
1
PAX Ophthalmicana
?
?
?
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
Q

2
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
RNA
Protein
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein
A

3
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
RNA
Protein
?
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first step is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code
Q

4
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
RNA
Protein
Transcription
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first step is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code
A

5
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
RNA
Protein
Transcription
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first step is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code; followed by
--the translation of the RNA code into a protein
?
Q

6
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
RNA
Protein
Transcription
Translation
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first step is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code; followed by
--the translation of the RNA code into a protein
A

7
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
RNA
Protein
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first step is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code; followed by
--the translation of the RNA code into a protein
Transcription
Translation
In this context, what is a transcription factor?
Q

8
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
RNA
Protein
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first step is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code; followed by
--the translation of the RNA code into a protein
Transcription
Translation
In this context, what is a transcription factor?
A protein that regulates the transcription
process for a specific gene
A

9
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
Protein
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first step is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code; followed by
--the translation of the RNA code into a protein
Transcription
Translation
In this context, what is a transcription factor?
A protein that regulates the transcription
process for a specific gene
Q
Do transcriptions factors play an important role
in the genetic process?
Indeed they do. In fact, about 10% of all
genes in humans code for transcription factors!
RNA

10
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
Protein
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first step is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code; followed by
--the translation of the RNA code into a protein
Transcription
Translation
In this context, what is a transcription factor?
A protein that regulates the transcription
process for a specific gene
A
Do transcriptions factors play an important role
in the genetic process?
Indeed they do. In fact, about 10% of all
genes in humans code for transcription factors!
RNA

The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor (genes)
that re especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--
PAX6!
11
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
Protein
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first ste p is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code; fo llowed by
--the translation of the RNA code into a protein
Translation
In this context, what is a transcription factor?
A protein that regulates the transcription
process for a specific gene
Transcription
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--
--
--
Q
Do transcriptions factors play an important role
in the genetic process?
Indeed they do. In fact, about 10% of all
genes in humans code for transcription factors!
RNA

The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor (genes)
that re especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--
PAX6!
12
PAX Ophthalmicana
DNA
Protein
With respect to genetics, to what does the term Central Dogma refer?
It refers to the two steps involved in transforming genetic information into protein:
--The first ste p is the transcription of DNA code into RNA code; fo llowed by
--the translation of the RNA code into a protein
Translation
In this context, what is a transcription factor?
A protein that regulates the transcription
process for a specific gene
Transcription
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--PAX6
A
Do transcriptions factors play an important role
in the genetic process?
Indeed they do. In fact, about 10% of all
genes in humans code for transcription factors!
RNA

The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor (genes)
that re especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--
PAX6!
13
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--PAX6
Q

The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor (genes)
that re especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--
PAX6!
14
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
It is a portmanteau of the term ‘PAired (homeo)boX’
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--PAX6
The Fundamentals book refers to PAX genes both
as ‘paired homeobox’ and ‘paired box’ genes
A

The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor (genes)
that re especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--
PAX6!
15
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
It is a portmanteau of the term ‘PAired (homeo)boX’
Generally speaking, what are PAX genes involved in?
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--PAX6
Q

The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor (genes)
that re especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--
PAX6!
16
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
It is a portmanteau of the term ‘PAired (homeo)boX’
Generally speaking, what are PAX genes involved in?
Morphogenesis
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--PAX6
A

The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor (genes)
that re especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--
PAX6!
17
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
It is a portmanteau of the term ‘PAired (homeo)boX’
Generally speaking, what are PAX genes involved in?
Morphogenesis
Of these three PAX genes, which is most important to the development of the eye?
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2?
--PAX3?
--PAX6?
Q

18
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
It is a portmanteau of the term ‘PAired (homeo)boX’
Generally speaking, what are PAX genes involved in?
Morphogenesis
Of these three PAX genes, which is most important to the development of the eye?
PAX6. The Fundamentals book refers to it as “the master switch for eye
development.” The Peds book says, “The PAX6 gene is the master control gene for
eye morphogenesis.”
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--
PAX6!
A

19
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
It is a portmanteau of the term ‘PAired (homeo)boX’
Generally speaking, what are PAX genes involved in?
Morphogenesis
Of these three PAX genes, which is most important to the development of the eye?
PAX6. The Fundamentals book refers to it as “the master switch for eye
development.” The Peds book says, “The PAX6 gene is the master control gene for
eye morphogenesis.”
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--
PAX6!
Next let’s take a closer look at PAX6

There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?
20
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
The mnemonic is…
P
A
X
6
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?
21
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
The mnemonic is…PAX6

P
A
X
6
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?
22
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
Start with the ‘P’ and work down

P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
23
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q/A
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?

