
Chemical and Physical
Properties

Cake Survey
• Vanilla or chocolate? Why?

• Why does a vanilla cake taste different than a
chocolate cake? They are both cakes aren’t they?

Property
• Property: a characteristic that describes a substance
(e.g. colour, reactivity, taste, smell, hardness).
• Pure gold properties:
-yellow
-very soft
• Iron properties:
-silver coloured
-very hard
•
Both are metals yet have different properties. Why?
•
All matter is made up of different types and combinations of
particles. The particles of gold (Au) are different than the
particles of Iron (Fe).

Classifying Matter
Property: a characteristic
that describes a substance
(e.g. colour, reactivity, taste,
smell, hardness).
Physical Property:
describes a characteristic of a
substance that can be
observed or measured without
changing the substance.
Chemical Property:
describes the ability of
a substance to change into
a new substance or substances.

More on Physical Properties
• Physical Change: the physical properties of a
substance can change without changing what
the substance actually is (which is a picture of
water?).
heat heat


Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
This coin is the colour of Gold

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
This coin is shiny Concrete is dull

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
A copper wire allows
electricity to flow
through it (conductor).
A fur coat traps all of my
body heat to stop me
(Insulator)

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
Copper is a metal that can be
stretched into long wire.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
Quartz scratches calcite

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
Aluminum (and play doh) can be
pounded or rolled into sheets. It can
be shaped without breaking.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
Water flows more (quicker) than
maple syrup.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
The bottle above is transparent and
green.

Some more on Clarity
• Transparent (clear):
Substances that you
can see through very
clearly (window glass).
• Translucent (clear):
Substances that you
can see through but not
as clearly (stain glass
windows).
• Opaque (not clear):
Substances that you
cannot see through at
all.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
Water begins to evaporate at 100 ºC.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Melting point, boiling point, freezing point
Ice can float on liquid water due to
this property.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Brittleness
My glass vase shattered into several
pieces when I dropped it.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Odour
• Malleability
• Viscosity
• Clarity
• Brittleness
This man’s urine smells like
asparagus. Note the way he is
“wafting”.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Ductility
• Odour
• Malleability
• Taste
• Clarity
• Brittleness
The lemon is sour. Why will we not
use this property very often in our
labs?

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Form (shape)
• Odour
• Malleability
• Taste
• Clarity
• Brittleness
Corn starch is an amorphous power.
Salt has a cube-shaped crystalline
structure.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Density
• Form (shape)
• Odour
• Malleability
• Physical state
• Clarity
• Brittleness
The Corn starch is solid.

Physical Properties
• Colour
• Lustre (shine)
• Conductivity
• Solubility
• Form (shape)
• Odour
• Malleability
• Physical state
• Clarity
• Brittleness
I can dissolve sugar (or sweetener) into my
coffee with a little bit of stirring.

1) No new substances are
formed when dissolving
sugar in coffee. The
coffee molecules
surround the sugar
molecules.
2) It is a mixture of two
substances that are not
chemically combined
(coffee remains coffee
and sugar remains
sugar).

Quantitative
Qualitative
Physical properties: Quantitative or
Qualitative (summary)
-Density: in g/ml
-Solubility: how much of a substance
can dissolve in a certain amount of
solvent.
-Melting/freezing/boiling point: in ºC
-Mass: in grams (g)
-Volume: in mL or L
-Colour/Lustre: Colour and shine
-Brittleness: Does it shatter?
-Texture/Form: Amorphous/Crystalline?
-Physical State: Solid, liquid, gas
-Odour: How does it smell?
-Taste: Salty/Sour/Bitter/Sweet?
-Malleability: Pounded into sheets?
-Ductility: Stretched into wire?
-Clarity: Transparent/Translucent/Opaque
-Hardness: Hard substances scratch soft.
-Conductivity: Conducts electricity/heat.

Property: a characteristic
that describes a substance
(e.g. colour, reactivity, taste,
smell, hardness).
Physical Property:
describes a characteristic of a
substance that can be
observed or measured without
changing the substance.
Chemical Property:
describes the ability of
a substance to change into
a new substance or substances.

More on Chemical Properties
• Chemical properties can only be observed when a
chemical change (new substance is formed)
occurs.
• Chemical changes occur during chemical reactions.
In this case the change in physical properties occurs
due to the formation of a new substance!
• Chemical reaction: Interaction between substances
that results in the formation of new substances.

Chemical Properties
• Absorbs heat during reaction
• Combustible
• Forms gas
• Reacts with acid
• Reacts with water
• Emits heat during reaction
• Forms a precipitate (solid) in a solution

Absorbs heat during a reaction
• Endothermic reaction:
• Absorbs heat during a
reaction.

Chemistry of Cold Packs
• The chemical cold pack is
• It also contains a small bag
or tub full of chemicals.
• The inner compartment
keeps its contents separated
from the water until it is time
to use the cold pack.
• When the inner bag is
popped open, the chemicals
within mix with the water in
the cold pack.
• The reaction removes heat
from the surroundings and
so feels cold to the touch.

How it works?
Membrane separating a
chemical from the water
Water
Chemical

Emits heat during a reaction
• Exothermic reaction:
• Emits heat during a
reaction.

