the Phone Keypad
You can reset the phone to the factory settings. The reset clears all the phone parameters.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
259

Procedure
Step 1 Remove power from the phone in one of these ways:
• Unplug the power adapter.
• Unplug the LAN cable.
Step 2 Wait for 5 seconds.
Step 3 Press and hold # and plug the phone back in. Release the # only when the Headset and Speaker buttons are
lit.
In some hardware versions, the Mute button also lights along with Headset and Speaker buttons
when you plug the phone back in. In that case, wait for all of them to go out and release # only
when the Headset and Speaker buttons are lit again.
Note
Step 4 Enter the following key sequence:
123456789*0#
The light for the Headset button turns off after you press the 1 key. After you enter the key sequence, the
Mute button lights.
Do not power down the phone until it completes the factory reset process, and the main screen
appears.
Caution
The phone resets.
Perform Reset All Settings from Phone Menu
Perform this task if you want to reset your user and network setup settings to the default values.
Procedure
Step 1 Press Applications .
Step 2 Choose Administrator settings > Reset settings > All settings.
If necessary, unlock the phone options.
Reboot Your Phone from the Backup Image
Your Cisco IP Phone has a second, backup image that allows you to recover the phone when the default image
has been compromised.
To reboot your phone from the backup image, perform the following procedure.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
260
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Perform Reset All Settings from Phone Menu

Procedure
Step 1 Disconnect the power supply.
Step 2 Press and hold the star (*) key.
Step 3 Reconnect the power. Continue pressing the star key until the Mute LED turns off.
Step 4 Release the star key.
The phone reboots from the backup image.
Perform Network Configuration Reset
Resets network configuration settings to their default values and resets the phone. This method causes DHCP
to reconfigure the IP address of the phone.
Procedure
Step 1 From the Administrator Settings menu, if required, unlock phone options.
Step 2 Choose Reset Settings > Network Setup.
Perform User Network Configuration Reset
Resets any user and network configuration changes that you have made, but that the phone has not written to
flash memory, to previously saved settings.
Procedure
Step 1 From the Administrator Settings menu, if required, unlock phone options.
Step 2 Choose Reset Settings > Reset Device.
Remove CTL File
Deletes only the CTL file from the phone.
Procedure
Step 1 From the Administrator Settings menu, if required, unlock phone options.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
261
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Perform Network Configuration Reset

Step 2 Choose Reset Settings > Security Settings.
Quality Report Tool
The Quality Report Tool (QRT) is a voice quality and general problem-reporting tool for the Cisco IP Phone.
The QRT feature is installed as part of Cisco Unified Communications Manager installation.
You can configure user Cisco IP Phones with QRT. When you do so, users can report problems with phone
calls by pressing Report Quality. This softkey or button is available only when the Cisco IP Phone is in the
Connected, Connected Conference, Connected Transfer, or OnHook states.
When a user presses Report Quality, a list of problem categories appears. The user selects the appropriate
problem category, and this feedback is logged in an XML file. Actual information that is logged depends on
the user selection and whether the destination device is a Cisco IP Phone.
For more information about using QRT, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release.
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
Voice Quality Monitoring
To measure the voice quality of calls that are sent and received within the network, Cisco IP Phones use these
statistical metrics that are based on concealment events. The DSP plays concealment frames to mask frame
loss in the voice packet stream.
• Concealment Ratio metrics—Show the ratio of concealment frames over total speech frames. An interval
conceal ratio is calculated every 3 seconds.
• Concealed Second metrics—Show the number of seconds in which the DSP plays concealment frames
due to lost frames. A severely “concealed second” is a second in which the DSP plays more than five
percent concealment frames.
Concealment ratio and concealment seconds are primary measurements based on frame loss. A Conceal Ratio
of zero indicates that the IP network is delivering frames and packets on time with no loss.
Note
You can access voice quality metrics from the Cisco IP Phone using the Call Statistics screen or remotely by
using Streaming Statistics.
Voice Quality Troubleshooting Tips
When you observe significant and persistent changes to metrics, use the following table for general
troubleshooting information.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
262
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Quality Report Tool