P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
24
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q/A
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?

P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
25
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q/A
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?

P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
If you use your imagination,
the 6 looks like a lower-case h…
h
26
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
three words
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
27
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
28
PAX Ophthalmicana
A

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
29
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
??
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
The Q

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
30
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
The Q

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
31
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
32
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
33
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
34
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
35
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.

Peters anomaly: Hazy cornea
PAX Ophthalmicana

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
37
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two very broad categories
based on a very fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
What purpose does the STUMPED mnemonic serve?
Remembering the DDx for a cloudy cornea in an infant
What are the other conditions in the mnemonic?
Sclerocornea; Stromal dystrophy (CHSD)
Trauma (eg, forcep injury)
Ulcer
Mucopolysaccharidosis
Peters anomaly
Endothelial dystrophy (CHED); Elevated IOP (congenital glaucoma)
Dermoid of the cornea
In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
38
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two very broad categories
based on a very fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
What purpose does the STUMPED mnemonic serve?
Remembering the DDx for a cloudy cornea in an infant
What are the other conditions in the mnemonic?
Sclerocornea; Stromal dystrophy (CHSD)
Trauma (eg, forcep injury)
Ulcer
Mucopolysaccharidosis
Peters anomaly
Endothelial dystrophy (CHED); Elevated IOP (congenital glaucoma)
Dermoid of the cornea

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
39
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two very broad categories
based on a very fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
What purpose does the STUMPED mnemonic serve?
Remembering the DDx for a cloudy cornea in an infant
What are the other conditions in the mnemonic?
S
T
U
M
Peters anomaly
Endothelial dystrophy (CHED); Elevated IOP (congenital glaucoma)
D
Note: There are two
S’s
and two
E’s
In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
40
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two very broad categories
based on a very fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
What purpose does the STUMPED mnemonic serve?
Remembering the DDx for a cloudy cornea in an infant
What are the other conditions in the mnemonic?
Sclerocornea; Stromal dystrophy (CHSD)
Trauma (eg, forcep injury)
Ulcer
Mucopolysaccharidosis
Peters anomaly
Endothelial dystrophy (CHED); Elevated IOP (congenital glaucoma)
Dermoid of the cornea
Note: There are two
S’s
and two
E’s

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
41
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
The BCSC emphasizes one other central
anterior-segment dysgenesis—what is it?
Posterior keratoconus
?

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
42
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Posterior
keratoconus
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
The BCSC emphasizes one other central
anterior-segment dysgenesis—what is it?
Posterior keratoconus

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
43
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Posterior
keratoconus
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
The BCSC emphasizes one other central
anterior-segment dysgenesis—what is it?
Posterior keratoconus
The BCSC emphasizes two peripheral
dysgeneses—what are they?
Posterior embryotoxon, and Axenfeld-
Reiger syndrome
??

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
44
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Posterior
keratoconus
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
The BCSC emphasizes one other central
anterior-segment dysgenesis—what is it?
Posterior keratoconus
The BCSC emphasizes two peripheral
dysgeneses—what are they?
Posterior embryotoxon, and Axenfeld-
Reiger syndrome
Posterior
embryotoxon
Axenfeld-Rieger
syndrome