Emits Light During a Reaction
When luciferin (a chemical in fireflies)
reacts with oxygen,
a reaction occurs and light is emitted.
Luciferin + O
2
Oxyluciferin + light

Forms a gas when
heated
• When baking powder is
heated, a reaction occurs
and carbon dioxide gas is
produced.
• In cooking, this helps lift the
cake and make it light/fluffy.
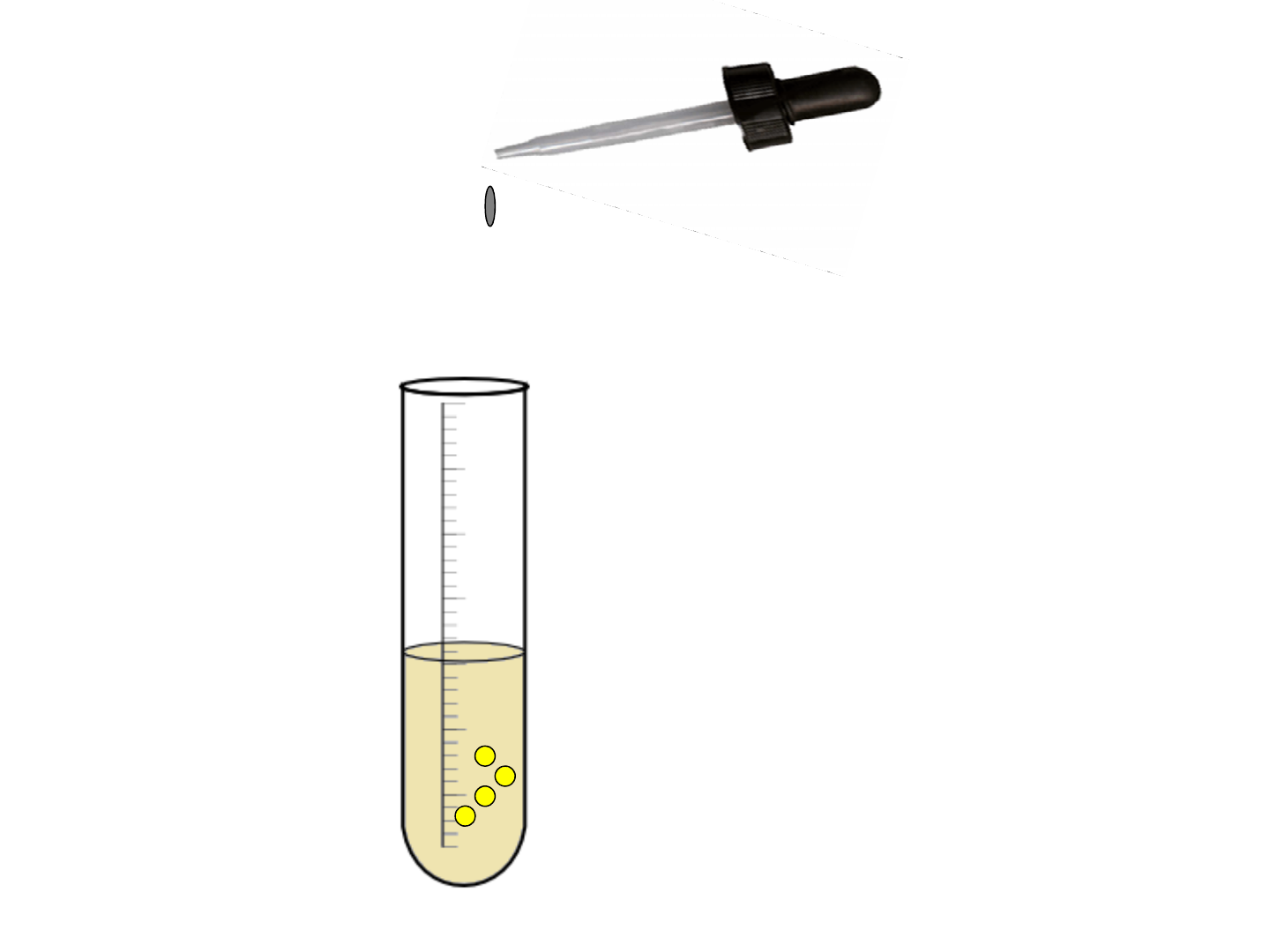
-Forms a
precipitate (solid)
in a solution.
-The precipitate
is a new
substance.

Combustibility
• The ability of a substance to react quickly with
oxygen to produce heat and light. When you
light a BBQ, propane gas reacts with oxygen to
produce carbon dioxide gas, water, and heat
(often seen as large explosions)!

Evidence of a chemical change
• 1) Colour change
• 2) Temperature change
• 3) Precipitate formation inside a liquid
• 4) Odour/taste change
• 5) Production of a new gas

Chemical Reactions
Reactant (s) Product (s)
A substance that undergoes a
chemical reaction (left)
A new substance that is formed
in a chemical reaction (right)

Evidence of Chemical Reactions
• 1) Colour Change: Lugol’s iodine solution.
• Is dissolving blue cool-aid into water to
give a blue coloured drink a chemical
change?

Lugol’s
Iodine
solution

Evidence of Chemical Reactions
• Temperature change (without you having to
add heat in or take heat out).

Evidence of Chemical Reactions
• Precipitate formation: Formation of a NEW
solid inside a liquid.
-Example:
• Ice water Liquid water = chemical
change?.

-Forms a
precipitate (solid)
in a solution.
-The precipitate
is a new
substance.
KI
(l)
+ PbNO
3(l)
PbI
(s)
+ KNO
3(l)
New substance
formed (precipitate)

Evidence of chemical reactions
• Production of a new gas.
When
vinegar and
baking soda
react, a new
gas (CO
2
) is
formed.

How do we know if it is a chemical
change or a physical change?
• The product is a different substance than the reactant!
Different

Heat
Heat
Heat
Heat
Heat
Liquid waterIce water

Heat Heat Heat
Heat
Heat
Heat
Liquid waterIce water