Table 55: Changes to Voice Quality Metrics
ConditionMetric Change
Network impairment from packet loss or high jitter.Conceal Ratio and Conceal Seconds increase
significantly
• Noise or distortion in the audio channel such as
echo or audio levels.
• Tandem calls that undergo multiple
encode/decode such as calls to a cellular network
or calling card network.
• Acoustic problems coming from a speakerphone,
handsfree cellular phone or wireless headset.
Check packet transmit (TxCnt) and packet receive
(RxCnt) counters to verify that voice packets are
flowing.
Conceal Ratio is near or at zero, but the voice quality
is poor.
Network impairment from packet loss or high jitter
levels:
• Average MOS LQK decreases may indicate
widespread and uniform impairment.
• Individual MOS LQK decreases may indicate
bursty impairment.
Cross-check the conceal ratio and conceal seconds
for evidence of packet loss and jitter.
MOS LQK scores decrease significantly
• Check to see if the phone is using a different
codec than expected (RxType and TxType).
• Check to see if the MOS LQK version changed
after a firmware upgrade.
MOS LQK scores increase significantly
Voice quality metrics do not account for noise or distortion, only frame loss.
Note
Cisco IP Phone Cleaning
To clean your Cisco IP Phone, use only a dry soft cloth to gently wipe the phone and the phone screen. Do
not apply liquids or powders directly to the phone. As with all non-weatherproof electronics, liquids and
powders can damage the components and cause failures.
When the phone is in sleep mode, the screen is blank and the Select button is not lit. When the phone is in
this condition, you can clean the screen, as long as you know that the phone will remain asleep until after you
finish cleaning.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
263
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Cisco IP Phone Cleaning

Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
264
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Cisco IP Phone Cleaning

CHAPTER 14
International User Support
• Unified Communications Manager Endpoints Locale Installer, on page 265
• International Call Logging Support, on page 265
• Language Limitation, on page 266
Unified Communications Manager Endpoints Locale Installer
By default, Cisco IP Phones are set up for the English (United States) locale. To use the Cisco IP Phones in
other locales, you must install the locale-specific version of the Unified Communications Manager Endpoints
Locale Installer on every Cisco Unified Communications Manager server in the cluster. The Locale Installer
installs the latest translated text for the phone user interface and country-specific phone tones on your system
so that they are available for the Cisco IP Phones.
To access the Locale Installer required for a release, access the Software Download page, navigate to your
phone model, and select the Unified Communications Manager Endpoints Locale Installer link.
For more information, see the documentation for your particular Cisco Unified Communications Manager
release.
The latest Locale Installer may not be immediately available; continue to check the website for updates.
Note
Related Topics
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Documentation, on page xv
International Call Logging Support
If your phone system is configured for international call logging (calling party normalization), the call logs,
redial, or call directory entries may display a plus (+) symbol to represent the international escape code for
your location. Depending on the configuration for your phone system, the + may be replaced with the correct
international dialing code, or you may need to edit the number before dialing to manually replace the + with
the international escape code for your location. In addition, while the call log or directory entry may display
the full international number for the received call, the phone display may show the shortened local version of
the number, without international or country codes.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
265

Language Limitation
There is no localized Keyboard Alphanumeric Text Entry (KATE) support for the following Asian locales:
• Chinese (Hong Kong)
• Chinese (Taiwan)
• Japanese (Japan)
• Korean (Korea Republic)
The default English (United States) KATE is presented to the user instead.
For example, the phone screen will show text in Korean, but the 2 key on the keypad will display a b c 2
A B C.
Chinese input works similar to PCs and mobile phones in Chinese. The Chinese locale installer is required
for Chinese input to function.
Cisco IP Phone 8800 Series Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
266
Cisco IP Phone Troubleshooting
Language Limitation