In three words, what sort of condition is Peters anomaly?
An anterior segment dysgenesis
P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
Fovea and optic nerve ypoplasia
h
45
PAX Ophthalmicana
Anterior segment
dysgenesis
Peripheral Central
Posterior
keratoconus
Peters anomaly
The BCSC divides anterior segment dysgeneses into two broad categories based
on a fundamental anatomic distinction. What is it?
It’s whether the dysgenesis involves the central vs peripheral anterior segment
Is Peters a peripheral, or central dysgenesis?
Central
How does Peters anomaly present?
As a corneal opacity at birth (it’s in the STUMPED mnemonic). The opacity ranges
in severity from a faint haze to an opaque, elevated and vascularized mess.
The BCSC emphasizes one other central
anterior-segment dysgenesis—what is it?
Posterior keratoconus
The BCSC emphasizes two peripheral
dysgeneses—what are they?
Posterior embryotoxon, and Axenfeld-
Reiger syndrome
Posterior
embryotoxon
Axenfeld-Rieger
syndrome
For more on the anterior segment dysgeneses, see slide-set FELT7

P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
ypoplasia
h
46
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?
Fovea and optic nerve
Endeavor to remember all of these. But if you have to pick just one to remember,
make it…

P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
ypoplasia
h
47
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?
Fovea and optic nerve
Endeavor to remember all of these. But if you have to pick just one to remember,
make it…aniridia.

P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
ypoplasia
h
48
PAX Ophthalmicana
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?
Fovea and optic nerve
Endeavor to remember all of these. But if you have to pick just one to remember,
make it…aniridia. Almost all cases of aniridia are 2ndry to problems involving PAX6.

P
A
X
6
eters anomaly
nirida
Congenital catara
ypoplasia
h
49
PAX Ophthalmicana
There are four ocular abnormalities attributed to the PAX6 gene. What are they?
Endeavor to remember all of these. But if you have to pick just one to remember,
make it…aniridia. Almost all cases of aniridia are 2ndry to problems involving PAX6.
Fovea and optic nerve
A final takeaway point
regarding aniridia…
Nystgamus is commonly associated True
Aniridia is associated with limbal stem cell deficiency True
Presents unilaterally and bilaterally in roughly equal rates False; it is
almost always bilateral
The term ‘aniridia’ is a misnomer because, in about ½ of cases, a
rudimentary iris root is present False; it’s a misnomer because a
Aniridia is strongly associated with foveal and optic nerve hypoplasia
True
Patients complain of (and infants suffer from) photophobia True
Familial cases are at risk for Wilms tumor False; 1/3 of sporadic cases
develop Wilms tumor as part of the WAGR complex
Aniridia is associated with glaucoma True
Aniridia is associated with early-onset cataracts True
50
PAX Ophthalmicana
Because all are tied to PAX6,
it shouldn’t surprise you to
hear that foveal hypoplasia,
ON hypoplasia and cataracts
are associated with it.

Nystgamus is commonly associated True
Aniridia is associated with limbal stem cell deficiency True
Presents unilaterally and bilaterally in roughly equal rates False; it is
almost always bilateral
The term ‘aniridia’ is a misnomer because, in about ½ of cases, a
rudimentary iris root is present False; it’s a misnomer because a
Aniridia is strongly associated with foveal and optic nerve hypoplasia
True
Patients complain of (and infants suffer from) photophobia True
Familial cases are at risk for Wilms tumor False; 1/3 of sporadic cases
develop Wilms tumor as part of the WAGR complex
Aniridia is associated with glaucoma True
Aniridia is associated with early-onset cataracts True
51
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
…But you need to know
the three other eye
findings closely associated
with aniridia:
(Hint forthcoming)
(Hint forthcoming)
(Hint forthcoming)

Nystgamus is commonly associated True
Aniridia is associated with limbal stem cell deficiency True
Presents unilaterally and bilaterally in roughly equal rates False; it is
almost always bilateral
The term ‘aniridia’ is a misnomer because, in about ½ of cases, a
rudimentary iris root is present False; it’s a misnomer because a
Aniridia is strongly associated with foveal and optic nerve hypoplasia
True
Patients complain of (and infants suffer from) photophobia True
Familial cases are at risk for Wilms tumor False; 1/3 of sporadic cases
develop Wilms tumor as part of the WAGR complex
Aniridia is associated with glaucoma True
Aniridia is associated with early-onset cataracts True
52
An eye movement issue
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
A corneal issue
Angle-related
condition
…But you need to know
the three other eye
findings closely associated
with aniridia:

Nystagamus is commonly associated True
Aniridia is associated with limbal stem cell deficiency True
Presents unilaterally and bilaterally in roughly equal rates False; it is
almost always bilateral
The term ‘aniridia’ is a misnomer because, in about ½ of cases, a
rudimentary iris root is present False; it’s a misnomer because a
Aniridia is strongly associated with foveal and optic nerve hypoplasia
True
Patients complain of (and infants suffer from) photophobia True
Familial cases are at risk for Wilms tumor False; 1/3 of sporadic cases
develop Wilms tumor as part of the WAGR complex
Aniridia is associated with glaucoma True
Aniridia is associated with early-onset cataracts True
53
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
…But you need to know
the three other eye
findings closely associated
with aniridia:
Nystagamus is commonly associated True
Aniridia is associated with limbal stem cell deficiency True
Presents unilaterally and bilaterally in roughly equal rates False; it is
almost always bilateral
The term ‘aniridia’ is a misnomer because, in about ½ of cases, a
rudimentary iris root is present False; it’s a misnomer because a
Aniridia is strongly associated with foveal and optic nerve hypoplasia
True
Patients complain of (and infants suffer from) photophobia True
Familial cases are at risk for Wilms tumor False; 1/3 of sporadic cases
develop Wilms tumor as part of the WAGR complex
Aniridia is associated with glaucoma True
Aniridia is associated with early-onset cataracts True
54
PAX Ophthalmicana
…But you need to know
the three other eye
findings closely associated
with aniridia:
The takeaway point: Don’t think of aniridia as an ‘iris’ condition!
The BCSC characterizes it is a panophthalmic disorder

Nystagamus is commonly associated True
Aniridia is associated with limbal stem cell deficiency True
Presents unilaterally and bilaterally in roughly equal rates False; it is
almost always bilateral
The term ‘aniridia’ is a misnomer because, in about ½ of cases, a
rudimentary iris root is present False; it’s a misnomer because a
Aniridia is strongly associated with foveal and optic nerve hypoplasia
True
Patients complain of (and infants suffer from) photophobia True
Familial cases are at risk for Wilms tumor False; 1/3 of sporadic cases
develop Wilms tumor as part of the WAGR complex
Aniridia is associated with glaucoma True
Aniridia is associated with early-onset cataracts True
55
PAX Ophthalmicana
…But you need to know
the three other eye
findings closely associated
with aniridia:
The takeaway point: Don’t think of aniridia as an ‘iris’ condition!
The BCSC characterizes it is a panophthalmic disorder

56
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
It is a portmanteau of the term ‘PAired (homeo)boX’
Generally speaking, what are PAX genes involved in?
Morphogenesis
Of these three PAX genes, which is most important to the development of the eye?
PAX6. The Fundamentals book refers to it as “the master switch for eye
development.” The Peds book says, “The PAX6 gene is the master control gene for
eye morphogenesis.”
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--PAX2
--PAX3
--PAX6
Next, we’ll do PAX3

57
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q
With what eponymous syndrome is PAX3 associated?

58
Waardenburg Syndrome
PAX Ophthalmicana
A
With what eponymous syndrome is PAX3 associated?

59
Waardenburg Syndrome
PAX Ophthalmicana
With what eponymous syndrome is PAX3 associated?
Sidebar: Isn’t it frustrating that, with its two AAs, Waardenburg syndrome is
not associated with PAX2? I mean, seriously: Would it have been that big a
deal to name Waardenburg’s gene PAX2, and the other one PAX3?

60
Waardenburg Syndrome
PAX Ophthalmicana
With what eponymous syndrome is PAX3 associated?
Sidebar: Isn’t it frustrating that, with its two AAs, Waardenburg syndrome is
not associated with PAX2? I mean, seriously: Would it have been that big a
deal to name Waardenburg’s gene PAX2, and the other one PAX3?
For me, this is so annoying that the annoyance itself serves as a memory aid;
ie, when trying to recall whether Waardenburg is PAX2 vs PAX3, in my head
pops ‘Oh yeah, that’s the condition that missed out on the perfect mnemonic,’
and so I know its PAX3.

61
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
--Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q

62
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
--Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
PAX Ophthalmicana
A

63
Waardenburg syndrome: Heterochromia iridis,
dystopia canthorum, and mild synophrys
(What the heck is synophrys?)
PAX Ophthalmicana

64
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
--Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
What the heck is synophrys?
The formal medical term for a unibrow
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q

65
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
--Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
What the heck is synophrys?
The formal medical term for a unibrow
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q/A

66
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
--Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
What the heck is synophrys?
The formal medical term for a unibrow
PAX Ophthalmicana
A

67
Waardenburg syndrome: Synophrys
PAX Ophthalmicana

68
Waardenburg syndrome: Heterochromia iridis,
dystopia canthorum, and mild synophrys
(What the heck is dystopia canthorum?)
PAX Ophthalmicana

69
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
--Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
What the heck is dystopia canthorum?
Lateral displacement of the canthi (ie, telecanthus) PLUS
laterally displaced lacrimal puncta
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q

70
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
--Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
What the heck is dystopia canthorum?
Lateral displacement of the canthi (ie, telecanthus) PLUS
laterally displaced lacrimal puncta
PAX Ophthalmicana
A

71
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
--Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
What the heck is dystopia canthorum?
Lateral displacement of the canthi (ie, telecanthus) PLUS
laterally displaced lacrimal puncta
How on earth are you supposed to recognize that the puncta are too lateral?
Draw an imaginary vertical line from the upper to the lower puncta. If this line crosses the cornea,
the puncta are displaced. (Next time you examine a pt at the slit-lamp, take note of whether such
a line crosses their cornea [it won’t].)
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q

72
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
--Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
What the heck is dystopia canthorum?
Lateral displacement of the canthi (ie, telecanthus) PLUS
laterally displaced lacrimal puncta
How on earth are you supposed to recognize that the puncta are too lateral?
Draw an imaginary vertical line from the upper to the lower puncta. If this line crosses the cornea,
the puncta are displaced. (Next time you examine a pt at the slit-lamp, take note of whether such
a line crosses their cornea [it won’t].)
PAX Ophthalmicana
A

73
Dystopia canthorum. Note the telecanthus,
and laterally displaced lacrimal puncta
PAX Ophthalmicana
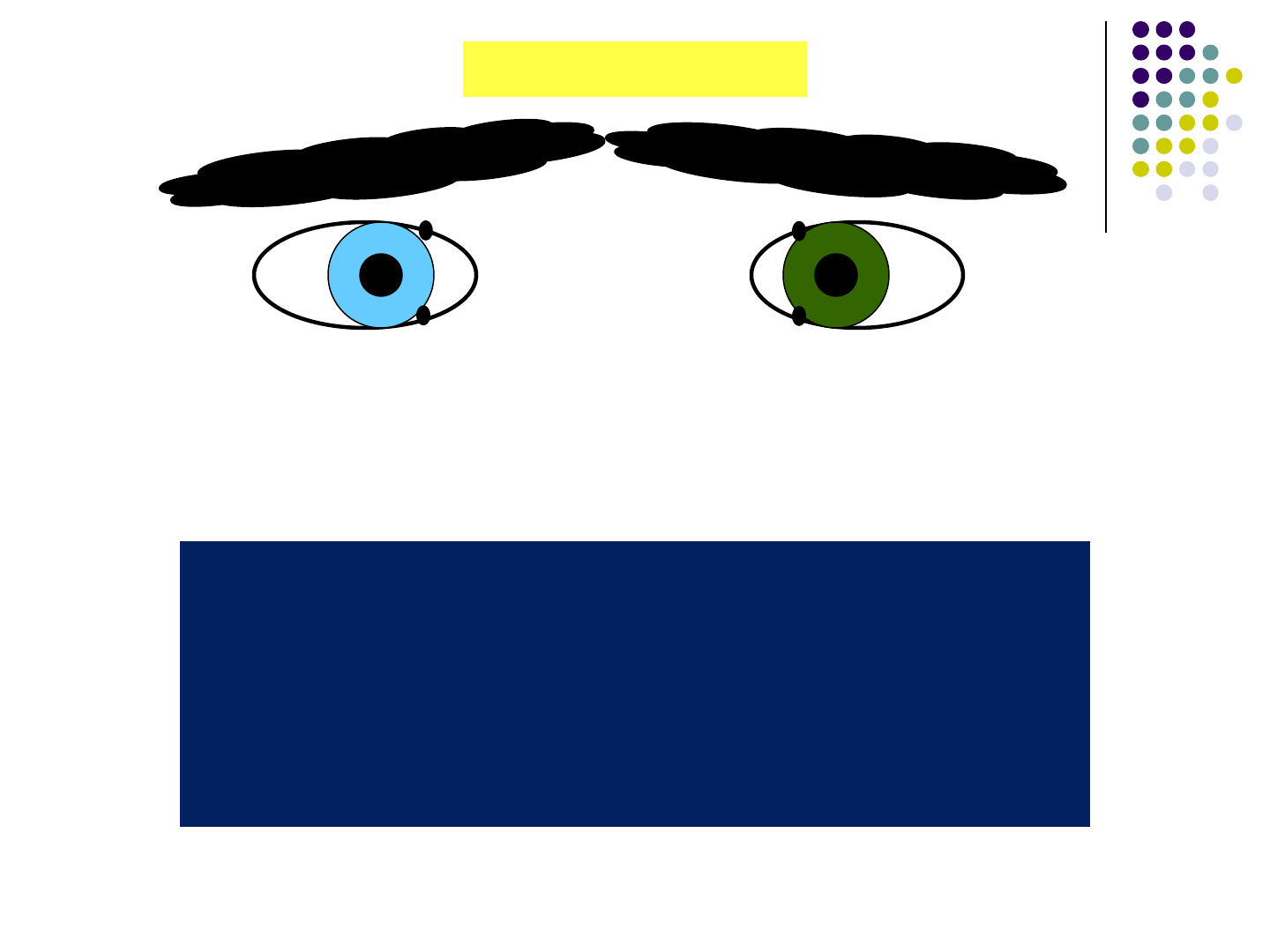
74
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
-- Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
PAX Ophthalmicana
Q

75
Waardenburg Syndrome
What 3 ophthalmic findings are classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
-- Heterochromia iridis
--Synophrys
--Dystopia canthorum
What non-ophthalmic finding is classic for Waardenburg syndrome?
The presence of a white forelock (ie, an isolated streak of white hair
in the forehead region)
aardenburg
White forelock
A

76
Waardenburg syndrome: White forelock
PAX Ophthalmicana

77
Note that Waardenburg syndrome has
forms that do not involve heterochromia
PAX Ophthalmicana

78
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
It is a portmanteau of the term ‘PAired (homeo)boX’
Generally speaking, what are PAX genes involved in?
Morphogenesis
Of these three PAX genes, which is most important to the development of the eye?
PAX6. The Fundamentals book refers to it as “the master switch for eye
development.” The Peds book says, “The PAX6 gene is the master control gene for
eye morphogenesis.”
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--
PAX2
--PAX3
--PAX6
Q
Last and most definitely least…PAX2 mutations present
with colobomas of the optic nerve, and renal hypoplasia
non-eye

79
PAX Ophthalmicana
In the present context, what is the origin of the word PAX? Where does it come from?
It is a portmanteau of the term ‘PAired (homeo)boX’
Generally speaking, what are PAX genes involved in?
Morphogenesis
Of these three PAX genes, which is most important to the development of the eye?
PAX6. The Fundamentals book refers to it as “the master switch for eye
development.” The Peds book says, “The PAX6 gene is the master control gene for
eye morphogenesis.”
The Fundamentals book lists three transcription-factor genes
that are especially important for the eye—what are they?
--
PAX2
--PAX3
--PAX6
A
Last and most definitely least…PAX2 mutations present
with colobomas of the optic nerve, and renal hypoplasia
